ISPGDX240VA-9B388I Lattice Semiconductor, ISPGDX240VA-9B388I Datasheet - Page 3
ISPGDX240VA-9B388I
Manufacturer Part Number
ISPGDX240VA-9B388I
Description
In-System Programmable 3.3V Generic Digital CrosspointTM
Manufacturer
Lattice Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.ISPGDX240VA-9B388I.pdf
(25 pages)
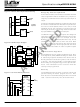
The ispGDXVA architecture is different from traditional
PLD architectures, in keeping with its unique application
focus. The block diagram is shown below. The program-
mable interconnect consists of a single Global Routing
Pool (GRP). Unlike ispLSI devices, there are no pro-
grammable logic arrays on the device. Control signals for
OEs, Clocks/Clock Enables and MUX Controls must
come from designated sets of I/O pins. The polarity of
these signals can be independently programmed in each
I/O cell.
Each I/O cell drives a unique pin. The OE control for each
I/O pin is independent and may be driven via the GRP by
one of the designated I/O pins (I/O-OE set). The I/O-OE
set consists of 25% of the total I/O pins. Boundary Scan
test is supported by dedicated registers at each I/O pin.
In-system programming is accomplished through the
standard Boundary Scan protocol.
Figure 1. ispGDXVA I/O Cell and GRP Detail (240 I/O Device)
Architecture
I/O Cell 118
I/O Cell 119
120 I/O Cells
I/O Cell 1
I/OCell 0
•
•
•
•
•
•
Logic “0” Logic “1”
Outputs Horizontal
240 Input GRP
Inputs Vertical
240 I/O Inputs
Programmable
Interconnect
I/O Group A
I/O Group B
I/O Group C
I/O Group D
• • • • • •
E
2
CMOS
Clock_Enables
Clocks /
Global
Y0-Y3
Global
Reset
N+2
N-1
N+1
of 2 Adjacent I/O Cells
From MUX Outputs
N-2
of 2 Adjacent I/O Cells
From MUX Outputs
Crossbar
120 I/O Cells
Switch
3
4x4
The various I/O pin sets are also shown in the block
diagram below. The A, B, C, and D I/O pins are grouped
together with one group per side.
I/O Architecture
Each I/O cell contains a 4:1 dynamic MUX controlled by
two select lines as well as a 4x4 crossbar switch con-
trolled by software for increased routing flexiability (Figure
1). The four data inputs to the MUX (called M0, M1, M2,
and M3) come from I/O signals in the GRP and/or
adjacent I/O cells. Each MUX data input can access one
quarter of the total I/Os. For example, in a 240-I/O
ispGDXVA, each data input can connect to one of 60 I/O
pins. MUX0 and MUX1 can be driven by designated I/O
pins called MUXsel1 and MUXsel2. Each MUXsel input
covers 25% of the total I/O pins (e.g. 60 out of 240). MUX0
and MUX1 can be driven from either MUXsel1 or MUXsel2.
ispGDXVA architecture enhancements over ispGDX (5V)
Specifications ispGDX240VA
M0
M1
M2
M3
4-to-1 MUX
MUX0
MUX1
I/O Cells below
I/O Cells above
To 2 Adjacent
To 2 Adjacent
I/O Cell 239
I/O Cell 238
I/O Cell 121
I/O Cell 120
• •
•
• •
•
A
B
Bypass Option
CLK
CLK_EN
D
Register
or Latch
Reset
Q
C
R
Prog. Slew Rate
2.5V/3.3V Output
Prog. Open Drain
Boundary
Scan Cell
(VCCIO)
Pull-up
Prog.
I/O Cell N
Bus Hold
Prog.
Latch
I/O
Pin