MAX8751ETJ+ Maxim Integrated Products, MAX8751ETJ+ Datasheet - Page 18
MAX8751ETJ+
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX8751ETJ+
Description
IC CNTRLR CCFL INV 32-TQFN
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Type
CCFL Controllerr
Datasheet
1.MAX8751ETJT.pdf
(27 pages)
Specifications of MAX8751ETJ+
Frequency
30 ~ 80 kHz
Current - Supply
3.2mA
Voltage - Supply
6 V ~ 28 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
32-TQFN Exposed Pad
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Current - Output
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Fixed-Frequency, Full-Bridge CCFL
Inverter Controller
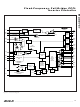
The secondary current limit provides fail-safe protection
in case of short circuit or leakage from the high-voltage
terminal to ground. ISEC monitors the voltage across a
sense resistor placed between the transformer’s low-
voltage secondary terminal and ground. The ISEC volt-
age is continuously compared to the ISEC regulation
threshold (1.22V, typ). Any time the ISEC voltage
exceeds the threshold, a controlled current is drawn
from COMP to reduce the on-time of the bridge’s high-
side switches. At the same time, the MAX8751 charges
the TFLT capacitor with a 126µA current. The MAX8751
latches off when the voltage on TFLT exceeds 4V.
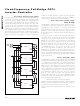
Figure 6. Master-Slave Operation
18
DIMMING
ON/OFF
______________________________________________________________________________________
VCC
Secondary Current Limit (ISEC)
CNTL
SHDN
HFCK
LFCK
CNTL
SHDN
HFCK
LFCK
CNTL
SHDN
HFCK
LFCK
CNTL
SHDN
HFCK
LFCK
MASTER
SLAVE 1
SLAVE 2
SLAVE N
DPWM
DPWM
DPWM
DPWM
PSCK
PSCK
PSCK
PSCK
HF
HF
HF
HF
LF
LF
LF
LF
Unlike the normal shutdown mode, the linear regulator
output (V
cycling the input power reactivates the device.
The MAX8751 supports master-slave operation. Up to
five MAX8751s can be connected in a daisy-chain con-
figuration as shown in Figure 6. The same device can
be used either as a master IC or as a slave IC. Each
MAX8751 is the master of the next IC in the chain and
at the same time, it is also the slave of the previous IC
in the chain.
Connecting CNTL to V
the slave mode, the switching frequency and DPWM
frequency are synchronized with the previous
MAX8751 in the chain. To synchronize the switching
frequency, connect the HFCK pins of the slave IC and
master IC together, and connect the PSCK pin of the
master IC to the HF pin of the slave IC. To synchronize
the DPWM frequency, connect the LFCK pins of the
slave IC and master IC together, and connect the
DPWM pin of the master IC to the LF pin of the slave IC.
The CNTL brightness control is disabled in the slave
mode. The master directly controls the brightness set-
ting of the slave by connecting the DPWM pin of master
to LF pin of slave.
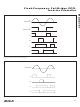
The MAX8751 provides phase shift for both the DPWM
operation and switching of MOSFETS when connected
in a daisy-chain configuration. This phase shift reduces
input ripple current, hence significantly reducing input
RMS current. This reduction of input RMS current
reduces the input capacitor requirement, hence the
size of capacitor. The phase shift can be programmed
using two logic input pins (PS1 and PS2). These two
pins combined together give four choices of phase
shift: 72°, 90°, 120°, and 180°. The selection of the
phase shift is based on the number of MAX8751s used
in the daisy-chain. Use the following equation to deter-
mine the appropriate phase shift:
Table 1 gives the suggested selection of phase shift for
different number of phases. All master and slave ICs
should use the same setting for PS1 and PS2.
Table 2 summarizes the MAX8751’s operation in all
modes.
Phase shift = 360° / number of phases
CC
) remains at 5.35V. Toggling SHDN or
Slave Operation (HFCK, LFCK,
CC
Phase Shift (PS1, PS2)
enables the slave mode. In
PSCK, DPWM)