LM22677TJE-5.0/NOPB National Semiconductor, LM22677TJE-5.0/NOPB Datasheet - Page 12

LM22677TJE-5.0/NOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LM22677TJE-5.0/NOPB
Description
IC REG SWITCH BUCK 5A 5V TO263-7
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Series
SIMPLE SWITCHER®r
Type
Step-Down (Buck)r
Datasheet
1.LM22677TJE-ADJNOPB.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of LM22677TJE-5.0/NOPB
Internal Switch(s)
Yes
Synchronous Rectifier
No
Number Of Outputs
1
Voltage - Output
5V
Current - Output
5A
Frequency - Switching
200kHz ~ 1MHz
Voltage - Input
4.5 ~ 42 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
TO-263-7 Thin
Primary Input Voltage
12V
No. Of Outputs
1
Output Voltage
5V
Output Current
5A
No. Of Pins
7
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To +125°C
Msl
MSL 1 - Unlimited
Filter Terminals
SMD
Rohs Compliant
Yes
For Use With
551600233-001 - WEBENCH BUILD IT LM2267X TO-263LM22677EVAL - BOARD EVALUATION FOR LM22677
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Power - Output
-
Other names
LM22677TJE-5.0TR
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM22677TJE-5.0/NOPB
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
www.national.com
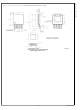
Circuit Board Layout
Board layout is critical for switching power supplies. First, the
ground plane area must be sufficient for thermal dissipation
purposes. Second, appropriate guidelines must be followed
to reduce the effects of switching noise. Switch mode con-
verters are very fast switching devices. In such devices, the
rapid increase of input current combined with the parasitic
trace inductance generates unwanted L di/dt noise spikes.
The magnitude of this noise tends to increase as the output
current increases. This parasitic spike noise may turn into
electromagnetic interference (EMI) and can also cause prob-
lems in device performance. Therefore, care must be taken
in layout to minimize the effect of this switching noise.
The most important layout rule is to keep the AC current loops
as small as possible.
converter. The top schematic shows a dotted line which rep-
resents the current flow during the FET switch on-state. The
middle schematic shows the current flow during the FET
switch off-state.
The bottom schematic shows the currents referred to as AC
currents. These AC currents are the most critical since current
is changing in very short time periods. The dotted lines of the
bottom schematic are the traces to keep as short as possible.
This will also yield a small loop area reducing the loop induc-
tance. To avoid functional problems due to layout, review the
PCB layout example. Providing 5A of output current in a very
low thermal resistance package such as the TO-263 THIN is
challenging considering the trace inductances involved. Best
results are achieved if the placement of the LM22677, the by-
pass capacitor, the Schottky diode and the inductor are
placed as shown in the example. It is also recommended to
use 2oz copper boards or thicker to help thermal dissipation
and to reduce the parasitic inductances of board traces.
It is very important to ensure that the exposed DAP on the
TO-263 THIN package is soldered to the ground area of the
PCB to reduce the AC trace length between the bypass ca-
pacitor ground and the ground connection to the LM22677.
Not soldering the DAP to the board may result in erroneous
operation due to excessive noise on the board.
FIGURE 6. Current Flow in a Buck Application
Figure 6
shows the current flow of a buck
30074124
12
Thermal Considerations
The two highest power dissipating components are the re-
circulating diode and the LM22677 regulator IC. The easiest
method to determine the power dissipation within the
LM22677 is to measure the total conversion losses (Pin –
Pout) then subtract the power losses in the Schottky diode
and output inductor. An approximation for the Schottky diode
loss is:
An approximation for the output inductor power is:
where R is the DC resistance of the inductor and the 1.1 factor
is an approximation for the AC losses. The regulator has an
exposed thermal pad to aid power dissipation. Adding several
vias under the device to the ground plane will greatly reduce
the regulator junction temperature. Selecting a diode with an
exposed pad will aid the power dissipation of the diode. The
most significant variables that affect the power dissipated by
the LM22677 are the output current, input voltage and oper-
ating frequency. The power dissipated while operating near
the maximum output current and maximum input voltage can
be appreciable. The junction-to-ambient thermal resistance of
the LM22677 will vary with the application. The most signifi-
cant variables are the area of copper in the PC board, the
number of vias under the IC exposed pad and the amount of
forced air cooling provided. The integrity of the solder con-
nection from the IC exposed pad to the PC board is critical.
Excessive voids will greatly diminish the thermal dissipation
capacity. The junction-to-ambient thermal resistance of the
LM22677 TO-263 THIN package is specified in the electrical
characteristics table under the applicable conditions. For
more information regarding the TO-263 THIN package, refer
to Application Note AN-1797 at www.national.com.
P = (1 - D) x I
P = I
OUT
2
x R x 1.1,
OUT
x V
D