MAX1771CSA Maxim Integrated Products, MAX1771CSA Datasheet - Page 9
MAX1771CSA
Manufacturer Part Number
MAX1771CSA
Description
IC DC/DC CTRLR STEP-UP HE 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Type
Step-Up (Boost)r
Datasheet
1.MAX1771CPA.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of MAX1771CSA
Internal Switch(s)
No
Synchronous Rectifier
No
Number Of Outputs
1
Voltage - Output
12V, 2 ~ 16.5 V
Current - Output
2A
Frequency - Switching
300kHz
Voltage - Input
2 ~ 16.5 V
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Power - Output
471mW
Output Voltage
12 V
Output Current
2 A
Input Voltage
2 V to 16.5 V
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
Case
SOP8
Dc
02+
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MAX1771CSA
Manufacturer:
MAX
Quantity:
7 031
Company:
Part Number:
MAX1771CSA
Manufacturer:
MAXIM
Quantity:
4
Part Number:
MAX1771CSA
Manufacturer:
MAXIM/美信
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
MAX1771CSA+T
Manufacturer:
NSC
Quantity:
6 219
The control circuitry allows the IC to operate in continu-
ous-conduction mode (CCM) while maintaining high
efficiency with heavy loads. When the power switch is
turned on, it stays on until either 1) the maximum on-
time one-shot turns it off (typically 16µs later), or 2) the
switch current reaches the peak current limit set by the
current-sense resistor.
The MAX1771 switching frequency is variable (depend-
ing on load current and input voltage), causing variable
switching noise. However, the subharmonic noise gen-
erated does not exceed the peak current limit times the
filter capacitor equivalent series resistance (ESR). For
example, when generating a 12V output at 500mA from
a 5V input, only 100mV of output ripple occurs using
the circuit of Figure 2a.
The MAX1771 features a low input voltage start-up oscil-
lator that guarantees start-up with no load down to 2V
when operating in bootstrapped mode and using inter-
nal feedback resistors. At these low voltages, the supply
voltage is not large enough for proper error-comparator
operation and internal biasing. The start-up oscillator
has a fixed 50% duty cycle and the MAX1771 disre-
gards the error-comparator output when the supply volt-
age is less than 2.5V. Above 2.5V, the error-comparator
and normal one-shot timing circuitry are used. The low-
voltage start-up circuitry is disabled if non-bootstrapped
mode is selected (FB is not tied to ground).
When SHDN is high, the MAX1771 enters shutdown
mode. In this mode, the internal biasing circuitry is
turned off (including the reference) and V
diode drop below V
input to the output). In shutdown mode, the supply
current drops to less than 5µA. SHDN is a TTL/CMOS
logic-level input. Connect SHDN to GND for normal
operation.
To set the output voltage, first determine the mode of
operation, either bootstrapped or non-bootstrapped.
Bootstrapped mode provides more output current capa-
bility, while non-bootstrapped mode reduces the supply
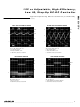
current (see the Typical Operating Characteristics). If a
decaying voltage source (such as a battery) is used,
see the additional notes in the Low Input Voltage
Operation section.
The MAX1771’s output voltage can be adjusted from
very high voltages down to 3V, using external resistors
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Setting the Output Voltage
IN
Low-Voltage Start-Up Oscillator
(due to the DC path from the
Design Procedure
12V or Adjustable, High-Efficiency,
Low I
Shutdown Mode
OUT
falls to a
Q
, Step-Up DC-DC Controller
R1 and R2 configured as shown in Figure 3. For
adjustable-output operation, select feedback resistor
R1 in the 10kΩ to 500kΩ range. R2 is given by:
where V
For preset-output operation, tie FB to GND (this
forces bootstrapped-mode operation.
Figure 2 shows various circuit configurations for boot-
strapped/non-bootstrapped, preset/adjustable operation.
Use the theoretical output current curves shown in
Figures 4a–4d to select R
using the minimum (worst-case) current-limit compara-
tor threshold value over the extended temperature
range (-40°C to +85°C). No tolerance was included for
R
assumed to be 0.5V, and the drop across the power
switch r
0.3V.
Practical inductor values range from 10µH to 300µH.
22µH is a good choice for most applications. In appli-
cations with large input/output differentials, the IC’s
output current capability will be much less when the
inductance value is too low, because the IC will always
operate in discontinuous mode. If the inductor value
is too low, the current will ramp up to a high level before
the current-limit comparator can turn off the switch.
The minimum on-time for the switch (t
Figure 3. Adjustable Output Circuit
SENSE
DS(ON)
REF
. The voltage drop across the diode was
MAX1771
equals 1.5V.
GND
and coil resistance was assumed to be
R2 = (R1)
Determining the Inductor (L)
FB
SENSE
(
Determining R
––––– -1
V
R1
V
OUT
R1 = 10kΩ TO 500kΩ
R2 = R1
V
REF
* SEE TEXT FOR VALUE
REF
. They were derived
= 1.5V
C5*
R2
(
)
V
V
OUT
REF
-1
)
ON
V
OUT
(min)) is
SENSE
9