MT48LC2M32B2TG-7IT Micron Semiconductor Products, MT48LC2M32B2TG-7IT Datasheet

MT48LC2M32B2TG-7IT
Available stocks
Related parts for MT48LC2M32B2TG-7IT
MT48LC2M32B2TG-7IT Summary of contents
Page 1
... MHz) 6ns (166 MHz) 7ns (143 MHz) • Operating Temperature Range Commercial (0° to +70°C) Extended (-40°C to +85°C) NOTE: 1. Off-center parting line 2. Available on -7 Part Number Example: MT48LC2M32B2TG-7 KEY TIMING PARAMETERS SPEED CLOCK ACCESS TIME GRADE FREQUENCY 200 MHz 4 ...
Page 2
... SDRAM PART NUMBER PART NUMBER ARCHITECTURE MT48LC2M32B2TG 2 Meg x 32 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The 64Mb SDRAM is a high-speed CMOS, dynamic random-access memory containing 67,108,864-bits internally configured as a quad-bank DRAM with a synchronous interface (all signals are registered on the positive edge of the clock signal, CLK). Each of the 16,777,216-bit banks is organized as 2,048 rows by 256 columns by 32 bits ...
Page 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS Functional Block Diagram - 2 Meg x 32 ................. Pin Descriptions ..................................................... Functional Description ......................................... Initialization ...................................................... Register Definition ............................................ Mode Register ............................................... Burst Length ............................................ Burst Type ............................................... CAS Latency ............................................ Operating Mode ...................................... Write Burst ...
Page 4
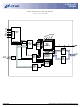
CKE CLK CONTROL CS# LOGIC WE# CAS# RAS# REFRESH COUNTER MODE REGISTER 11 11 A0-A10, ADDRESS 13 BA0, BA1 REGISTER 8 64Mb: x32 SDRAM 64MSDRAMx32_5.p65 – Rev. 9/00 FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM 2 Meg x 32 SDRAM BANK0 11 BANK0 ROW- ...
Page 5
PIN DESCRIPTIONS PIN NUMBERS SYMBOL 68 CLK 67 CKE 20 CS# 17, 18, 19 WE#, CAS#, RAS# 16, 71, 28, 59 DQM0- DQM3 22, 23 BA0, BA1 25-27, 60-66, 24 A0-A10 10, 11, 13, DQ0-DQ31 ...
Page 6
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION In general, this 64Mb SDRAM (512K banks quad-bank DRAM that operates at 3.3V and includes a synchronous interface (all signals are regis- tered on the positive edge of the clock signal, CLK). ...
Page 7
BURST TYPE Accesses within a given burst may be programmed to be either sequential or interleaved; this is referred to as the burst type and is selected via bit M3. The ordering of accesses within a burst is determined by ...
Page 8
CAS Latency The CAS latency is the delay, in clock cycles, between the registration of a READ command and the availabil- ity of the first piece of output data. The latency can be set to one, two or three clocks. ...
Page 9
Commands Truth Table 1 provides a quick reference of available commands. This is followed by a written description of each command. Three additional Truth Tables appear TRUTH TABLE 1 – COMMANDS AND DQM OPERATION (Note: 1) NAME (FUNCTION) COMMAND INHIBIT ...
Page 10
COMMAND INHIBIT The COMMAND INHIBIT function prevents new commands from being executed by the SDRAM, regard- less of whether the CLK signal is enabled. The SDRAM is effectively deselected. Operations already in progress are not affected. NO OPERATION (NOP) The ...
Page 11
BURST TERMINATE The BURST TERMINATE command is used to trun- cate either fixed-length or full-page bursts. The most recently registered READ or WRITE command prior to the BURST TERMINATE command will be truncated, as shown in the Operation section of ...
Page 12
Operation BANK/ROW ACTIVATION Before any READ or WRITE commands can be issued to a bank within the SDRAM, a row in that bank must be “opened.” This is accomplished via the ACTIVE command, which selects both the bank and the ...
Page 13
READs READ bursts are initiated with a READ command, as shown in Figure 5. The starting column and bank addresses are pro- vided with the READ command, and auto precharge is either enabled or disabled for that burst access. If ...
Page 14
Figure 7 for CAS latencies of one, two and three; data element either the last of a burst of four or the last desired of a longer burst. This 64Mb SDRAM uses a ...
Page 15
CLK COMMAND ADDRESS DQ CAS Latency = 1 CLK COMMAND ADDRESS DQ CLK COMMAND ADDRESS DQ NOTE: Each READ command may be to either bank. DQM is LOW. 64Mb: x32 SDRAM 64MSDRAMx32_5.p65 – Rev. 9/ READ ...
Page 16
Data from any READ burst may be truncated with a subsequent WRITE command, and data from a fixed- length READ burst may be immediately followed by data from a WRITE command (subject to bus turn- around limitations). The WRITE burst ...
Page 17
A fixed-length READ burst may be followed by, or truncated with, a PRECHARGE command to the same bank (provided that auto precharge was not activated), and a full-page burst may be truncated with a PRECHARGE command to the same bank. ...
Page 18
The disadvantage of the PRECHARGE command is that it requires that the command and address buses be available at the appro- priate time to issue the command; the ...
Page 19
WRITEs WRITE bursts are initiated with a WRITE command, as shown in Figure 13. The starting column and bank addresses are pro- vided with the WRITE command, and auto precharge is either enabled or disabled for that access. If auto ...
Page 20
READ command, and data for a fixed- length WRITE burst may be immediately followed by a READ command. Once the READ command is regis- tered, the data inputs will be ignored, and WRITEs will not be executed. An example ...
Page 21
BURST TERMINATE command. When truncating a WRITE burst, the input data applied coincident with the BURST TERMINATE command will be ignored. The last data written (provided that DQM is LOW at that time) will be the input ...
Page 22
CLOCK SUSPEND The clock suspend mode occurs when a column access/burst is in progress and CKE is registered LOW. In the clock suspend mode, the internal clock is deacti- vated, “freezing” the synchronous logic. For each positive clock edge on ...
Page 23
CONCURRENT AUTO PRECHARGE An access command to (READ or WRITE) another bank while an access command with auto precharge enabled is executing is not allowed by SDRAMs, unless the SDRAM supports CONCURRENT PRECHARGE. Micron SDRAMs support CONCUR- RENT AUTO PRECHARGE. ...
Page 24
WRITE WITH AUTO PRECHARGE 3. Interrupted by a READ (with or without auto precharge): A READ to bank m will interrupt a WRITE on bank n when registered, with the data- out appearing CAS latency later. The PRECHARGE t to ...
Page 25
TRUTH TABLE 2 – CKE (Notes: 1-4) CKE CKE CURRENT STATE n Power-Down Self Refresh Clock Suspend L H Power-Down Self Refresh Clock Suspend H L All Banks Idle All Banks Idle Reading or Writing H H ...
Page 26
TRUTH TABLE 3 – CURRENT STATE BANK n, COMMAND TO BANK n (Notes: 1-6; notes appear below and on next page) CURRENT STATE CS# RAS# CAS# WE# Any Idle L L ...
Page 27
NOTE (continued): Write w/Auto Precharge Enabled: 5. The following states must not be interrupted by any executable command; COMMAND INHIBIT or NOP commands must be applied on each positive clock edge during these states. Refreshing: Starts with registration of an ...
Page 28
TRUTH TABLE 4 – CURRENT STATE BANK n, COMMAND TO BANK m (Notes: 1-6; notes appear below and on next page) CURRENT STATE CS# RAS# CAS# WE# Any Idle Row L ...
Page 29
NOTE (continued): 4. AUTO REFRESH, SELF REFRESH, and LOAD MODE REGISTER commands may only be issued when all banks are idle BURST TERMINATE command cannot be issued to another bank; it applies to the bank represented by the ...
Page 30
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS* Voltage Supply DD DD Relative to V ........................................ -1V to +4.6V SS Voltage on Inputs I/O Pins Relative to V ........................................ -1V to +4.6V SS Operating Temperature ........................ ...
Page 31
I SPECIFICATIONS AND CONDITIONS DD (Notes 11, 13, 27; notes appear on page 35) (V PARAMETER/CONDITION OPERATING CURRENT: Active Mode; t Burst = 2; READ or WRITE CAS latency = 3 STANDBY CURRENT: Power-Down Mode; CKE ...
Page 32
CAPACITANCE (Note: 2; notes appear on page 35) PARAMETER Input Capacitance: CLK Input Capacitance: All other input-only pins Input/Output Capacitance: DQs ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND RECOMMENDED AC OPERATING CONDITIONS (Notes 11; notes appear on page 35) AC ...
Page 33
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND RECOMMENDED AC OPERATING CONDITIONS (Notes 11; notes appear on page 35) AC CHARACTERISTICS PARAMETER Access time from CLK (pos. edge) Address hold time Address setup time CLK high-level width CLK low-level width Clock ...
Page 34
AC FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS (Notes 11; notes appear on page 35) PARAMETER READ/WRITE command to READ/WRITE command CKE to clock disable or power-down entry mode CKE to clock enable or power-down exit setup mode DQM to ...
Page 35
NOTES 1. All voltages referenced This parameter is sampled MHz 25°C; pin under test biased at 1.4V can range from 0pF to 6pF dependent on ...
Page 36
INITIALIZE AND LOAD MODE REGISTER CLK ( ( ) ) t CKH t CKS ( ( ) ) CKE ( ( ) ) t CMH t CMS t CMH t CMS ( ( ) ) COMMAND ...
Page 37
CLK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND PRECHARGE DQM 0-3 A0-A9 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High-Z DQ Two clock cycles Precharge all All banks idle, ...
Page 38
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND READ NOP t CMS t CMH DQM0 A0-A9 COLUMN ...
Page 39
T0 T1 CLK t CK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND PRECHARGE NOP DQM 0-3 A0-A9 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High Precharge all active banks ...
Page 40
T0 T1 CLK t CK CKE t CKS t CKH t CMS t CMH COMMAND PRECHARGE NOP DQM 0-3 A0-A9 ALL BANKS A10 SINGLE BANK BA0, BA1 BANK(S) High Precharge all active banks ...
Page 41
T0 CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE DQM / DQML, DQMH A0-A9, A11 ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ TIMING PARAMETERS ...
Page 42
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM 0 ROW A0- ROW A10 DISABLE AUTO PRECHARGE t AS ...
Page 43
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM 0 A0-A9 ROW ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ROW A10 ...
Page 44
ALTERNATING BANK READ ACCESSES CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM 0 ROW A0- ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ROW A10 ...
Page 45
CLK CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP READ t CMS DQM 0 A0-A9 COLUMN m 2 ROW ...
Page 46
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM 0 A0-A9 ROW ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ROW A10 DISABLE AUTO PRECHARGE t ...
Page 47
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE DQM / DQML, DQMH A0-A9, A11 ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ ...
Page 48
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM 0 A0-A9 ROW ROW A10 DISABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ...
Page 49
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP WRITE t CMS DQM 0 A0-A9 COLUMN m 3 ROW ENABLE AUTO PRECHARGE ...
Page 50
ALTERNATING BANK WRITE ACCESSES CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP t CMS DQM 0 COLUMN m 3 ROW A0- ...
Page 51
CLK CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM 0 A0-A9 ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK ...
Page 52
CLK t CKS t CKH CKE t CMS t CMH COMMAND ACTIVE NOP DQM 0 A0-A9 ROW ROW A10 BA0, BA1 BANK DQ t ...
Page 53
TYP 0.20 R .75 (2X) PIN # 1.00 (2X) 1. All dimensions in millimeters MAX or typical where noted. NOTE: 2. Package width and length do not include mold protrusion; allowable mold protrusion is 0.025mm ...