CMX969 Consumer Microcircuits Limited, CMX969 Datasheet

CMX969
Available stocks
Related parts for CMX969
CMX969 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Brief Description The CMX969 is a CMOS integrated circuit that contains all of the baseband signal processing and Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol functions required for a high performance DataTAC dual mode (RD-LAP 19200 bps and MDC 4800 bps) FSK Wireless Packet Data Modem suitable for use with the Motient/ARDIS network ...
Page 2
... Control Register.........................................................................12 1.5.5.3 Mode Register ............................................................................13 1.5.5.4 Command Register ....................................................................15 1.5.5.5 Status Register...........................................................................26 1.5.5.6 Data Quality Register ................................................................28 1.6 Application Notes....................................................................................29 1.6.1 Autonomous Frame Sync Detect Function............................29 1.6.2 Rx Control Procedure................................................................30 1.7 Performance Specification.....................................................................32 1.7.1 Electrical Performance..............................................................32 1.7.1.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings .....................................................32 1.7.1.2 Operating Limits.........................................................................32 1.7.1.3 Operating Characteristics ........................................................33 1.7.2 Packaging....................................................................................36 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited CONTENTS 2 CMX969 Page D/969/5 ...
Page 3
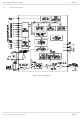
... RD-LAP/MDC4800 Motient/ARDIS 1.2 Block Diagram 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited Figure 1 Block Diagram 3 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 4
... No connection should be made to these pins (reserved for possible NC future use) O/P The Tx signal output from the modem. O/P A bias line for the internal circuitry, held at ½ V decoupled capacitor mounted close to the device pins. SS I/P The input to the Rx input amplifier. 4 CMX969 Description is required This pin must be DD D/969/5 SS ...
Page 5
... Power The positive supply rail. Levels and voltages are dependent upon this supply. This pin should be decoupled Bidirectional connection C1 0.1 µF 20% C2 0.1 µF 20% C3 20%, see Note 1 5 CMX969 Description by a capacitor. SS and 20%, see Note 1 C5 100pF 5% C6 100pF ...
Page 6
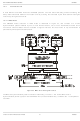
... A 12-byte buffer used to hold receive or transmit data to or from the µC. CRC Generator/Checker A circuit which generates (in transmit mode) or checks (in receive mode) the Cyclic Redundancy Checksum bits, which are included in transmitted data blocks so that the receive modem can detect transmission errors. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited Figure 3 Typical Modem µC Connections 6 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 7
... These components may form part of any dc level-shifting and gain adjustment circuitry. C5 should be positioned to give maximum attenuation of high frequency noise into the modulator. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited (½ See section 1.7.1.3 for details of BIAS DD unless the RXEYE bit of the Control Register is '1', when it BIAS 7 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 8
... Forward Error Correction coding and Interleaving. Details of the message formats handled by the modem are given in Section 1.5.4 and Figures 5a and 5b. To reduce the processing load on the associated C, the CMX969 modem has been designed to perform as much as possible of the computationally intensive work involved in Frame formatting and de-formatting and - when in receive mode - in searching for and synchronising onto the Frame Preamble. In normal operation the modem will only require servicing by the µ ...
Page 9
... Forward Error Correcting coding scheme for the block oriented tasks THB, TIB, TLB, TSID, RHB, RILB and RSID described in Section 1.5.5.4. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited symbol ms bit ls bit + msb sent first 9 lsb sent last CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 10
... RD-LAP/MDC4800 Motient/ARDIS 1.5.4 Frame Structure In both RD-LAP and MDC modes the CMX969 performs all of the block formatting and de-formatting, the binary data transferred between the modem and its C being that enclosed by the thick dashed rectangles near the top of Figures 5a and 5b. 1.5.4.1 MDC Mode The CMX969 Frame Structure in MDC mode is illustrated in Figure 5a, and consists of a Frame Synchronisation pattern followed by one or more 'Header’ ...
Page 11
... RD-LAP Mode The CMX969 Frame Structure in RD-LAP mode is illustrated in Figure 5b, and consists of a Frame Preamble (comprising a 24-symbol Frame Synchronisation pattern and Station ID block) followed by one or more 'Header’ blocks, one or more 'Intermediate’ blocks and a 'Last’ block. Channel Status (S) symbols are included at regular intervals ...
Page 12
... Symbol Rate 4.9152 MHz 7.3728 MHz 9.8304 MHz See note 12 Read from Modem Data Buffer Status Register Data Quality Register Reserved for other uses. Division ratio: Xtal frequency / MDC4800 Symbol Rate 512 1024 768 1536 1024 2048 1536 3072 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 13
... Control Register B2: MDC - MDC Mode If this bit is ‘0’ the CMX969 operates in RD-LAP mode, setting this bit to ‘1’ selects MDC mode. Changing between RD-LAP and MDC modes will cancel any current task. Control Register B1: FSTOL - Frame Sync Detect Tolerance In RD-LAP mode this bit affects the number of errors tolerated by the Frame Sync detector when running SFS or SFP tasks or AFSD ...
Page 14
... Note that changing between receive and transmit modes will cancel any current task. Mode Register B4 Zero Power Setting this bit to ‘1’ removes power from all of the CMX969’s circuitry, including the Xtal oscillator, the Vbias supply and the Tx o/p buffer. The µC interface will continue to operate except for the Command Register which will not recognise or execute commands when ZP is ‘ ...
Page 15
... Note that the Command Register uses internal clocks derived from the XTAL input to decode and carry out any task written to it advisable to postpone writing to the Command Register until about 20 msec after power is applied to the CMX969 or the Mode Register ZP bit is changed from ‘1’ to ‘0’, to allow time for the Xtal oscillator to start up. ...
Page 16
... The µC should not write a task (other than NULL or RESET) to the Command Register or write to or read from the Data Buffer when the BFREE (Buffer Free) bit of the Status Register is '0'. Different tasks apply in RD-LAP and MDC receive and transmit modes. CMX969 Modem Tasks, Transmit Mode ...
Page 17
... Register will be set to '1', indicating to the µC that it may write the data and command byte for the next task to the modem. The following tables show what data has to be written to the Data Block Buffer to transmit the CMX969 Symbol and Frame Sync sequences: ...
Page 18
... FEC bits, interleaves the result, inserts channel status bits and transmits the result as a formatted ‘Last’ Block. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited Values written to Data Block Buffer Binary Byte 0: 00100010 Byte 1: 00110111 Byte 2: 01001001 Byte 3: 11110010 Byte 4: 01011011 Byte 5: 00011011 18 CMX969 Hex D/969/5 ...
Page 19
... Xtal oscillator to start up) when applied or the ZP bit of the Mode Register changed from ‘1’ to ‘0’ to set the modem into a known state. Note that due to delays in the transmit low pass filter, it will take several symbol times for any change to appear at the TXOP pin. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 19 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 20
... RD-LAP/MDC4800 Motient/ARDIS CMX969 Modem Tasks, Receive Mode NULL SFP RHB RILB SFS R4S RSID RESET When the modem is in receive mode, the µC should wait until the BFREE bit of the Status Register is '1', then write the desired task to the Command Register ...
Page 21
... This task causes the modem to read the next 69 symbols (RD-LAP) or 112 bits (MDC 'Intermediate' or 'Last' block (the µC can tell from the 'Header' block how many blocks are in the frame, and hence when to expect the 'Last' block). 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 21 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 22
... FEC) into the Data Block Buffer. The BFREE and IRQ bits of the Status Register will then be set to '1' to indicate that the µC may read the data byte from the Data Block Buffer and write the next task to the Command Register. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 22 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 23
... BFREE bit of the Status Register to ‘1’, without setting the IRQ bit. Writing a RESET task to the CMX969 also resets an internal received signal buffer memory used by AFSD function, so that if a RESET task is written while the CMX969 is receiving a Frame Sync pattern then that pattern will not be recognised by the AFSD function. ...
Page 24
... Figure 10 Receive Task Timing Diagram 24 Time Task (symbol times) Any T24S 5 TSID 6 THB/TIB/TLB 16 T4S 0 T24S/TSID 24 THB/TIB/TLB 69 T4S 4 T24S 18 TSID 17 THB/TIB/TLB 52 T4S 3 Time Task (bit times) Any T40B 0.5 THB/TIB/TLB 0.5 T8B 0.5 T40B 40 THB/TIB/TLB 112 T8B 8 T40B 38 THB/TIB/TLB 110 T8B 6 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 25
... CMX969 Time Task (symbol times) ...
Page 26
... In transmit mode, this bit signals ‘Interleave Buffer Empty’ and will be set to '1' - also setting the IRQ bit - when less than two symbols remain in the Interleave Buffer. Any transmit task written to the modem after this bit goes to '1' will be too late to avoid a gap in the transmit output signal. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 26 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 27
... TXRXN PSAVE bits of the Mode Register. Status Register B1, B0: RD-LAP Mode: SVAL - Received 'S' Symbol Value In receive RD-LAP mode these two bits reflect the value of the latest received 'S' symbol. In transmit mode, these two bits will be '0'. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 27 CMX969 th bit) has th bit) has D/969/5 ...
Page 28
... Data Quality Register In receive mode, the CMX969 continually measures the 'quality' of the received signal, by comparing the actual received waveform against an internally generated 'ideal 4-level FSK baseband signal. The result is placed into bits 3-7 of the Data Quality Register for the µC to read at any time, bits 0-2 being always set to '0' ...
Page 29
... On detecting a Frame Sync pattern the AFSD function sets the AFSDET and IRQ bits of the Status Register and terminates any other current task. AFSD should be enabled to look for a Frame Sync pattern whenever the CMX969 is switched to receive mode or the radio is switched to a new receive channel or when the transmitter may have been switched off - in fact in any circumstance where the correct levels and timing need to be re-established ...
Page 30
... RD-LAP/MDC4800 Motient/ARDIS 1.6.2 Rx Control Procedure The following procedure illustrates how the CMX969 can be controlled to receive one or more messages in MDC mode. RD-LAP mode is similar except that the first block of each message will be a Station ID block. Step Action 0 Switch radio onto receive channel. CMX969 Mode Register IRQNEN, INVSYM and SSIEN bits should be set as required, other bits 0 ...
Page 31
... Status Register BFREE bit to 1, whereas AFSD sets the AFSDET bit. 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited If we want to continue receiving the rest of this Rx message then tell the CMX969 to receive and decode the next block. Keep the AFSD function running in case a new transmitter starts up on this channel (SFR) ...
Page 32
... SS Operating Temperature Symbol Rate Xtal Frequency 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited Min. -0.3 -0.3 pins -30 SS -20 Min. -55 -40 Min. -55 -40 Min. -55 -40 Notes Min. 2.7 -40 2000 1.0 32 CMX969 Max. Units 7 0 +30 mA +20 mA Max. Units 800 mW 13 mW/°C +125 °C +85 °C Max. Units 400 mW 5.3 mW/°C +125 ° ...
Page 33
... 120µ 5.0V and Tamb = 25° Min. Typ. Max. 4.0 9.0 2.5 5.0 1.5 0.8 10.0 1.0 2.5 1.6 2.0 2.4 0.71 0.89 1.07 -0.25 +0.25 10.0 300 1.0 2.5 0.5 1.2 -1.0 +1.0 40.0 40.0 10.0 20.0 70% 30% 5.0 +5.0 - 10.0 92 CMX969 Units µ p V/V V p µ µ D/969/5 ...
Page 34
... S/N dB (Noise Symbol Rate Bandwidth S/N dB (Noise in Bit Rate Bandwidth 5.0V and Tamb = 25°C. The optimum input DD . Signal peaks should not go outside the DD BER with FEC BER without FEC BER with FEC BER without FEC CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 35
... Xtal clock cycles at the XTAL pin. 11. With 30pF max to V 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited Notes Min. 10 6.0 90 200 200 pins. SS Figure 14 µC Parallel Interface Timings 35 Typ. Max. Units clock cycles 175 145 50.0 0 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 36
... RD-LAP/MDC4800 Motient/ARDIS 1.7.2 Packaging Figure 15 E2 Mechanical Outline: Order as part no. CMX969E2 Figure 16 P4 Mechanical Outline: Order as part no. CMX969P4 2001 Consumer Microcircuits Limited 36 CMX969 D/969/5 ...
Page 37
... RD-LAP/MDC4800 Motient/ARDIS Modem Figure 17 D5 Mechanical Outline: Order as part no. CMX969D5 Handling precautions: This product includes input protection, however, precautions should be taken to prevent device damage from electro-static discharge. CML does not assume any responsibility for the use of any circuitry described. No IPR or circuit patent licences are implied ...
Page 38
... CML Microcircuits Product Prefix Codes Until the latter part of 1996, the differentiator between products manufactured and sold from MXCOM, Inc. and Consumer Microcircuits Limited were denoted by the prefixes MX and FX respectively. These products use the same silicon etc. and today still carry the same prefixes. ...