PEB2080 SIEMENS [Siemens Semiconductor Group], PEB2080 Datasheet

PEB2080
Available stocks
Related parts for PEB2080
PEB2080 Summary of contents
Page 1
Contents 1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 2
...
Page 3
S/T Bus Interface Circuit (SBC) Preliminary Data 1 Features Full duplex S/T-interface transceiver according to CCITT I.430 Conversion of the frame structure between the S/T and IOM ® interfaces D-channel access control Activation and deactivation procedures according ...
Page 4
The S-Bus Interface Circuit (SBC) PEx 2080 implements the four-wire S/T-interface used to link voice/data terminals to an ISDN. Through selection of operating mode, the device may be employed in all types of applications involving an S interface. Two or ...
Page 5
Pin Configuration (top view) P-DIP-22 Semiconductor Group P-LCC-28-R 7 Features ...
Page 6
Pin Definitions and Functions Pin No. Pin No. Symbol P-LCC P-DIP 3 2 SX1 4 3 SX2 7 5 SDO 10 8 SDI 8 6 DCL 9 7 FSC ...
Page 7
Logic Symbol Semiconductor Group 9 Features ...
Page 8
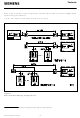
Block Diagram Semiconductor Group 10 Features ...
Page 9
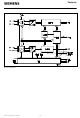
System Integration The SBC implements the four-wire S and T interfaces used in the ISDN basic access. It may be used at both ends of these interfaces. The applications include: ISDN terminals (TE) ISDN network termination (NT) ISDN subscriber ...
Page 10
Some of the S interface wiring configurations possible with the SBC are shown in figure 2 with approximate typical distances. *) (N.B.: “TR” stands for terminating resistor of value 100 ). Figure 2 Some S-Interface Wiring Configurations *) The maximum ...
Page 11
Figure 3 ISDN Oriented Modular (IOM Semiconductor Group ® ) Architecture 13 ...
Page 12
Figure 3 gives an example of an application of the SBC in an IOM (ISDN Oriented Modular) architecture. By separate implementation of OSI layer-1 and layer-2 functions, and through unified control procedures, the architecture provides flexibility with respect to various ...
Page 13
Semiconductor Group 15 ...
Page 14
Functional Description The S-bus interface circuit PEx 2080 performs the layer-1 functions for the S/T interface of the ISDN basic access. 2.1 General Functions and Device Architecture The common functions for all operating modes are: Iine transceiver functions for ...
Page 15
Digital Functions A DPLL circuitry working with a frequency of 7.68 MHz line clock from the reference clock delivered by the network and to extract the 192-kHz line clock from the receive data stream. The 7.68-MHz clock may be generated ...
Page 16
Table 1 Operating Modes and Functions of Mode Specific Pins of SBC Application TE TE Operation Inverted Inverted of IOM Mode Mode Interface DCL o: o: 512 kHz* 512 kHz* FSC ...
Page 17
The other uses of the auxiliary pins are: ENCK input BUS input ECHO output push-pull SSZ input RDY output CON input DEX input DE input/output open drain with integrated pull- up resistor TS0 to TS2 inputs Semiconductor Group Enable Clock. ...
Page 18
Figure 4 Clocking of SBC in Different Operating Modes Semiconductor Group Functional Description 19 ...
Page 19
Interfaces S Interface According to CCITT recommendation I.430, pseudo-ternary encoding with 100 % pulse width is used on the S interface. A logical 1 corresponds to a neutral level (no current), whereas logical 0´s are encoded as alternating positive ...
Page 20
Digital Interface IOM Frame Structure The SBC is provided with a digital interface, the IOM interface, for communication with other ISDN devices, in other words with units realizing OSI layer-1 functions (such as the ISDN Echo Cancellation Circuit IEC PEB ...
Page 21
The basic frame consists of a total of 32 bits, or four octets (18 bits) plus 14 bits of MONITOR and control information. The data in both directions are synchronous and in phase (figure 8). ...
Page 22
IOM-1 Mode This timing mode is applicable in all operating modes of the SBC. Nominal bit rate of data (SDI and SDO): Nominal frequency of DCL: Nominal frequency of FSC: Transitions of the data occur after even-numbered rising edges of ...
Page 23
The bursts are allocated to consecutive time slots in a frame by the static inputs X0 (TS0), X1 (TS1), X2 (TS2). Table 2 indicates the allocations. Figure 11 gives the positions of the respective frames. Figure 10 Timing of Data ...
Page 24
Figure 11 Position of IOM ® Frames as a Function of Time Slot Allocation in IOM Semiconductor Group Functional Description ® -2 and Inverted Mode 25 ...
Page 25
The IOM-2 mode may be used to link up to eight SBC´s over a single 2048 kbit/s interface to an exchange or PABX (figure 12). Figure 12 IOM ® Interface 2048 kbit/s MUX Mode Semiconductor Group Functional Description 26 ...
Page 26
Individual Functions The SBC transmits data between the IOM interface and the line interface. The relative frame positions have been selected to minimize the round trip delays of the B channels, which are: 125 s for TE, NT and ...
Page 27
Figure 13b nd Example of 2 Order RC Network Note: Following component values are recommended to give a 500 kHz cutoff, and 600 nS ( 170 nS) propagation delay time ...
Page 28
NT and LT-S Applications The 192-kHz transmit bit clock is synchronized to the IOM clock DCL. In the receive direction two cases have to be distinguished depending whether a bus or a point-to-point operation is programmed (pin X3:BUS). Bus Operation ...
Page 29
Figure 14 Clock System of the SBC Semiconductor Group Functional Description 30 ...
Page 30
D-channel access control The D-channel access control ensures that only one terminal shall have access to the D channel at any time. This is achieved through collision detection by each terminal (CCITT I.430). The SBC MONITORS the received D-echo channel, ...
Page 31
By sending the BUSY bit the ISDN Communication Controller in anticipation of the S-bus D- channel “ready” state, the first valid D bits will emerge from the SBC at exactly the moment an access is allowed. D-channel ...
Page 32
Figure 16 D-Channel Access Control of the SBC Semiconductor Group Functional Description 33 ...
Page 33
Q Channel The SBC provides Q-channel support by transmitting a binary “1” in each frame in which a “1” is received in the F -bit position of the NT-to-TE frame. Thus interference the Q bits in passive ...
Page 34
Additional Functions Test Functions Test loops Two kinds of test loops may be closed in the SBC, which depend on the selected mode of operation. In both test loops, all three channels (B1, B2 and D) are looped back. ...
Page 35
Test Signals Two kinds of test signals may be sent by the SBC: single pulses and continuous pulses. The single pulses are of alternating polarity, one S-interface bit period wide, 0.25 ms apart, with a repetition frequency 2 kHz. Single ...
Page 36
Use of ECHO Local communication of terminals connected bus may be implemented by using the auxiliary ECHO output (pin X2 mode only). The timing of ECHO is identical to that of output SDO: however, the ...
Page 37
Operational Description 3.1 General The internal finite state machine of the SBC controls the activation/deactivation procedures, switching of test loops and transmission of special pulse patterns. Such actions can be initiated by signals on the S transmission line (INFO’s) ...
Page 38
In NT mode the IOM interface is activated by the upstream unit turning on the clocking signals. Simultaneously the upstream unit must send the desired command in the C/l channel. In the case where activation is requested from a terminal, ...
Page 39
As an alternative to clock activation via SDI, the asynchronous wake-up pin ENCK ( mode) can be grounded. In this case the timing given in figure 22 applies. When ENCK is tied to ground the IOM-clock pulses are ...
Page 40
Control of Layer 1 The state diagrams are shown in figures 24 to 26. The activation/deactivation implemented by the SBC in its different operating modes agrees with the requirements set forth in CCITT re- commendations. State identifiers F1-F8 (TE/LT-T) ...
Page 41
Commands / Indications and State Diagrams LT-T Table 5 Command (upstream) Timing Reset Send continuous zeros Send single zeros Activate request, set priority 8 Activate request, set priority 10 Activate request loop Deactivate indication Indication (downstream) Power ...
Page 42
TE / LT-T Mode F3 power down This is the deactivated state of the physical protocol.The receive line awake unit is active except during a RST pulse. Clocks are disabled if ENCK = 1 (TE mode). The power consumption in ...
Page 43
Unconditional States Loop3 closed On Activate Request Loop command, INFO3 is sent by the line transmitter internally to the line receiver (INFO0 is transmitted to the line). The receiver is not yet synchronized. Loop3 activated The receiver is synchronized on ...
Page 44
Figure 24a State Diagram of TE/LT-T Mode Semiconductor Group Operational Description 45 ...
Page 45
Figure 24b State Diagram of TE/LT-T Mode: Unconditional Transitions Semiconductor Group Operational Description 46 ...
Page 46
Commands / Indications and State Diagrams in LT-S Mode Table 3 Command (downstream) Abbr. Deactivate request Send continuous zeros Send single zeros Activate request Activate request loop Deactivate indication Indication (upstream) Lost signal level Lost framing Activate request Activate indication ...
Page 47
LT-S Mode G1 deactivated The SBC is not transmitting. No signal detected on the S interface, and no activation command is received in C/l channel. G2 synchronized As a result of an INFO1 detected on the S line or an ...
Page 48
Figure 25 State Diagram of LT-S Mode Semiconductor Group Operational Description 49 ...
Page 49
Commands / Indications and State Diagrams in NT Table 4 Command (downstream) Abbr. Deactivate request Resynchronization of U-interface Activate request Activate request loop Deactivate indication Activate indication Activate indication loop Send single zeros Indication (upstream) Timing Lost signal level Lost ...
Page 50
NT Mode G1 deactivated The SBC is not transmitting. No signal is detected on the S/T interface, and no activation command is received in C/l channel output as a response to RST, DIU is output in the normal ...
Page 51
Figure 26 State Diagram of NT Mode Semiconductor Group Operational Description 52 ...
Page 52
Example of Activation / Deactivation An example of an activation/deactivation of the S interface, with the aforementioned time relationships, is shown in figure 27, in the case of an SBC in TE and LT-S modes. Figure 27 Example of Activation ...
Page 53
Electrical Characteristics Absolute Maximum Ratings Parameter Ambient temperature under bias PEB 2080 PEF 2080 Storage temperature Voltage on any pin with respect to ground Power dissipation Stresses above those listed here may cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure ...
Page 54
Transmitter Input Current The destruction limits for negative input signals with R 200 are given in figure 29. i Figure 29 Receiver Input Current The destruction limits are given in figure 30. R 300 . i Figure 30 Semiconductor Group ...
Page 55
DC Characteristics ˚ Parameter L-input voltage H-input voltage L-output voltage L-output voltage (SDO) H-output voltage H-output voltage Power supply current operational power down Power supply current operational ...
Page 56
Capacitances – ˚ Parameter Input capacitance I/O capacitance Output capacitance against V Load capacitance Recommended Oscillator Circuit Figure 31 The integrated oscillator uses a parallel resonance crystal. Unmeasured pins ...
Page 57
Table 6 Output Stages Application TE TE Operation Inverted Inverted of IOM Mode Mode Interface DCL Push/ Push/ Pull Pull FSC Push/ Push/ Pull Pull CP Push/ Push/ Pull Pull X2 ...
Page 58
Table 7 SBC Clock Signals *Application TE TE Operation Inverted Inverted of IOM Mode Mode Interface DCL o: o: 512 kHz* 512 kHz* 1:2 1:2 FSC o:8 kHz* o:8 kHz* o:8 ...
Page 59
AC Characteristics ˚ for PEB 2080 – ˚ The AC testing input/output waveform is shown below. ...
Page 60
Figure 33 Phase Relationships of Auxiliary Clocks Tables give the timing characteristics of the clock. Figure 34 Definition of Clock Period and Width Semiconductor Group Electrical Characteristics 61 ...
Page 61
Table 8 XTAL1,2 Parameter High phase of crystal/clock Low phase of crystal/clock Table 9 DCL Parameter (TE) 512 kHz (TE) 512 kHz 2:1 (TE) 512 kHz 2:1 (TE) 512 kHz 1:2 (TE) 512 kHz 1:2 (NT, LT-S, LT-T) (NT, LT-S, ...
Page 62
Table 11 X1 Parameter Symbol (TE) 3840 kHz (TE) 3840 kHz W HQ (TE) 3840 kHz Table 12 X2 Parameter Symbol (TE) 2560 kHz (TE) 2560 kHz W HQ (TE) 2560 ...
Page 63
CP, DCL and FSC Relationships in IOM Figure 35 Parameter Clock delay CP - DCL Clock delay CP - FSC Delay DCL - FSC Semiconductor Group ® Master Mode Symbol Limit Values min. max ...
Page 64
IOM Interface Normal Mode Master Mode (TE) Figure 36 Parameter Frame sync delay C = 100 pF L IOM output data delay C = 100 pF L IOM input data setup IOM input data hold Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit ...
Page 65
Slave Mode (NT, LT-S, LT-T) Figure 37 Parameter Frame sync hold Frame sync setup Frame sync high Frame sync low IOM data output delay IOM input data setup IOM input data hold *) For push-pull output. For open drain output ...
Page 66
Inverted Mode Figure 38 Parameter Frame sync delay C = 100 pF L IOM output data delay C = 100 pF L IOM input data setup IOM input data hold Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit Values min. max. t – 20 ...
Page 67
Inverted Mux Mode Figure 39 Parameter Frame sync hold Frame sync setup Frame sync high Frame sync low IOM data output delay 150 pF IOM input data setup IOM output data hold ...
Page 68
Timing of Special Function Pins RST Characteristics Parameter Length of active (low) state RDY Characteristics Figure 40 Parameter Length of low state Length of high state Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit Values min. max Symbol Limit Values ...
Page 69
DE Characteristics The form of the DE input/output (pin X0, NT mode) is given by figure 41 for the case of two S interfaces having a minimum frame delay and a maximum frame delay, respectively. Figure 41 Star Configuration in ...
Page 70
Figure 42 Timing of DE Output Figure 43 Timing of DE Input Table 13 Parameter DE delay C = 100 setup DE hold Semiconductor Group Symbol Limit Values min. max DED t 3 DES t ...
Page 71
Figure 44 Timing of DE Semiconductor Group Electrical Characteristics 72 ...
Page 72
ECHO Characteristics The timing of the ECHO output (pin X2, TE mode) is identical with that of output SDO: however, the signal is “1” everywhere except in bit positions 24 and 25 (“D”-bit positions) of IOM frame, where it is ...
Page 73
Package Outlines Plastic Dual-in-Line Package, P-DIP-22 Plastic-Leaded Chip Carrier, P-LCC-28-R (SMD) SMD = Surface Mounted Device Semiconductor Group Package Outlines 75 Dimensions in mm ...
Page 74
... This datasheet has been download from: www.datasheetcatalog.com Datasheets for electronics components. ...