PEB2080 SIEMENS [Siemens Semiconductor Group], PEB2080 Datasheet - Page 15

PEB2080
Manufacturer Part Number
PEB2080
Description
S/T Bus Interface Circuit(SBC)
Manufacturer
SIEMENS [Siemens Semiconductor Group]
Datasheet
1.PEB2080.pdf
(74 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PEB2080
Manufacturer:
SIEMENS
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
PEB2080
Manufacturer:
SIE
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
PEB2080N
Manufacturer:
SIEMENS
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
PEB2080NVB1
Manufacturer:
SIEMENS
Quantity:
7 755
Company:
Part Number:
PEB2080P
Manufacturer:
SIEMENS
Quantity:
5 510
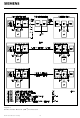
Digital Functions
A DPLL circuitry working with a frequency of 7.68 MHz
line clock from the reference clock delivered by the network and to extract the 192-kHz line clock
from the receive data stream.
The 7.68-MHz clock may be generated with the use of an external crystal between pins XTAL1 and
XTAL2. It may also be provided by an external oscillator, in which case XTAL2 is left unconnected.
The “Control” block includes the logic to detect layer-1 commands and to communicate with
external layer-1 or layer-2 devices via the IOM interface.
An incorporated finite state machine controls ISDN layer-1 activation/deactivation.
The D-channel access procedure according to CCITT I.430 including priority management is fully
implemented in the SBC. When used as an S-bus master in a multipoint configuration, the device
generates the echo bits necessary for D-channel collision detection. In the NT-mode, moreover, the
echo channel may be made externally available through an auxiliary pin and thus “intelligent NT’s”
(star configuration) may be implemented.
In terminal applications (TE) the Q channel as specified by I.430 is supported (stepping A6 and up.
The SBC sends a binary one in F
transmission capacity.)
The buffer memory serves to adapt the different bit rates of the S and the IOM interface. In addition,
in trunk line applications it absorbs the possible deviation between two system clocks, according to
CCITT Q.503 (slip detection).
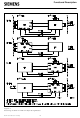
2.2
The operating modes are determined by pin strapping on pins M0 to M2. The four basic operating
modes are: TE, NT, LT-S, LT-T.
In three of these operating modes, the IOM may be programmed to function in the IOM-1 mode, in
the IOM -2 mode or in the inverted mode. To see which IOM timing mode is applicable in the four
basic operating modes, refer to table 1.
In table 1, the functions of the operating mode specific pins are given: these pins are DCL (IOM
interface data clock, input/output), FSC (IOM interface frame sync, input/output), CP (auxiliary
clock/test pin), and X0 to X3.
Depending on the selected mode, pins CP, X2 and X1 provide auxiliary clocks, either asynchronous
or synchronous to the S-interface:
3840 kHz
2560 kHz
1280 kHz
1536 kHz
512 kHz
These auxiliary clocks may be used to drive, e.g. a codec filter, or a microprocessor system (TE
applications).
Semiconductor Group
Operating Modes
clocks derived from the 7680-kHz crystal
clocks synchronized to S interface
A
-bit position to allow another terminal to use the extra
16
100 ppm serves to generate the 192-kHz
Functional Description