AS5040 PB austriamicrosystems, AS5040 PB Datasheet - Page 20

AS5040 PB
Manufacturer Part Number
AS5040 PB
Description
BOARD PROGRAM AS5040
Manufacturer
austriamicrosystems
Datasheet
1.AS5040_PB.pdf
(33 pages)
Specifications of AS5040 PB
Module/board Type
ZIF Socket
For Use With/related Products
AS5000 Programmer, AS5040
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free by exemption / RoHS compliant by exemption
Other names
AS5045 PB
AS5140H PB
AS5145 PB
AS5140H PB
AS5145 PB
AS5040
Data Sheet
Repeated OTP Programming
Although a single AS5040 OTP register bit can be programmed only once (from 0 to 1), it is possible to program other,
unprogrammed bits in subsequent programming cycles. However, a bit that has already been programmed should not
be programmed twice. Therefore it is recommended that bits that are already programmed are set to “0” during a
programming cycle.
Non-permanent Programming
It is also possible to re-configure the AS5040 in a non-permanent way by overwriting the OTP register.
This procedure is essentially a “Write Data” sequence (see Figure 14) without a subsequent OTP programming cycle.
The “Write Data” sequence may be applied at any time during normal operation. This configuration remains set while
the power supply voltage is above the power-on reset level (see 0).
See Application Note AN5000-20 for further information.
Analog Readback Mode
Non-volatile programming (OTP) uses on-chip zener diodes, which become permanently low resistive when subjected
to a specified reverse current.
The quality of the programming process depends on the amount of current that is applied during the programming
process (up to 130mA). This current must be provided by an external voltage source. If this voltage source cannot
provide adequate power, the zener diodes may not be programmed properly.
In order to verify the quality of the programmed bits, an analog level can be read for each zener diode, giving an
indication whether this particular bit was properly programmed or not.
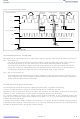
To put the AS5040 in analog readback mode, a digital sequence must be applied to pins CSn, Prog and CLK as
shown in Figure 17. The digital level for this pin depends on the supply configuration (3.3V or 5V; see section 14).
The second rising edge on CSn (OutpEN) changes pin Prog to a digital output and the log. high signal at pin Prog
must be removed to avoid collision of outputs (grey area in Figure 17).
The following falling slope of CSn changes pin Prog to an analog output, providing a reference voltage V
be saved as a reference for the calculation of the subsequent programmed and unprogrammed OTP bits.
Following this step, each rising slope of CLK outputs one bit of data in the reverse order as during programming.
(see Figure 17: Md0-MD1-Div0,Div1-Indx-Z0…Z9, ccw)
During analog readback, the capacitor at pin Prog (see Figure 16) should be removed to allow a fast readout rate. . If
the capacitor is not removed the analog voltage will take longer to stabilize due to the additional capacitance.
The measured analog voltage for each bit must be subtracted from the previously measured V
value gives an indication on the quality of the programmed bit: a reading of <100mV indicates a properly programmed
bit and a reading of >1V indicates a properly unprogrammed bit.
A reading between 100mV and 1V indicates a faulty bit, which may result in an undefined digital value, when the OTP
is read at power-up.
Following the 16
Figure 17: OTP Register Analog Read
www.austriamicrosystems.com
P ro g
C S n
C L K
P ro g E N
t
L o a d P ro g
th
clock (after reading bit “ccw”), the chip must be reset by disconnecting the power supply.
O u tp E N
In te rn a l
te s t b it
d ig ita l
P ro g c h a n g e s to O u tp u t
V
re f
M d 0
1
M d 1
D iv 0
C L K
D iv1
A n a lo g R e a d b a c k D a ta a t P ro g
Revision 2.10
A re a d
V
u n p ro g ra m m e d
V
p ro g ra m m e d
Z 5
Z 6
Z 7
Z 8
Z 9
ref
1 6
ccw
, and the resulting
P o w e r-o n -
R e se t;
tu rn o ff
s u p p ly
ref
, that must
20 - 33