C8051F067-GQ Silicon Laboratories Inc, C8051F067-GQ Datasheet - Page 54

C8051F067-GQ
Manufacturer Part Number
C8051F067-GQ
Description
IC 8051 MCU 32K FLASH 64TQFP
Manufacturer
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Series
C8051F06xr
Specifications of C8051F067-GQ
Core Processor
8051
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
25MHz
Connectivity
SMBus (2-Wire/I²C), SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
24
Program Memory Size
32KB (32K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
4.25K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 2x16b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-TQFP, 64-VQFP
Processor Series
C8051F0x
Core
8051
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
4.25 KB
Interface Type
I2C, SMBus, SPI, UART
Maximum Clock Frequency
25 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
24
Number Of Timers
5
Operating Supply Voltage
2.7 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
PK51, CA51, A51, ULINK2
Development Tools By Supplier
C8051F060DK
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
16 bit, 1 Channel
On-chip Dac
12 bit, 2 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Other names
336-1222
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F067-GQ
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
210
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F067-GQ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F067-GQR
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 54 of 328
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
C8051F060/1/2/3/4/5/6/7
5.3.
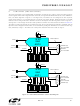
ADC0 and ADC1 have a maximum conversion speed of 1 Msps. The conversion clocks for the ADCs are
derived from the system clock. The ADCnSC bits in the ADCnCF register determine how many system
clocks (from 1 to 16) are used for each conversion clock.
5.3.1. Starting a Conversion
For ADC0, conversions can be initiated in one of four ways, depending on the programmed states of the
ADC0 Start of Conversion Mode bits (AD0CM1, AD0CM0) in ADC0CN. For ADC0, conversions may be ini-
tiated by:
ADC1 conversions can be initiated in five different ways, according to the ADC1 Start of Conversion Mode
bits (AD1CM2-AD1CM0) in ADC1CN. For ADC1, conversions may be initiated by:
The ADnBUSY bit is set to logic 1 during conversion and restored to logic 0 when conversion is complete.
The falling edge of ADnBUSY triggers an interrupt (when enabled) and sets the ADnINT interrupt flag
(ADCnCN.5). In single-ended mode, the converted data for ADCn is available in the ADCn data word MSB
and LSB registers, ADCnH, ADCnL. In differential mode, the converted data (combined from ADC0 and
ADC1) is available in the ADC0 data word MSB and LSB registers, ADC0H, ADC0L.
When initiating conversions by writing a ‘1’ to ADnBUSY, the ADnINT bit should be polled to determine
when a conversion has completed (ADCn interrupts may also be used). The recommended polling proce-
dure is shown below.
When an external start-of-conversion source is required in differential mode the two pins (CNVSTR0 and
CNVSTR1) should be tied together.
5.3.2. Tracking Modes
The ADnTM bit in register ADCnCN controls the ADCn track-and-hold mode. When the ADC is enabled,
the ADC input is continuously tracked when a conversion is not in progress. When the ADnTM bit is logic
1, each conversion is preceded by a tracking period (after the start-of-conversion signal). When the
CNVSTRn signal is used to initiate conversions, the ADC will track until a rising edge occurs on the
CNVSTRn pin (see Figure 5.4 and Table 5.1 for conversion timing parameters). Setting ADnTM to 1 can
be useful to ensure that settling time requirements are met when an external multiplexer is used on the
analog input (see
54
ADC Modes of Operation
1. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD0BUSY bit of ADC0CN;
2. A Timer 3 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
3. A rising edge detected on the external ADC convert start signal, CNVSTR0;
4. A Timer 2 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions).
1. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD1BUSY bit of ADC1CN;
2. A Timer 3 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
3. A rising edge detected on the external ADC convert start signal, CNVSTR1;
4. A Timer 2 overflow (i.e. timed continuous conversions);
5. Writing a ‘1’ to the AD0BUSY bit of ADC0CN.
Step 1. Write a ‘0’ to ADnINT;
Step 2. Write a ‘1’ to ADnBUSY;
Step 3. Poll ADnINT for ‘1’;
Step 4. Process ADCn data.
Section “5.3.3. Settling Time Requirements” on page
Rev. 1.2
56).
Related parts for C8051F067-GQ
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
SMD/C°/SINGLE-ENDED OUTPUT SILICON OSCILLATOR
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
N/A N/A/SI4010 AES KEYFOB DEMO WITH LCD RX
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
N/A N/A/SI4010 SIMPLIFIED KEY FOB DEMO WITH LED RX
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
N/A/-40 TO 85 OC/EZLINK MODULE; F930/4432 HIGH BAND (REV E/B1)
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
EZLink Module; F930/4432 Low Band (rev e/B1)
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4460 10 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 434 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4461 14 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 868 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4463 20 DBM RFSWITCH RADIO TEST CARD 460 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4463 20 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 868 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4463 27 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 868 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4463 SKYWORKS 30 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 915 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
N/A N/A/-40 TO 85 OC/4463 RFMD 30 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 915 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Part Number:
Description:
I°/4463 20 DBM RADIO TEST CARD 169 MHZ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc