LT1764ET-2.5#06PBF Linear Technology, LT1764ET-2.5#06PBF Datasheet - Page 13
LT1764ET-2.5#06PBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LT1764ET-2.5#06PBF
Description
IC REG LDO 2.5V 3A TO220-5
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Datasheet
1.LT1764EQ-2.5.pdf
(20 pages)
Specifications of LT1764ET-2.5#06PBF
Regulator Topology
Positive Fixed
Voltage - Output
2.5V
Voltage - Input
Up to 20V
Voltage - Dropout (typical)
0.34V @ 3A
Number Of Regulators
1
Current - Output
3A
Current - Limit (min)
3.1A
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
TO-220-5 (Bent and Staggered Leads)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
* Device is mounted on topside
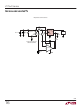
APPLICATIONS
Thermal Considerations
The power handling capability of the device is limited
by the maximum rated junction temperature (125°C).
The power dissipated by the device is made up of two
components:
1. Output current multiplied by the input/output voltage
2. GND pin current multiplied by the input voltage:
The GND pin current can be found using the GND Pin
Current curves in the Typical Performance Characteris-
tics. Power dissipation will be equal to the sum of the two
components listed above.
The LT1764 series regulators have internal thermal limit-
ing designed to protect the device during overload condi-
tions. For continuous normal conditions, the maximum
junction temperature rating of 125°C must not be
exceeded. It is important to give careful consideration to
all sources of thermal resistance from junction to ambient.
Additional heat sources mounted nearby must also be
considered.
For surface mount devices, heat sinking is accomplished
by using the heat spreading capabilities of the PC board
and its copper traces. Surface mount heatsinks and plated
through-holes can also be used to spread the heat gener-
ated by power devices.
The following tables list thermal resistance for several
different board sizes and copper areas. All measurements
were taken in still air on 1/16" FR-4 board with one ounce
copper.
Table 1. Q Package, 5-Lead DD
TOPSIDE*
2500mm
1000mm
125mm
differential: (I
(I
GND
COPPER AREA
)(V
2
2
2
IN
BACKSIDE
2500mm
2500mm
2500mm
).
OUT
U
2
2
2
)(V
BOARD AREA
IN
2500mm
2500mm
2500mm
INFORMATION
– V
U
OUT
2
2
2
), and
W
(JUNCTION-TO-AMBIENT)
THERMAL RESISTANCE
23°C/W
25°C/W
33°C/W
U
* Device is mounted on topside
Table 2. FE Package, 16-Lead TSSOP
T Package, 5-Lead TO-220
Thermal Resistance (Junction-to-Case) = 2.5°C/W
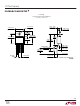
Calculating Junction Temperature
Example: Given an output voltage of 3.3V, an input voltage
range of 4V to 6V, an output current range of 0mA to
500mA and a maximum ambient temperature of 50°C,
what will the maximum junction temperature be?
The power dissipated by the device will be equal to:
where,
So,
Using a DD package, the thermal resistance will be in the
range of 23°C/W to 33°C/W depending on the copper
area. So the junction temperature rise above ambient will
be approximately equal to:
The maximum junction temperature will then be equal to
the maximum junction temperature rise above ambient
plus the maximum ambient temperature or:
TOPSIDE*
2500mm
1000mm
225mm
100mm
I
I
V
I
P = 500mA(6V – 3.3V) + 10mA(6V) = 1.41W
1.41W(28°C/W) = 39.5°C
T
OUT(MAX)
OUT(MAX)
GND
JMAX
IN(MAX)
COPPER AREA
at (I
2
2
2
2
= 50°C + 39.5°C = 89.5°C
= 6V
OUT
(V
BACKSIDE
= 500mA
2500mm
2500mm
2500mm
2500mm
IN(MAX)
= 500mA, V
2
2
2
2
– V
BOARD AREA (JUNCTION-TO-AMBIENT)
2500mm
2500mm
2500mm
2500mm
OUT
IN
) + I
= 6V) = 10mA
2
2
2
2
GND
LT1764 Series
THERMAL RESISTANCE
(V
IN(MAX)
38°C/W
43°C/W
48°C/W
60°C/W
)
13
1764fb