S29JL064H90TFI000 Spansion Inc., S29JL064H90TFI000 Datasheet

S29JL064H90TFI000
Specifications of S29JL064H90TFI000
Available stocks
Related parts for S29JL064H90TFI000
S29JL064H90TFI000 Summary of contents
Page 1
... S29JL064H 64 Megabit ( 8-Bit 16-Bit) CMOS 3.0 Volt-only, Simultaneous Read/Write Flash Memory Data Sheet For new designs involving Fine-pitch Ball Grid Array (FBGA) packages, S29PL064J supersedes S29JL064H and is the factory recommended migration path. Please refer to the S29PL-J Data Sheet for specifications and ordering information. ...
Page 2
... Spansion Inc. The information is intended to help you evaluate this product. Do not design in this product without contacting the factory. Spansion Inc. reserves the right to change or discontinue work on this proposed product without notice.” ...
Page 3
... Cycling Endurance: 1 Million Cycles per Sector Typical Data Retention: 20 years typical Software Features Supports Common Flash Memory Interface (CFI) Erase Suspend/Erase Resume – Suspends erase operations to read data from, or program data to, a sector that is not being erased, then resumes the erase operation Data# Polling and Toggle Bits – ...
Page 4
... Autoselect Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 8.10 Sector/Sector Block Protection and Unprotection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 8.11 Write Protect (WP 8.12 Temporary Sector Unprotect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 8.13 Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 8.14 Hardware Data Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 9. Common Flash Memory Interface (CFI 10. Command Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 10.1 Reading Array Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 10.2 Reset Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 10 ...
Page 5
AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 6
Figures Figure 4.1 48-Pin Standard TSOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
Tables Table 8.1 S29JL064H Device Bus Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 8
... General Description The S29JL064H megabit, 3.0 volt-only flash memory device, organized as 4,194,304 words of 16 bits each or 8,388,608 bytes of 8 bits each. Word mode data appears on DQ15–DQ0; byte mode data appears on DQ7–DQ0. The device is designed to be programmed in-system with the standard 3.0 volt V and can also be programmed in standard EPROM programmers ...
Page 9
... Hardware data protection measures include a low V during power transitions. The hardware sector protection feature disables both program and erase operations in any combination of the sectors of memory. This can be achieved in-system or via programming equipment. The device offers two power-saving features. When addresses have been stable for a specified amount of time, the device enters the automatic sleep mode ...
Page 10
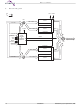
Block Diagram Mux A21–A0 RY/BY# A21–A0 STATE RESET# CONTROL WE# & CE# COMMAND REGISTER BYTE# WP#/ACC DQ0–DQ15 A21–A0 Mux OE# BYTE# Bank 1 Bank 1 ...
Page 11
Connection Diagrams A15 A14 A13 A12 A11 A10 A9 A8 A19 A20 WE# RESET# A21 WP#/ACC RY/BY# A18 A17 Figure 4.2 63-Ball Fine-Pitch BGA (FBGA) - Top View, Balls Facing Down A8 ...
Page 12
Pin Description A21–A0 22 Addresses DQ14–DQ0 15 Data Inputs/Outputs (x16-only devices) DQ15/A-1 DQ15 (Data Input/Output, word mode), A-1 (LSB Address Input, byte mode) CE# Chip Enable OE# Output Enable WE# Write Enable WP#/ACC Hardware Write Protect/Acceleration Pin RESET# Hardware ...
Page 13
... B = Fine-pitch Ball-Grid Array Package (Not for new designs - Speed Option Product Family S29JL064H: 3.0 Volt-only, 64 Megabit ( 16-Bit 8-Bit) Simultaneous Read/Write Flash Memory Manufactured on 130 nm process technology S29JL064H Valid Combinations Package, Material, Set and Temperature Range Model Number TAI TFI 00 BAI, BFI ...
Page 14
... This section describes the requirements and use of the device bus operations, which are initiated through the internal command register. The command register itself does not occupy any addressable memory location. The register is a latch used to store the commands, along with the address and data information needed to execute the command ...
Page 15
... The internal state machine is set for reading array data upon device power-up, or after a hardware reset. This ensures that no spurious alteration of the memory content occurs during the power transition. No command is necessary in this mode to obtain array data. Standard microprocessor read cycles that assert valid addresses on the device address inputs produce valid data on the device data outputs ...
Page 16
... Simultaneous Read/Write Operations with Zero Latency This device is capable of reading data from one bank of memory while programming or erasing in the other bank of memory. An erase operation may also be suspended to read from or program to another location within the same bank (except the sector being erased). ...
Page 17
Output Disable Mode When the OE# input impedance state. Bank Sector SA0 SA1 SA2 SA3 SA4 SA5 SA6 SA7 SA8 SA9 SA10 Bank 1 SA11 SA12 SA13 SA14 SA15 SA16 SA17 SA18 SA19 SA20 SA21 SA22 ...
Page 18
Bank Sector SA23 SA24 SA25 SA26 SA27 SA28 SA29 SA30 SA31 SA32 SA33 SA34 SA35 SA36 SA37 SA38 SA39 SA40 SA41 SA42 SA43 SA44 SA45 SA46 Bank 2 SA47 SA48 SA49 SA50 SA51 SA52 SA53 SA54 SA55 SA56 SA57 SA58 ...
Page 19
Bank Sector SA71 SA72 SA73 SA74 SA75 SA76 SA77 SA78 SA79 SA80 SA81 SA82 SA83 SA84 SA85 SA86 SA87 SA88 SA89 SA90 SA91 SA92 SA93 SA94 Bank 3 SA95 SA96 SA97 SA98 SA99 SA100 SA101 SA102 SA103 SA104 SA105 SA106 ...
Page 20
Bank Sector SA119 SA120 SA121 SA122 SA123 SA124 SA125 SA126 SA127 SA128 SA129 Bank 4 SA130 SA131 SA132 SA133 SA134 SA135 SA136 SA137 SA138 SA139 SA140 SA141 Note The address range is A21:A-1 in byte mode (BYTE Bank ...
Page 21
Autoselect Mode The autoselect mode provides manufacturer and device identification, and sector protection verification, through identifier codes output on DQ7–DQ0. This mode is primarily intended for programming equipment to automatically match a device to be programmed with its corresponding ...
Page 22
Sector/Sector Block Protection and Unprotection (Note: For the following discussion, the term sector applies to both sectors and sector blocks. A sector block consists of two or more adjacent sectors that are protected or unprotected at the same time ...
Page 23
Table 8.6 S29JL064H Boot Sector/Sector Block Addresses for Protection/Unprotection (Sheet Sector SA131–SA133 SA134 SA135 SA136 SA137 SA138 SA139 SA140 SA141 Sector protect/Sector Unprotect requires V system or via programming equipment. on page 54 shows the timing diagram. ...
Page 24
Temporary Sector Unprotect (Note: For the following discussion, the term sector applies to both sectors and sector blocks. A sector block consists of two or more adjacent sectors that are protected or unprotected at the same time (see on ...
Page 25
Figure 8.2 In-System Sector Protect/Unprotect Algorithms START PLSCNT = 1 RESET Wait 1 µs No First Write Temporary Sector Cycle = 60h? Unprotect Mode Yes Set up sector address Sector Protect: Write 60h to sector address with ...
Page 26
... If the security feature is not required, the Secured Silicon Sector can be treated as an additional Flash memory space. The Secured Silicon Sector can be read any number of times, but can be programmed and locked only once. Note that the accelerated programming (ACC) and unlock bypass functions are not available when programming the Secured Silicon Sector ...
Page 27
... The Secured Silicon Sector lock must be used with caution since, once locked, there is no procedure available for unlocking the Secured Silicon Sector area and none of the bits in the Secured Silicon Sector memory space can be modified in any way. 8.14 Hardware Data Protection ...
Page 28
... Common Flash Memory Interface (CFI) The Common Flash Interface (CFI) specification outlines device and host system software interrogation handshake, which allows specific vendor-specified software algorithms to be used for entire families of devices. Software support can then be device-independent, JEDEC ID-independent, and forward- and backward-compatible for the specified flash device families ...
Page 29
Addresses (Word Addresses Mode) (Byte Mode) 27h 4Eh 28h 50h 29h 52h 2Ah 54h 2Bh 56h 2Ch 58h 2Dh 5Ah 2Eh 5Ch 2Fh 5Eh 30h 60h 31h 62h 32h 64h 33h 66h 34h 68h 35h 6Ah 36h 6Ch 37h 6Eh ...
Page 30
Addresses Addresses (Word Mode) (Byte Mode) 40h 80h 41h 82h 42h 84h 43h 86h 44h 88h 45h 8Ah 46h 8Ch 47h 8Eh 48h 90h 49h 92h 4Ah 94h 4Bh 96h 4Ch 98h 4Dh 9Ah 4Eh 9Ch 4Fh 9Eh 50h A0h ...
Page 31
Command Definitions Writing specific address and data commands or sequences into the command register initiates device operations. Table 10.1 on page 36 and data values or writing them in the improper sequence may place the device in an unknown ...
Page 32
... Secured Silicon Sector command sequence returns the device to normal operation. The Secured Silicon Sector is not accessible when the device is executing an Embedded Program or embedded Erase algorithm. Table 10.1 on page 36 Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region on page 26 and unlock bypass modes are not available when the Secured Silicon Sector is enabled. 10.5 Byte/Word Program Command Sequence The system may program the device by word or byte, depending on the state of the BYTE# pin ...
Page 33
Unlock Bypass Command Sequence The unlock bypass feature allows the system to program bytes or words to a bank faster than using the standard program command sequence. The unlock bypass command sequence is initiated by first writing two unlock ...
Page 34
... Embedded Erase algorithm. The device does not require the system to preprogram prior to erase. The Embedded Erase algorithm automatically preprograms and verifies the entire memory for an all zero data pattern prior to electrical erase. The system is not required to provide any controls or timings during these operations. ...
Page 35
... In the erase-suspend-read mode, the system can also issue the autoselect command sequence. The device allows reading autoselect codes even at addresses within erasing sectors, since the codes are not stored in the memory array. When the device exits the autoselect mode, the device reverts to the Erase Suspend mode, and is ready for another valid operation. Refer to Command Sequence on page 32 To resume the sector erase operation, the system must write the Erase Resume command ...
Page 36
... RA = Address of the memory location to be read Data read from location RA during read operation Address of the memory location to be programmed. Addresses latch on the falling edge of the WE# or CE# pulse, whichever happens later Data to be programmed at location PA. Data latches on the rising edge of WE# or CE# pulse, whichever happens first. ...
Page 37
The data is 00h for an unprotected sector/sector block and 01h for a protected sector/sector block. 12. The Unlock Bypass command is required prior to the Unlock Bypass Program command. 13. The Unlock Bypass Reset command is required to ...
Page 38
Notes Valid address for programming. During a sector erase operation, a valid address is any sector address within the sector being erased. During chip erase, a valid address is any non-protected sector address. 2. DQ7 should be ...
Page 39
DQ6: Toggle Bit I Toggle Bit I on DQ6 indicates whether an Embedded Program or Erase algorithm is in progress or complete, or whether the device has entered the Erase Suspend mode. Toggle Bit I may be read at ...
Page 40
Note The system should recheck the toggle bit even if DQ5 = 1 because the toggle bit may stop toggling as DQ5 changes to 1. See the subsections on DQ6 and DQ2 for more information. 11.4 DQ2: Toggle Bit II ...
Page 41
Reading Toggle Bits DQ6/DQ2 Refer to Figure 11.2 on page 40 toggle bit status, it must read DQ15–DQ0 (or DQ7–DQ0 for x8-only device) at least twice in a row to determine whether a toggle bit is toggling. Typically, the ...
Page 42
Embedded Program Algorithm Standard Mode Embedded Erase Algorithm Erase Erase-Suspend-Read Suspend Mode Erase-Suspend-Program Notes 1. DQ5 switches to 1 when an Embedded Program or Embedded Erase operation has exceeded the maximum timing limits. Refer to the section on DQ5 for ...
Page 43
Operating Ranges Industrial (I) Devices Ambient Temperature (T V Supply Voltages CC V for standard voltage range CC Operating ranges define those limits between which the functionality of the device is guaranteed. 14. DC Characteristics 14.1 CMOS Compatible Parameter ...
Page 44
Zero-Power Flash Figure 14 Note Addresses are switching at 1 MHz Note ° ...
Page 45
Test Conditions Note Diodes are IN3064 or equivalent Test Condition Output Load Output Load Capacitance, C (including jig capacitance) Input Rise and Fall Times Input Pulse Levels Input timing measurement reference levels Output timing measurement reference levels 16. Key ...
Page 46
AC Characteristics 17.1 Read-Only Operations Parameter JEDEC Std Read Cycle Time AVAV Address to Output Delay AVQV ACC t t Chip Enable to Output Delay ELQV Output Enable to Output Delay ...
Page 47
Hardware Reset (RESET#) Parameter JEDEC Std RESET# Pin Low (During Embedded Algorithms) to Read t Ready Mode RESET# Pin Low (NOT During Embedded Algorithms Ready Read Mode t RESET# Pulse Width RP t Reset High Time Before ...
Page 48
Word/Byte Configuration (BYTE#) Parameter JEDEC Std. t ELFL/ t FLQZ t FHQV BYTE# Switching from word to byte BYTE# Switching from byte to word mode CE# WE# BYTE# Note Refer to the Erase/Program Operations table for ...
Page 49
Erase and Program Operations Parameter JEDEC Std t t AVAV AVWL AS t ASO t t WLAX AH t AHT t t DVWH WHDX DH t OEPH t t GHWL GHWL t t ...
Page 50
Addresses CE# OE# WE# Data RY/BY VCS Notes program address program data Illustration shows device in word mode WP#/ACC ...
Page 51
Addresses CE# OE# WE# Data RY/BY Notes sector address (for Sector Erase Valid Address for reading status data (see 2. These waveforms are for the word mode Valid PA Addresses ...
Page 52
Addresses CE OE# WE# DQ7 DQ0–DQ6 t BUSY RY/BY# Note VA = Valid address. Illustration shows first status cycle after command sequence, last status read cycle, and array data read cycle Addresses CE# WE# OE Valid ...
Page 53
Enter Erase Embedded Suspend Erasing Erase Erase Suspend WE# DQ6 DQ2 Note DQ2 toggles only when read at an address within an erase-suspended sector. The system may use OE# or CE# to toggle DQ2 and DQ6. 17.5 Temporary Sector Unprotect ...
Page 54
Figure 17.13 Sector/Sector Block Protect and Unprotect Timing Diagram RESET# SA, A6, A1, A0 Sector Group Protect/Unprotect Data 60h 1 µs CE# WE# OE# Note * For sector protect ...
Page 55
Figure 17.14 Alternate CE# Controlled Write (Erase/Program) Operation Timings Addresses WE# OE# CE# Data RESET# RY/BY# Notes 1. Figure indicates last two bus cycles of a program or erase operation program address sector address, PD ...
Page 56
Erase and Programming Performance Parameter Sector Erase Time Chip Erase Time Byte Program Time Word Program Time Accelerated Byte/Word Program Time Byte Mode Chip Program Time (Note 3) Word Mode Accelerated Chip Programming Time Notes 1. Typical program and ...
Page 57
Physical Dimensions 20.1 FBE063—63-Ball Fine-Pitch Ball Grid Array (BGA package September 8, 2009 S29JL064H_00_A8 S29JL064H Dwg rev AF; 10/99 57 ...
Page 58
TS 048—48-Pin Standard TSOP S29JL064H S29JL064H_00_A8 September 8, 2009 Dwg rev AA; 10/99 ...
Page 59
Revision History 21.1 Revision A (January 22, 2004) Initial release. 21.2 Revision A1 (March 26, 2004) Removed Latchup Characteristics section. 21.3 Revision A 2 (April 28, 2004) Updated data sheet status from Preliminary to Data sheet. 21.4 Revision A3 ...
Page 60
... S29JL064H Autoselect Codes, (High Voltage Method) Table Deleted code for 'customer locked' under column "DQ7 to DQ0" 21.9 Revision A8 (September 8, 2009) In-System Sector Protect/Unprotect Algorithms Updated Figure Secured Silicon Sector Flash Memory Region Modified section Word/Byte Configuration (BYTE#) Changed t condition from Min. to Max FHQV ...
Page 61
... Spansion assumes no liability for any damages of any kind arising out of the use of the information in this document. Copyright © 2004-2009 Spansion Inc. All rights reserved. Spansion EcoRAM™ and combinations thereof, are trademarks and registered trademarks of Spansion LLC in the United States and other countries. ...