ADC0804LCN National Semiconductor, ADC0804LCN Datasheet - Page 29
ADC0804LCN
Manufacturer Part Number
ADC0804LCN
Description
IC, ADC, 8BIT, 9708SPS, DIP-20
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.ADC0804LCN.pdf
(41 pages)
Specifications of ADC0804LCN
Resolution (bits)
8bit
Sampling Rate
9.708kSPS
Input Channel Type
Differential
Data Interface
CMOS, Parallel, TTL
Supply Current
1.9mA
Digital Ic Case Style
DIP
No. Of Pins
20
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ADC0804LCN
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
2 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADC0804LCN
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
432
Company:
Part Number:
ADC0804LCN
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
100
Part Number:
ADC0804LCN
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ADC0804LCN*
Manufacturer:
S/PHI
Quantity:
19
Company:
Part Number:
ADC0804LCN/NOPB
Manufacturer:
MICRON
Quantity:
1 000
Functional Description
A15) during I/O input instructions. For example, MUX chan-
nel selection for the A/D can be accomplished with this
operating mode.
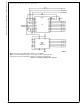
4.3 Interfacing 6800 Microprocessor Derivatives
(6502, etc.)
The control bus for the 6800 microprocessor derivatives
does not use the RD and WR strobe signals. Instead it
employs a single R/W line and additional timing, if needed,
can be derived fom the 2 clock. All I/O devices are memory
mapped in the 6800 system, and a special signal, VMA,
indicates that the current address is valid. Figure 15 shows
an interface schematic where the A/D is memory mapped in
the 6800 system. For simplicity, the CS decoding is shown
using
already decoded 4/5 line is brought out to the common bus
at pin 21. This can be tied directly to the CS pin of the A/D,
provided that no other devices are addressed at HX ADDR:
4XXX or 5XXX.
The following subroutine performs essentially the same func-
tion as in the case of the 8080A interface and it can be called
from anywhere in the user’s program.
In Figure 16 the ADC0801 series is interfaced to the M6800
microprocessor through (the arbitrarily chosen) Port B of the
MC6820 or MC6821 Peripheral Interface Adapter, (PIA).
Here the CS pin of the A/D is grounded since the PIA is
Note 20: Numbers in parentheses refer to MC6800 CPU pin out.
Note 21: Number or letters in brackets refer to standard M6800 system common bus code.
1
⁄
2
DM8092. Note that in many 6800 systems, an
(Continued)
FIGURE 15. ADC0801-MC6800 CPU Interface
29
already memory mapped in the M6800 system and no CS
decoding is necessary. Also notice that the A/D output data
lines are connected to the microprocessor bus under pro-
gram control through the PIA and therefore the A/D RD pin
can be grounded.
A sample interface program equivalent to the previous one is
shown below Figure 16 . The PIA Data and Control Registers
of Port B are located at HEX addresses 8006 and 8007,
respectively.
5.0 GENERAL APPLICATIONS
The following applications show some interesting uses for
the A/D. The fact that one particular microprocessor is used
is not meant to be restrictive. Each of these application
circuits would have its counterpart using any microprocessor
that is desired.
5.1 Multiple ADC0801 Series to MC6800 CPU Interface
To transfer analog data from several channels to a single
microprocessor system, a multiple converter scheme pre-
sents several advantages over the conventional multiplexer
single-converter approach. With the ADC0801 series, the
differential inputs allow individual span adjustment for each
channel. Furthermore, all analog input channels are sensed
simultaneously, which essentially divides the microproces-
sor’s total system servicing time by the number of channels,
since all conversions occur simultaneously. This scheme is
shown in Figure 17 .
DS005671-24
www.national.com