TISP61089AD Bourns Inc., TISP61089AD Datasheet - Page 6

TISP61089AD
Manufacturer Part Number
TISP61089AD
Description
SCRs Dual P Gate Forward Conducting
Manufacturer
Bourns Inc.
Datasheet
1.TISP61089ADR-S.pdf
(8 pages)
Specifications of TISP61089AD
Breakover Current Ibo Max
11 A
Rated Repetitive Off-state Voltage Vdrm
120 V
Off-state Leakage Current @ Vdrm Idrm
0.005 mA
Holding Current (ih Max)
150 mA
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Package / Case
SOIC-8
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
TISP61089AD
Manufacturer:
BOURNS/伯恩斯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
TISP61089ADR
Manufacturer:
BOURNS
Quantity:
3 085
Part Number:
TISP61089ADR
Manufacturer:
BOURNS/伯恩斯
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
TISP61089ADR-S
Manufacturer:
BOURNS/伯恩斯
Quantity:
20 000
This section covers three topics. First, it is explained why gated protectors are needed. Second, the voltage limiting action of the protector is
described. Third, an example application circuit is described.
Fixed voltage thyristor overvoltage protectors have been used since the early 1980s to protect monolithic SLICs (Subscriber Line Interface
Circuits) against overvoltages on the telephone line caused by lightning, a.c. power contact and induction. As the SLIC was usually powered
from a fixed voltage negative supply rail, the limiting voltage of the protector could also be a fixed value. The TISP1072F3 is a typical example
of a fixed voltage SLIC protector.
SLICs have become more sophisticated. To minimize power consumption, some designs automatically adjust the supply voltage, V
value that is just sufficient to drive the required line current. For short lines the supply voltage would be set low, but for long lines, a higher
supply voltage would be generated to drive sufficient line current. The optimum protection for this type of SLIC would be given by a protection
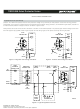
voltage which tracks the SLIC supply voltage. This can be achieved by connecting the protection thyristor gate to the SLIC supply, Figure 3.
This gated (programmable) protection arrangement minimizes the voltage stress on the SLIC, no matter what value of supply voltage.
Figures 4 and 5 show how the ’61089 device limits negative and positive overvoltages. Positive overvoltages (Figure 5) are clipped by the
antiparallel diodes in the ’61089 protector and the resulting current is diverted to ground. Negative overvoltages (Figure 4) are initially clipped
close to the SLIC negative supply rail value (V
into a low voltage on-state condition. As the overvoltage subsides the high holding current of the crowbar prevents d.c. latchup. The
protection voltage will be the sum of the gate supply (V
increased if there is a long connection between the gate decoupling capacitor, C1, and the gate terminal. During the initial rise of a fast
impulse, the gate current (I
printed wiring track. To minimize this inductive voltage increase of protection voltage, the length of the capacitor to gate terminal tracking
should be minimized. Inductive voltages in the protector cathode wiring will also increase the protection voltage. These voltages can be
minimized by routing the SLIC connection through the protector as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 6 shows a typical ’61089 part SLIC card protection circuit. The incoming line conductors, Ring (R) and Tip (T), connect to the relay
matrix via the series overcurrent protection. Fusible resistors, fuses and positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistors can be used for
overcurrent protection. Resistors will reduce the prospective current from the surge generator for both the ’61089 device and the ring/test
Application Circuit
Purpose of Gated Protectors
Operation of Gated Protectors
Gated Protectors
TISP61089 Gated Protector Series
G
) is the same as the cathode current (I
RESISTANCE
GENERATOR
GENERATOR
0 - 600 V rms
SOURCE
600
600
AC
WIRE
WIRE
RING
TIP
Figure 3. ‘61089 Buffered Gate Protector
BAT
). If sufficient current is available from the overvoltage, then the protector (Th5) will crowbar
RSa
40
RSb
40
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
BAT
) and the peak gate-cathode voltage (V
K
). Rates of 70 A/µs can cause inductive voltages of 0.7 V in 2.5 cm of
'61089
220 nF
C1
Th4
Th5
I
G
Customers should verify actual device performance in their specific applications.
I
SLIC
SLIC
I
BAT
GK(BO)
V
BAT
SWITCHING M ODE
). The protection voltage will be
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
POWER SUPPLY
C2
D1
Tx
AI6XAGB
NOVEMBER 1995 - REVISED JULY 2008
BAT
, to a