AD1377KD Analog Devices Inc, AD1377KD Datasheet - Page 10

AD1377KD
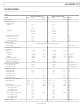
Manufacturer Part Number
AD1377KD
Description
IC ADC SNGL 16BIT 32-CDIP
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD1376JD.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of AD1377KD
Data Interface
Parallel
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Number Of Bits
16
Sampling Rate (per Second)
111k
Number Of Converters
1
Power Dissipation (max)
800mW
Voltage Supply Source
Dual ±
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
32-DIP (0.900", 22.86)
Resolution (bits)
16bit
Sampling Rate
100kSPS
Input Channel Type
Single Ended
Supply Voltage Range - Digital
4.75V To 5.25V
Supply Current
-23mA
Digital Ic Case Style
DIP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
AD1376/AD1377
HIGH RESOLUTION DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM
The essential details of a high resolution data acquisition system
using a 16-bit sample-and-hold amplifier (SHA) and the
AD1376/AD1377 are shown in Figure 14. Conversion is
initiated by the falling edge of the CONVERT START pulse.
This edge drives the device’s STATUS line high. The inverter
then drives the SHA into hold mode. STATUS remains high
throughout the conversion and returns low once the conversion
is completed. This allows the SHA to re-enter track mode.
This circuit can exhibit nonlinearities arising from transients
produced at the ADC’s input by the falling edge of CONVERT
START. This edge resets the ADC’s internal DAC; the resulting
transient depends on the SHA’s present output voltage and the
ADC’s prior conversion result. In the circuit of Figure 15, the
falling edge of CONVERT START also places the SHA into hold
mode (via the ADC’s STATUS output), causing the reset
transient to occur at the same moment as the SHA’s track-and-
hold transition. Timing skews and capacitive coupling can cause
some of the transient signal to add to the signal being acquired
by the SHA, introducing nonlinearity.
–10V TO +10V
1
Figure 14. Basic Data Acquisition System Interconnections 16-Bit SHA
ANALOG
CONVERT
INPUT
10µF
START
+
SHA
10µF
–10V TO +10V
+
10µF
+
26
27
24
22
19
30
18
AD1376/
AD1377
21
BITS
1–16
31
28
Rev. D | Page 10 of 12
+15V
–15V
+5V
A much safer approach is to add a flip-flop, as shown in
Figure 15. The rising edge of CONVERT START places the
track-and-hold device into hold mode before the ADC reset
transients begin. The falling edge of STATUS places the SHA
back into track mode. System throughput will be reduced if a
long CONVERT START pulse is used. Throughput can be
calculated from
where:
T
T
T
The combination of the AD1376 and a 16-bit SHA can provide
greater than 50 kHz throughput. No significant track-and-hold
droop error will be introduced, provided the width of
CONVERT START is small compared with the ADC’s
conversion time.
CONVERT
–10V TO +10V
ACQ
CONV
CS
START
is the duration of CONVERT START.
ANALOG
Throughput
is the track-and-hold acquisition time.
is the time required for the ADC conversion.
INPUT
10µF
+5V
Figure 15. Improved Data Acquisition System
+
K
J
HC112
S
R
=
Q
Q
T
SHA
ACQ
+
10µF
T
CONV
1
–10V TO +10V
+
10µF
+
T
CS
+
26
27
24
22
19
30
18
AD1376/
AD1377
21
BITS
1–16
31
28
+15V
–15V
+5V