CS493105-CLZ Cirrus Logic Inc, CS493105-CLZ Datasheet - Page 38

CS493105-CLZ
Manufacturer Part Number
CS493105-CLZ
Description
IC DECODER AUD MULTI STD 44PLCC
Manufacturer
Cirrus Logic Inc
Type
Audio Decoderr
Datasheet
1.CS493105-CLZR.pdf
(90 pages)
Specifications of CS493105-CLZ
Applications
DVD
Voltage - Supply, Analog
2.37 V ~ 2.63 V
Voltage - Supply, Digital
2.37 V ~ 2.63 V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
44-PLCC
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
598-1670
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZ
Manufacturer:
CRYSTAL
Quantity:
95
Company:
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZ
Manufacturer:
CRYSTAL
Quantity:
174
Company:
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZ
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZ
Manufacturer:
CS
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZR
Manufacturer:
MXIC
Quantity:
3 300
Company:
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZR
Manufacturer:
Cirrus Logic Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
CS493105-CLZR
Manufacturer:
CS
Quantity:
20 000
4) After the falling edge of the serial control clock
5) If INTREQ is still low, another byte should be
6) When INTREQ has risen, the chip select line of
Understanding the role of INTREQ is important for
successful communication. INTREQ is guaranteed
to remain low (once it has gone low) until the
second to last rising edge of SCCLK of the last byte
to be transferred out of the CS493XX. If there is no
more data to be transferred, INTREQ will go high
at this point. For SPI this is the rising edge for the
second to last bit of the last byte to be transferred.
After going high, INTREQ is guaranteed to stay
high until the next rising edge of SCCLK. This end
of transfer condition signals the host to end the
read transaction by clocking the last data bit out
and raising CS. If INTREQ is still low after the
second to last rising edge of SCCLK, the host
should continue reading data from the serial
control port.
It should be noted that all data should be read out
of the serial control port during one cycle or a loss
of data will occur. In other words, all data should be
read out of the chip until INTREQ signals the last
byte by going high as described above. Please see
Section 6.1.3, “INTREQ Behavior: A Special Case”
on page 41
INTREQ behavior.
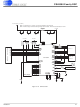
Figure 21, "SPI Timing" on page 39
shows the relative edges of the control lines for an
SPI read and write.
38
significant bit set to 1 to designate a read.
(SCCLK) for the read/write bit, the data is ready
to be clocked out on the control data out pin
(CDOUT). Data clocked out by the host is valid
on the rising edge of SCCLK and data
transitions occur on the falling edge of SCCLK.
The serial clock should be default low so that
eight transitions from low to high to low will
occur for each byte.
clocked out of the CS493XX. Please see the
discussion below for a complete description of
INTREQ behavior.
the CS493XX should be raised to end the read
transaction.
for a more detailed description of
timing diagram
6.1.2. I
I
accomplished with 3 communication lines: serial
control
input/output line and an interrupt request line to
signal that the DSP has data to transmit to the host.
See Figure 4, "I
page 38 shows the mnemonic, pin name, and pin
number of each of these signals on the CS493XX.
Typically in I
drain line with a pull-up. A logic one is placed on
the line by three-stating the output and allowing the
pull-up to raise the line. At this point another device
can drive the line low if necessary. Three-stating
SCDIO can have two effects: 1. To send out a one
when writing data or sending a “no acknowledge”;
2. release the line when another chip is writing
data.
6.1.2.1. Writing in I
When writing to the device in I
protocol will be used whether writing a byte, a
message or even an application code image. The
examples shown in this document can be
expanded to fit any write situation.
shows a typical write sequence:
The following is a detailed description of an I
write sequence with the CS493XX.
1) An I
2) Next a 7-bit address with the read/write bit set
2
C
Bi-Directional Data
Interrupt Request
condition which is defined as the data (SCDIO)
line falling while the clock (SCCLK) is held
high.
low for a write should be sent to the CS493XX.
The address for the CS493XX defaults to
0000000b. It is necessary to clock this address
in prior to any transfer in order for the
CS493XX to accept the write. In other words a
byte of 0x00 should be clocked into the device
Serial Clock
communication
Mnemonic
Table 4. I
2
2
C
C Communication
clock,
®
2
transfer is initiated with an I
C
®
2
2
C
communication SCDIO is an open
CS49300 Family DSP
C® Communication Signals" on
a
®
Communication Signals
bi-directional
2
with
Pin Name
C
INTREQ
SCCLK
SCDIO
®
the
2
C
CS493XX
Pin Number
®
serial
the same
Figure 23
2
19
20
DS339F7
7
C
®
data
start
2
C
is
®