LM2588S-3.3 National Semiconductor, LM2588S-3.3 Datasheet - Page 23
LM2588S-3.3
Manufacturer Part Number
LM2588S-3.3
Description
SIMPLE SWITCHER 5A Flyback Regulator with
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM2588S-3.3.pdf
(29 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LM2588S-3.3
Manufacturer:
NS
Quantity:
400
Application Hints
LM2588 SPECIAL FEATURES
SHUTDOWN CONTROL
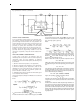
A feature of the LM2588 is its ability to be shut down using
the ON /OFF pin (pin 1). This feature conserves input power
by turning off the device when it is not in use. For proper op-
eration, an isolation diode is required (as shown in Figure
41 ).
The device will shut down when 3V or greater is applied on
the ON /OFF pin, sourcing current into pin 1. In shut down
mode, the device will draw typically 56 µA of supply current
(16 µA to V
vice back on, leave pin 1 floating, using an (isolation) diode,
as shown in Figure 41 (for normal operation, do not source
or sink current to or from this pin — see the next section).
FREQUENCY ADJUSTMENT
The switching frequency of the LM2588 can be adjusted with
the use of an external resistor. This feature allows the user to
optimize the size of the magnetics and the output capaci-
tor(s) by tailoring the operating frequency. A resistor con-
nected from pin 1 (the Freq. Adj. pin) to ground will set the
switching frequency from 100 kHz to 200 kHz (maximum).
As shown in Figure 41 , the pin can be used to adjust the fre-
quency while still providing the shut down function. A curve in
the Performance Characteristics Section graphs the resistor
value to the corresponding switching frequency. The table in
Figure 42 shows resistor values corresponding to commonly
used frequencies.
However, changing the LM2588’s operating frequency from
its nominal value of 100 kHz will change the magnetics se-
lection and compensation component values.
FIGURE 42. Frequency Setting Resistor Guide
IN
FIGURE 41. Shutdown Operation
R
and 40 µA to the ON /OFF pin). To turn the de-
SET
Open
200
47
33
22
(k )
Frequency (kHz)
100
125
150
175
200
DS012420-54
23
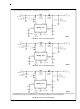
FREQUENCY SYNCHRONIZATION
Another feature of the LM2588 is the ability to synchronize
the switching frequency to an external source, using the
sync pin (pin 6). This feature allows the user to parallel mul-
tiple devices to deliver more output power.
A negative falling pulse applied to the sync pin will synchro-
nize the LM2588 to an external oscillator (see Figure 43 and
44 ).
Use of this feature enables the LM2588 to be synchronized
to an external oscillator, such as a system clock. This opera-
tion allows multiple power supplies to operate at the same
frequency,
problems.
The scope photo in Figure 44 shows a LM2588 12V Boost
Regulator synchronized to a 200 kHz signal. There is a 700
ns delay between the falling edge of the sync signal and the
turning on of the switch.
PROGRAMMING OUTPUT VOLTAGE
(SELECTING R1 AND R2)
Referring to the adjustable regulator in Figure 45 , the output
voltage is programmed by the resistors R1 and R2 by the fol-
lowing formula:
Resistors R1 and R2 divide the output voltage down so that
it can be compared with the 1.23V internal reference. With
R2 between 1k and 5k, R1 is:
For best temperature coefficient and stability with time, use
1% metal film resistors.
SHORT CIRCUIT CONDITION
Due to the inherent nature of boost regulators, when the out-
put is shorted (see Figure 45 ), current flows directly from the
input, through the inductor and the diode, to the output, by-
passing the switch. The current limit of the switch does not
limit the output current for the entire circuit. To protect the
V
R1 = R2 (V
OUT
FIGURE 44. Waveforms of a Synchronized
FIGURE 43. Frequency Synchronization
= V
REF
thus
OUT
(1 + R1/R2)
12V Boost Regulator
/V
eliminating
REF
− 1)
frequency-related
where V
where V
REF
REF
www.national.com
= 1.23V
= 1.23V
DS012420-55
DS012420-64
noise