adc1225ccd-1 National Semiconductor Corporation, adc1225ccd-1 Datasheet - Page 9

adc1225ccd-1
Manufacturer Part Number
adc1225ccd-1
Description
12-bit Plus Sign Mp Compatible A/d Converters
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.ADC1225CCD-1.pdf
(18 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ADC1225CCD-1
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
74
Functional Description
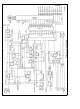
1 0 THE A D CONVERSION
1 1 STARTING A CONVERSION
When using the ADC1225 or ADC1205 with a microproces-
sor starting an A-to-D conversion is like writing to an exter-
nal memory location The WR and CS lines are used to start
the conversion The simplified logic ( Figure 6 ) shows that
the falling edge of WR with CS low clocks the D-type flip-
flop and initiates the conversion sequence A new conver-
sion can therefore be restarted before the end of the previ-
ous sequence INT going low indicates the conversion’s
end
1 2 THE CONVERSION PROCESS (Numbers designated
by
The SARS LOGIC 2 controls the A-to-D conversion pro-
cess When ‘sars’ goes high the clock (clk) is gated to the
TIMING GENERATOR 9 One of the outputs of the TIM-
ING GENERATOR T
sive Approximation Register SAR LOGIC 5 The T
rate is
Inputs to the 12-BIT DAC 11 and control of the SAMPLED
DATA COMPARATOR 10 sign logic are provided by the
SAR LOGIC The first step in the conversion process is to
set the sign to positive (logic ‘0’) and the input of the DAC to
000 (HEX notation) If the differential input V
is positive the sign bit will remain low If it is negative the
sign bit will be set high Differential inputs of only a few
hundred microvolts are enough to provide full logic swings
at the output of the SAMPLED DATA COMPARATOR
The sign bit indicates the polarity of the differential input If it
is set high the negative input must have been greater than
the positive input By reversing the polarity of the differential
input V
sees the negative input as positive The input polarity rever-
sal is done digitally by changing the timing on the input sam-
pling switches of the SAMPLED DATA COMPARATOR
Thus with almost no additional circuitry the A D is extend-
ed from a unipolar 12-bit to a bipolar 12-bit (12-bit plus sign)
device
After determining the input polarity the conversion pro-
ceeds with the successive approximation process The SAR
LOGIC successively tries each bit of the 12-BIT DAC The
most significant bit (MSB) B11 has a weight of
The next bit B10 has a weight of
bit is reduced in weight by a factor of 2 which gives the least
significant bit (LSB) a weight of 1 4096 V
When the MSB is tried the comparator compares the DAC
output V
greater than V
set the MSB If the analog input is less than V
comparator tells the SAR LOGIC to reset the MSB On the
next bit-test the DAC output will either be
V
lowing this sequence through for each successive bit will
approximate the analog input to within 1-bit (one part in
4096)
On completion of the LSB bit-test the conversion-complete
flip-flop (CC) is set signifying that the conversion is finished
The end-of-conversion (EOC) and interrupt (INT) lines are
not changed at this time Some internal housekeeping tasks
must be completed before the outside world is notified that
the conversion is finished
REF
refer to portions of Figure 6 )
depending on whether the MSB was set or not Fol-
IN(
REF
of the CLK IN frequency
a
)
2 to the analog input If the analog input is
REF
and V
2 the comparator tells the SAR LOGIC to
IN(
z
b
provides the clock for the Succes-
)
are interchanged and the DAC
V
REF
REF
Each successive
IN(
a
V
REF
REF
)
b
of V
V
z
IN(
2 the
clock
or
REF
b
)
9
Setting CC enables the UPDATE LOGIC 12
controls the transfer of data from the SAR LOGIC to the
OUTPUT LATCH 6 and resets the internal logic in prepa-
ration for a new conversion This means that when EOC
goes high a new conversion can be immediately started
since the internal logic has already been reset In the same
way data is transferred to the OUTPUT LATCH prior to is-
suing an interrupt This assures that data can be read imme-
diately after INT goes low
2 0 READING THE A D
The ADC 1225 makes all thirteen bits of the conversion
result available in parallel Taking CS and RD low enables
the TRI-STATE
represented in 2’s complement format
The ADC1205 makes the conversion result available in two
eight-bit bytes The output format is 2’s complement with
extended sign Data is right justified and presented high
byte first With CS low and STATUS high the high byte
(DB12 – DB8) will be enabled on the output buffers the first
time RD goes low When RD goes low a second time the
low byte (DB7 – DB0) will be enabled On each read opera-
tion the ‘byst’ flip-flop is toggled so that on successive
reads alternate bytes will be available on the outputs The
‘byst’ flip-flop is always reset to the high byte at the end of a
conversion Table 1 below shows the data bit locations on
the ADC1205
The ADC1205’s STATUS pin makes it possible to read the
conversion status and the state of the ‘byst’ flip-flop With
RD STATUS and CS low this information appears on the
data bus The ‘byst’ status appears on pin 18 (DB2 DB10)
A low output on pin 18 indicates that the next data read will
be the high byte A high output indicates that the next data
read will be the low byte A high status bit on pin 22 (DB6
DB12) indicates that the conversion is in progress A high
output appears on pin 17 (DB1 DB9) when the conversion
is completed and the data has been transferred to the out-
put latch A high output on pin 16 (DB0 DB8) indicates that
the conversion has been completed and the data is ready to
read This status bit is reset when a new conversion is initia-
ted data is read or status is read When reading status or a
conversion result STATUS should always change states at
least 600 ns before RD goes low If the conversion status
information is not needed the STATUS pin should be hard-
wired to V
status bits
HIGH BYTE DB12 DB12 DB12 DB12 DB11 DB10 DB9 DB8
LOW BYTE DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 DB3 DB2 DB1 DB0
Location
Status
DB6
DB2
Bit
TABLE II Status Bit Locations and Meanings
TABLE I Data Bit Locations ADC1205
a
Status
SARS
BYST
Table 2 summarizes the meanings of the four
Bit
output buffers The conversion result is
‘‘High’’ indicates that
‘‘High’’ indicates that
‘‘Low’’ indicates that
the next data read is
the next data read is
the conversion is in
the high byte
the low byte
Meaning
progress
Condition to
Clear Status
Status write
or toggle it
with data
This logic
read
Bit