ad1848 Analog Devices, Inc., ad1848 Datasheet - Page 25

ad1848
Manufacturer Part Number
ad1848
Description
Parallel-port 16-bit Soundport Stereo Codec
Manufacturer
Analog Devices, Inc.
Datasheet
1.AD1848.pdf
(28 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ad1848JP
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
2 490
Company:
Part Number:
ad1848KP
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
3 376
Part Number:
ad1848KP
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
REV. 0
APPLICATIONS CIRCUITS
The AD1848K Stereo Codec has been designed to require a
minimum of external circuitry. The recommended circuits are
shown in Figures 17 through 25. Analog Devices estimates that
the total cost of all the components shown in these figures, in-
cluding crystals but not including connectors, to be less than
$10 in the U.S.A. in 10,000 quantities.
See Figure 1 for an illustration of the connection between the
AD1848K SoundPort Codec and the Industry Standard Archi-
tecture (ISA) computer bus, also known as the “PC-AT bus.”
Note that the 74_245 transceiver receives its enable and direc-
tion signals directly from the Codec. Analog Devices recom-
mends using the “slowest” 74_245 adequately fast to meet all
AD1848K and computer bus timing and drive requirements. So
doing will minimize switching transients of the 74_245. This in
turn will minimize the digital feedthrough effects of the trans-
ceiver when driving the AD1848K, which can cause the audio
noise floor to rise.
Industry-standard compact disc “line-levels” are 2 V rms cen-
tered around analog ground. (For other audio equipment, “line
level” is much more loosely defined.) The AD1848K SoundPort
is a +5 V only powered device. Line level voltage swings for the
AD1848K are defined to be 1 V rms for a sine wave ADC input
and 0.707 V rms for a sine wave DAC output. Thus, 2 V rms
input analog signals must be attenuated and either centered
around the reference voltage intermediate between 0 V and
+5 V or ac-coupled. The V
voltage, nominally 2.25 V. It has limited drive but can be used
as a dc bias to an op amp input. Note, however, that dc-coupled
inputs are not recommended, as they provide no performance
benefits with the AD1848K architecture. Furthermore, dc offset
differences between multiple dc-coupled inputs create the
potential for “clicks” when changing the input mux selection.
A circuit for 2 V rms line-level inputs and auxiliaries is shown in
Figure 17. Note that this is a divide-by-two resistive divider.
The input resistor and 560 pF capacitor provides the single-pole
of anti-alias filtering required for the ADCs. If line-level inputs
are already at the 1 V rms levels expected by the AD1848K, the
resistors in parallel with the 560 pF capacitors can be omitted.
The AD1848K Codec contains an optional +20 dB gain block
to accommodate condenser microphones. Particular system re-
quirements will depend upon the characteristics of the intended
microphone. Figure 18 illustrates one example of how an elec-
tret condenser mike requiring phantom power could be con-
nected to the AD1848K. V
a transistor like a 2N4124 will also work fine for this purpose.
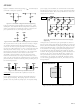
Figure 17. AD1848K 2 V rms Line-Level Input Circuit
5.1k
5.1k
560pF
560pF
NPO
NPO
REF
REF
pin will be at this intermediate
is shown buffered by an op amp;
5.1k
5.1k
0.33 F
0.33 F
L_LINE
L_AUX1
L_AUX2
R_LINE
R_AUX1
R_AUX2
–25–
Note that if a battery-powered microphone is used, the buffer
and R
chosen in light of the mic characteristics and intended gain.
Typical values for these might be R
C = 220 pF.
Figure 19 shows ac-coupled line outputs. The resistors are used
to center the output signals around analog ground. If
dc-coupling is desired, V
mentioned previously.
A circuit for headphone drive is illustrated in Figure 20. Drive is
supplied by +5 V operational amplifiers. The circuit shown ac
couples the line output to the headphones.
Figure 18. AD1848K "Phantom-Powered" Microphone
Input Circuit
LEFT ELECTRET
RIGHT ELECTRET
MICROPHONE
Figure 20. AD1848K Headphone Drive Connections
CONDENSER
MICROPHONE
L_OUT
R_OUT
CONDENSER
2
V
s are not needed. The values of R
Figure 19. AD1848K Line Output Connections
REF
INPUT
INPUT
R_OUT
L_OUT
20k
20k
R
R
2
2
1/2 SSM-2135
REF
1 F
1 F
OR AD820
SSM-2135
1 F
1 F
could be used with op amps as
18k
18k
5.1k
5.1k
1
47k
47k
= 20 k , R
470 F
470 F
R
1
R
C
C
, R
1
1
1/2 SSM-2135
1/2 SSM-2135
OR AD820
OR AD820
2
, and C should be
AD1848K
2
HEADPHONE
LEFT
HEADPHONE
RIGHT
= 2 k , and
0.33 F
0.33 F
L_MIC
R_MIC
V
V
REF
REF