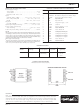
ad1317kz Analog Devices, Inc., ad1317kz Datasheet - Page 4

ad1317kz
Manufacturer Part Number
ad1317kz
Description
Ultrahigh Speed Window Comparator With Latch
Manufacturer
Analog Devices, Inc.
Datasheet
1.AD1317KZ.pdf
(12 pages)
AD1317
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Vos
dV
Ibca
Ibci
Ibsa
Ibsi
Rinc
Rins
C
V
V
CMRR
I
I
V
IH
IL
CM
DIFF
OH
IN
OS
/dT OFFSET DRIFT—The ratio of the change in input
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE—The voltage that
must be applied between either VINA and VINA/B or
VINB and VINA/B to obtain zero voltage between
outputs QA and QA, or QB and QB, respectively.
offset voltages, over the operating temperature range,
to the change in temperature.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (VINA/B, ACTIVE)—
The bias current of the window comparator’s com-
mon input with inputs enabled.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (VINA/B, INHIBIT)—
The bias current of the window comparator’s com-
mon input with inputs inhibited.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (VINA or VINB,
ACTIVE)—The bias current of either single input
with inputs active.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (VINA or VINB,
INHIBIT)—The bias current of either single input
with inputs inhibited.
INPUT RESISTANCE (VINA/B)—The input
resistance looking into the window comparator’s
common input.
INPUT RESISTANCE (VINA or VINB)—The
input resistance looking into either single input.
INPUT CAPACITANCE (VINA/B)—The capaci-
tance looking into the window comparator’s common
input.
INPUT COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE RANGE—
The range of voltages on the input terminals for
which the offset and propagation delay specifications
apply.
INPUT DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE RANGE—
The maximum difference between any input terminal
voltages.
COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO—The
ratio of common-mode input voltage range to the
peak-to-peak change in input offset voltage over this
range.
LOGIC “1” INPUT CURRENT—The logic high
current flowing into (+) or out of (–) a logic input.
LOGIC “0” INPUT CURRENT—The logic low
current flowing into (+) or out of (–) a logic input.
LOGIC “1” OUTPUT VOLTAGE—The logic high
output voltage with a specified load.
–4–
V
I
I
I+
I–
PSRR
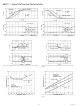
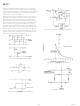
AD1317 SWITCHING TERMS (See Figure 3)
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
PDR
PDF
S
H
PW
LO
ID
IE
OH
OL
OL
LOGIC “0” OUTPUT VOLTAGE—The logic low
output voltage with a specified load.
LOGIC “1” OUTPUT CURRENT—The logic high
output source current.
LOGIC “0” OUTPUT CURRENT—The logic low
output source current.
POSITIVE SUPPLY CURRENT—The current
required from the +V
NEGATIVE SUPPLY CURRENT—The current
required from the –V
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION RATIO—The ratio
of power supply voltage change to the peak-to-peak
change in input offset voltage.
INPUT TO OUTPUT RISING EDGE DELAY—
The propagation delay measured from the time
VINA/B crosses either VINA or VINB, in a low to
high transition, to the time QA and QA or QB and
QB cross, respectively.
INPUT TO OUTPUT FALLING EDGE DELAY—
The propagation delay measured from the time
VINA/B crosses either VINA or VINB, in a high to
low transition, to the time QA and QA or QB and
QB cross, respectively.
MINIMUM LATCH SET-UP TIME—The minium
time before LE goes high with respect to LE that an
input signal change must be present in order to be
acquired and held at the outputs.
MINIMUM LATCH HOLD TIME—The minium
time after LE goes high with respect to LE that the
input signal must remain unchanged in order to be
acquired and held at the outputs.
MINIMUM LATCH ENABLE PULSE WIDTH—
The minimum time that LE must be held high with
respect to LE in order to acquire and hold an input
change.
LATCH ENABLE TO OUTPUT DELAY—The
time between when LE goes high with respect to LE
that QA and QA or QB and QB cross.
INPUT STAGE DISABLE TIME—The time be-
tween when IE goes high with respect to IE that the
input bias currents drop to 10% of their nominal
value.
INPUT STAGE ENABLE TIME—The time be-
tween when IE goes high with respect to IE that the
input bias currents rise to 90% of their nominal values.
S
S
supply.
supply.
REV. A