lm5035bsqx National Semiconductor Corporation, lm5035bsqx Datasheet - Page 14

lm5035bsqx
Manufacturer Part Number
lm5035bsqx
Description
Pwm Controller With Integrated Half-bridge And Syncfet Drivers
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.LM5035BSQX.pdf
(28 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
lm5035bsqx/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI
Quantity:
1 001
www.national.com
Soft-Start
The soft-start circuit allows the regulator to gradually reach a
steady state operating point, thereby reducing start-up stress-
es and current surges. When bias is supplied to the LM5035B,
the SS pin capacitor is discharged by an internal MOSFET.
When the UVLO, VCC and REF pins reach their operating
thresholds, the SS capacitor is released and charged with a
110 µA current source. The PWM comparator control voltage
is clamped to the SS pin voltage by an internal amplifier.
When the PWM comparator input reaches 1V, output pulses
commence with slowly increasing duty cycle. The voltage at
the SS pin eventually increases to 5V, while the voltage at the
PWM comparator increases to the value required for regula-
tion as determined by the voltage feedback loop.
One method to shutdown the regulator is to ground the SS
pin. This forces the internal PWM control signal to ground,
reducing the output duty cycle quickly to zero. Releasing the
SS pin begins a soft-start cycle and normal operation re-
sumes. A second shutdown method is discussed in the UVLO
section.
Soft-Stop
If the UVLO pin voltage falls below the 1.25V standby thresh-
old but above the 0.4V shutdown threshold, the 110 µA SS
pin source current is disabled and a 110 µA sink current dis-
charges the soft-start capacitor. As SS voltage falls and
clamps the PWM comparator input, the PWM duty cycle will
gradually fall to zero. The soft-stop feature produces a grad-
ual reduction of the power converter output voltage. This soft-
stop method of turning off the converter reduces energy in the
output capacitor before control of the main and synchronous
rectification MOSFETs is disabled. The PWM pulses may
cease before the SS voltage reduces the duty cycle if the VCC
or REF voltage drops below the respective under-voltage
thresholds during the soft-stop process.
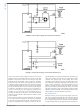
PWM Comparator
The pulse width modulation (PWM) comparator compares the
voltage ramp signal at the RAMP pin to the loop error signal.
This comparator is optimized for speed in order to achieve
minimum controllable duty cycles. The loop error signal is re-
ceived from the external feedback and isolation circuit is in
the form of a control current into the COMP pin. The COMP
pin current is internally mirrored by a matched pair of NPN
transistors which sink current through a 5 kΩ resistor con-
nected to the 5V reference. The resulting control voltage
FIGURE 4. Optocoupler to COMP Interface
14
passes through a 1V level shift before being applied to the
PWM comparator.
An opto-coupler detector can be connected between the REF
pin and the COMP pin. Because the COMP pin is controlled
by a current input, the potential difference across the opto-
coupler detector is nearly constant. The bandwidth limiting
phase delay which is normally introduced by the significant
capacitance of the opto-coupler is thereby greatly reduced.
Higher loop bandwidths can be realized since the bandwidth-
limiting pole associated with the opto-coupler is now at a
much higher frequency. The PWM comparator polarity is con-
figured such that with no current into the COMP pin, the
controller produces the maximum duty cycle at the main gate
driver outputs, HO and LO.
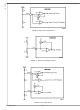
Feed-Forward Ramp and Volt •
Second Clamp
An external resistor (R
VIN, AGND, and the RAMP pin are required to create the
PWM ramp signal. The slope of the signal at RAMP will vary
in proportion to the input line voltage. This varying slope pro-
vides line feed-forward information necessary to improve line
transient response with voltage mode control. The RAMP sig-
nal is compared to the error signal by the pulse width modu-
lator comparator to control the duty cycle of the HO and LO
outputs. With a constant error signal, the on-time (T
inversely with the input voltage (VIN) to stabilize the Volt •
Second product of the transformer primary signal. The power
path gain of conventional voltage-mode pulse width modula-
tors (oscillator generated ramp) varies directly with input volt-
age. The use of a line generated ramp (input voltage feed-
forward) nearly eliminates this gain variation. As a result, the
feedback loop is only required to make very small corrections
for large changes in input voltage.
In addition to the PWM comparator, a Volt • Second Clamp
comparator also monitors the RAMP pin. If the ramp ampli-
tude exceeds the 2.5V threshold of the Volt • Second Clamp
comparator, the on-time is terminated. The C
itor is discharged by an internal 32Ω discharge MOSFET
controlled by the V•S Clamp comparator. If the RAMP signal
does not exceed 2.5V before the end of the clock period, then
the internal clock will enable the discharge MOSFET to reset
capacitor C
By proper selection of R
time of HO and LO can be set to the desired duration. The on-
time set by the Volt • Second Clamp varies inversely to the
line voltage because the RAMP capacitor is charged by a re-
FF
.
FF
FF
) and capacitor (C
and C
FF
values, the maximum on-
30091317
FF
FF
) connected to
ramp capac-
ON
) varies