cop888fh National Semiconductor Corporation, cop888fh Datasheet - Page 30

cop888fh
Manufacturer Part Number
cop888fh
Description
8-bit Cmos Rom Based Microcontrollers With 12k Memory, Comparators, Usart And Hardware Multiply/divide
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor Corporation
Datasheet
1.COP888FH.pdf
(49 pages)
www.national.com
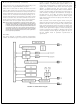
Note 22: y is a variable which represents the VIS block. VIS and the vector table must be located in the same 256-byte block except if VIS is located at the last ad-
dress of a block. In this case, the table must be in the next block.
Interrupts
ample, if the Software Trap routine is located at 0310 Hex,
then the vector location 0yFE and -0yFF should contain the
data 03 and 10 Hex, respectively. When a Software Trap in-
terrupt occurs and the VIS instruction is executed, the pro-
gram jumps to the address specified in the vector table.
The interrupt sources in the vector table are listed in order of
rank, from highest to lowest priority. If two or more enabled
and pending interrupts are detected at the same time, the
one with the highest priority is serviced first. Upon return
from the interrupt service routine, the next highest-level
pending interrupt is serviced.
If the VIS instruction is executed, but no interrupts are en-
abled and pending, the lowest-priority interrupt vector is
used, and a jump is made to the corresponding address in
the vector table. This is an unusual occurrence, and may be
the result of an error. It can legitimately result from a change
in the enable bits or pending flags prior to the execution of
the VIS instruction, such as executing a single cycle instruc-
tion which clears an enable flag at the same time that the
pending flag is set. It can also result, however, from inadvert-
ent execution of the VIS command outside of the context of
an interrupt.
The default VIS interrupt vector can be useful for applica-
tions in which time critical interrupts can occur during the
servicing of another interrupt. Rather than restoring the pro-
VIS Execution
When the VIS instruction is executed it activates the arbitra-
tion logic. The arbitration logic generates an even number
between E0 and FE (E0, E2, E4, E6 etc...) depending on
which active interrupt has the highest arbitration ranking at
the time of the 1st cycle of VIS is executed. For example, if
the software trap interrupt is active, FE is generated. If the
external interrupt is active and the software trap interrupt is
not, then FA is generated and so forth. If the only active inter-
(1) Highest
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16) Lowest
(Continued)
Arbitration
Ranking
Software
Reserved
External
Timer T0
Timer T1
Timer T1
MICROWIRE/PLUS
Reserved
UART
UART
Timer T2
Timer T2
Timer T3
Timer T3
Port L/Wakeup
Default VIS
Source
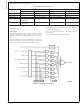
TABLE 6. Interrupt Vector Table
30
INTR Instruction
Pin G0 Edge
Underflow
T1A/Underflow
T1B
BUSY Goes Low
Receive
Transmit
T2A/Underflow
T2B
T3A/Underflow
T3B
Port L Edge
Reserved
gram context (A, B, X, etc.) and executing the RETI instruc-
tion, an interrupt service routine can be terminated by return-
ing to the VIS instruction. In this case, interrupts will be
serviced in turn until no further interrupts are pending and
the default VIS routine is started. After testing the GIE bit to
ensure that execution is not erroneous, the routine should
restore the program context and execute the RETI to return
to the interrupted program.
This technique can save up to fifty instruction cycles (t
more, (50µs at 10 MHz oscillator) of latency for pending in-
terrupts with a penalty of fewer than ten instruction cycles if
no further interrupts are pending.
To ensure reliable operation, the user should always use the
VIS instruction to determine the source of an interrupt. Al-
though it is possible to poll the pending bits to detect the
source of an interrupt, this practice is not recommended. The
use of polling allows the standard arbitration ranking to be al-
tered, but the reliability of the interrupt system is compro-
mised. The polling routine must individually test the enable
and pending bits of each maskable interrupt. If a Software
Trap interrupt should occur, it will be serviced last, even
though it should have the highest priority. Under certain con-
ditions, a Software Trap could be triggered but not serviced,
resulting in an inadvertent “locking out” of all maskable inter-
rupts by the Software Trap pending flag. Problems such as
this can be avoided by using VIS instruction.
rupt is software trap, than E0 is generated. This number re-
places the lower byte of the PC. The upper byte of the PC re-
mains unchanged. The new PC is therefore pointing to the
vector of the active interrupt with the highest arbitration rank-
ing. This vector is read from program memory and placed
into the PC which is now pointed to the 1st instruction of the
service routine of the active interrupt with the highest arbitra-
tion ranking.
Description
0yFE–0yFF
0yFC–0yFD
0yFA–0yFB
0yF8–0yF9
0yF6–0yF7
0yF4–0yF5
0yF2–0yF3
0yF0–0yF1
0yEE–0yEF
0yEC–0yED
0yEA–0yEB
0yE8–0yE9
0yE6–0yE7
0yE4–0yE5
0yE2–0yE3
0yE0–0yE1
Hi-Low Byte
Address
Vector
c
), or