ht82k68a Holtek Semiconductor Inc., ht82k68a Datasheet - Page 7

ht82k68a
Manufacturer Part Number
ht82k68a
Description
Ht82k68a -- Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-bit Mask Mcu
Manufacturer
Holtek Semiconductor Inc.
Datasheet
1.HT82K68A.pdf
(39 pages)
Certain locations in the program memory are reserved
for special usage:
Note: *11~*0: Table location bits
Rev. 1.70
TABRDC [m]
TABRDL [m]
Location 000
This area is reserved for the initialization program. Af-
ter chip reset, the program always begins execution at
location 000H.
Location 004H
Location 004H is reserved for external interrupt ser-
vice program. If the PC2 (external input pin) is acti-
vated, the interrupt is enabled, and the stack is not full,
the program begins execution at location 004H. The
pin PE0 determine whether the rising or falling edge of
the PC2 to activate external interrupt service program.
Location 008H
This area is reserved for the timer counter interrupt
service program. If timer interrupt results from a timer
counter overflow, and if the interrupt is enabled and
the stack is not full, the program begins execution at
location 008H.
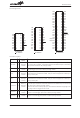
Table location
Any location in the ROM space can be used as
look-up tables. The instructions TABRDC [m] (the cur-
rent page, one page=256 words) and TABRDL [m]
(the last page) transfer the contents of the lower-order
byte to the specified data memory, and the
higher-order byte to TBLH (08H). Only the destination
of the lower-order byte in the table is well-defined, the
other bits of the table word are transferred to the lower
portion of TBLH, the remaining 1 bit is read as 0. The
Table Higher-order byte register (TBLH) is read only.
Instruction(s)
@7~@0: Table location bits
Program Memory
P11
11
1
P10
10
0
P9
1
9
P8
1
8
@7
@7
7
7
Table Location
Stack Register - STACK
This is a special part of the memory which is used to
save the contents of the Program Counter only. The
stack is organized into six levels and is neither part of
the data nor part of the program space, and is neither
readable nor writeable. The activated level is indexed by
the stack pointer (SP) and is neither readable nor
writeable. At a subroutine call or interrupt acknowledg-
ment, the contents of the program counter are pushed
onto the stack. At the end of a subroutine or an interrupt
routine, signaled by a return instruction (RET or RETI),
the program counter is restored to its previous value
from the stack. After a chip reset, the SP will point to the
top of the stack.
Data Memory - RAM
The data memory is designed with 184 8 bits. It is di-
vided into two functional groups: special function regis-
ters and general purpose data memory (160 8). Most of
them are read/write, but some are read only.
The special function registers include the Indirect Ad-
dressing register 0 (00H), the Memory Pointer register 0
(MP0;01H), the Indirect Addressing register 1 (02H), the
Memory Pointer register 1 (MP1;03H), the Accumulator
(ACC;05H), the Program Counter Lower-byte register
(PCL;06H), the Table Pointer (TBLP;07H), the Table
Higher-order byte register (TBLH;08H), the Watchdog
Timer option Setting register (WDTS;09H), the Status reg-
ister (STATUS;0AH), the Interrupt Control register
P11~P8: Current program counter bits
@6
@6
The TBLH is read only and cannot be restored. If the
main routine and the ISR (Interrupt Service Routine)
both employ the table read instruction, the contents of
the TBLH in the main routine are likely to be changed
by the table read instruction used in the ISR. Errors
can occur. In other words, using the table read instruc-
tion in the main routine and the ISR simultaneously
should be avoided. However, if the table read instruc-
tion has to be applied in both the main routine and the
ISR, the interrupt is supposed to be disabled prior to
the table read instruction. It will not be enabled until
the TBLH has been backed up. The table pointer
(TBLP) is a read/write register (07H), which indicates the
table location. Before accessing the table, the location
must be placed in TBLP. All table related instructions
need 2 cycles to complete the operation. These areas
may function as normal program memory depending
upon the requirements.
6
@5
@5
5
@4
@4
4
@3
@3
3
@2
@2
2
December 26, 2005
HT82K68A
@1
@1
1
@0
@0
0