DSP56F801PB MOTOROLA [Motorola, Inc], DSP56F801PB Datasheet

DSP56F801PB
Related parts for DSP56F801PB
DSP56F801PB Summary of contents
Page 1
Preliminary Technical Data DSP56F801 16-bit Digital Signal Processor • MIPS operation at 80 MHz core frequency • DSP and MCU functionality in a unified, C-efficient architecture • MCU-friendly instruction set supports both DSP and controller functions: MAC, ...
Page 2
Part 1 Overview 1.1 DSP56F801 Features 1.1.1 Digital Signal Processing Core • Efficient 16-bit DSP56800 family DSP engine with dual Harvard architecture • As many as 40 Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS MHz core frequency • Single-cycle 16 ...
Page 3
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) with configurable four-pin port (or four additional GPIO lines) • Eleven multiplexed General Purpose I/O (GPIO) pins • Computer-Operating Properly (COP) watchdog timer • One dedicated external interrupt pin • External reset pin for hardware ...
Page 4
... DSP56F801 Summary description and block diagram of the DSP56F801 Product Brief core, memory, peripherals and interfaces 4 are required for a complete description and proper design with the Description DSP56F801 Preliminary Technical Data Order Number DSP56800FM/D DSP56F801-7UM/D DSP56F801/D DSP56F801PB/D MOTOROLA ...
Page 5
Data Sheet Conventions This data sheet uses the following conventions: OVERBAR This is used to indicate a signal that is active when pulled low. For example, the RESET pin is active when low. “asserted” A high true (active high) ...
Page 6
V DD Power Port V SS Ground Port V DDA Power Port V SSA Ground Port VCAPC Other Supply Port EXTAL (GPIOB2) PLL and Clock or GPIO XTAL (GPIOB3) TMS JTAG/OnCE TDO Port TRST * includes TCS pin which is ...
Page 7
Power and Ground Signals No. of Pins Signal Name 4 V Power—These pins provide power to the internal structures of the chip, and should DD all be attached Analog Power—These pins supply an analog power ...
Page 8
Table 6. PLL and Clock (Continued) No. of Signal Signal Pins Name Type During Reset 1 XTAL Output GPIOB3 Input/ Output 2.4 Interrupt and Program Control Signals Table 7. Interrupt and Program Control Signals No. of Signal Signal State During ...
Page 9
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Signals Table 9. Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Signals No. of Signal Signal Pins Name Type 1 MISO Input/ Output GPIOB6 Input/ Output 1 MOSI Input/ Output GPIOB5 Input/ Output 1 SCLK Input/ Output GPIOB4 Input/ ...
Page 10
Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Signals Table 10. Serial Communications Interface (SCI0) Signals No. of Signal Signal Pins Name Type 1 TXD0 Output GPIOB0 Input/ Output 1 RXD0 Input GPIOB1 Input/ Output 2.8 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Signals Table 11. Analog ...
Page 11
JTAG/OnCE Table 13. JTAG/On-Chip Emulation (OnCE) Signals No. of Signal Signal State During Pins Name Type Reset 1 TCK Input Input, pulled low internally 1 TMS Input Input, pulled high internally 1 TDI Input Input, pulled high internally 1 ...
Page 12
Part 3 Specifications 3.1 General Characteristics The DSP56F801 is fabricated in high-density CMOS with 5-volt tolerant TTL-compatible digital inputs. The term “5-volt tolerant” refers to the capability of an I/O pin, built on a 3.3V compatible process technology, to withstand ...
Page 13
Table 15. Recommended Operating Conditions Characteristic Supply voltage Ambient operating temperature Table 16. Thermal Characteristics Characteristic Thermal resistance junction-to-ambient (estimated) I/O pin power dissipation Power dissipation Maximum allowed See Section 5.1 for more detail. 3.2 DC Electrical ...
Page 14
Table 17. DC Electrical Characteristics (Continued) Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic Input capacitance Output capacitance 1 PWM pin output source current 2 PWM pin output sink current V supply current DD 4 Run 5 Wait Stop 6 ...
Page 15
Digital (VDD=3.6V) 180 150 120 Figure 3. Maximum Run IDD vs. Frequency (see Note 4 above) 3.3 AC Electrical Characteristics Timing waveforms in Section 3.3 all pins except XTAL, which is tested using the input ...
Page 16
Data1 Valid Data1 Data Invalid State Data Active 3.4 Flash Memory Characteristics Table 18. Flash Memory Truth Table 1 Mode XE Standby L Read H Word Program H Page Erase H Mass Erase address enable, all rows ...
Page 17
Characteristic PROG/ERASE to NVSTR set up time NVSTR hold time NVSTR hold time(mass erase) NVSTR to program set up time Program hold time Address/data set up time Address/data hold time Recovery time Cumulative program HV period Program time Erase time ...
Page 18
Table 21. Flash Timing Parameters (Continued) Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic Recovery time 2 Cumulative program HV period 1. Program specification guaranteed from T 2. Thv is the cumulative high voltage programming time to the same row ...
Page 19
IFREN XADR XE YE=SE=OE=MAS1=0 ERASE Tnvs NVSTR IFREN XADR XE MAS1 YE=SE=OE=0 ERASE Tnvs NVSTR Figure 8. Flash Mass Erase Cycle MOTOROLA Terase Figure 7. Flash Erase Cycle Tme DSP56F801 Preliminary Technical Data Flash Memory Characteristics Tnvh Trcv Tnvh1 Trcv ...
Page 20
External Clock Operation The DSP56F801 device clock is derived from either 1) an internal crystal oscillator circuit working in conjunction with an external crystal external frequency source on-chip relaxation oscillator. To generate a reference ...
Page 21
External Clock Source The recommended method of connecting an external clock is given in source is connected to XTAL and the EXTAL pin is grounded. Figure 11. Connecting an External Clock Signal Table 22. External Clock Operation Timing Requirements ...
Page 22
Use of On-Chip Relaxation Oscillator Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic External reference crystal frequency for the PLL 2 PLL output frequency (F /2) out PLL stabilization time ...
Page 23
Figure 13. Typical Relaxation Oscillator Frequency vs. Temperature Figure ...
Page 24
Reset, Stop, Wait, Mode Select, and Interrupt Timing Table 25. Reset, Stop, Wait, Mode Select, and Interrupt Timing Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic RESET Assertion to Address, Data and Control Signals High Impedance Minimum RESET Assertion ...
Page 25
RESET t RAZ A0–A15, D0–D15 PS, DS, RD, WR Figure 15. Asynchronous Reset Timing IRQA, IRQB Figure 16. External Interrupt Timing (Negative-Edge-Sensitive) A0–A15 IDM , IRQA IRQB General Purpose I/O Pin t ...
Page 26
IRQA, IRQB A0–A15, PS, DS, RD, WR Figure 18. Interrupt from Wait State Timing t IW IRQA A0–A15, PS, DS, RD, WR Figure 19. Recovery from Stop State Using Asynchronous Interrupt Timing IRQA A0–A15 PS, DS, RD, WR Figure 20. ...
Page 27
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic Cycle time Master Slave Enable lead time Master Slave Enable lag time Master Slave Clock (SCK) high time Master Slave Clock (SCK) low time Master Slave ...
Page 28
SS (Input) SCLK (CPOL = 0) (Output) SCLK (CPOL = 1) (Output MISO (Input) MOSI (Output) Figure 21. SPI Master Timing (CPHA = 0) SS (Input) SCLK (CPOL = 0) (Output) SCLK (CPOL = 1) (Output) MISO (Input) ...
Page 29
SS (Input) SCLK (CPOL = 0) (Input) t ELD SCLK (CPOL = 1) (Input) t MISO Slave MSB out (Output MOSI (Input) Figure 23. SPI Slave Timing (CPHA = 0) SS (Input) SCLK (CPOL = 0) (Input) SCLK ...
Page 30
Quad Timer Timing Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic Timer input period Timer input high/low period Timer output period Timer output high/low period 1. In the formulas listed clock cycle. For 80 MHz operation, T ...
Page 31
RXD SCI receive data pin (Input) TXD SCI receive data pin (Input) 3.10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Characteristics Operating Conditions SSA ADC clock = 4MHz, 3.0–3 – Characteristic Input ...
Page 32
Table 29. ADC Characteristics (Continued) Operating Conditions SSA ADC clock = 4MHz, 3.0–3 – Characteristic Bandwidth ADC Quiescent Current (both ADCs) V Quiescent Current (both ADCs) REF V ...
Page 33
JTAG Timing Operating Conditions SSA Characteristic 2 TCK frequency of operation TCK cycle time TCK clock pulse width TMS, TDI data setup time TMS, TDI data hold time TCK low to TDO data valid TCK ...
Page 34
TCK (Input) TDI TMS (Input) TDO (Output) t TDO (Output ) t TDO (Output) Figure 30. Test Access Port Timing Diagram TRST (Input) t TRST Figure 31. TRST Timing Diagram Figure 32. OnCE—Debug Event ...
Page 35
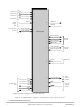
Part 4 Packaging 4.1 Package and Pin-Out Information DSP56F801 This section contains package and pin-out information for the 48-pin LQFP configuration of the DSP56F801. TDO TD1 TD2 PIN 1 /SS MISO MOSI SCLK TXDO VSS VDD RXD0 DE Figure 33. ...
Page 36
Table 31. DSP56F801 Pin Identification by Pin Number Pin No. Signal Name Pin No. 1 TD0 13 2 TD1 14 3 TD2 MISO 17 6 MOSI 18 7 SCLK 19 8 TXD0 ...
Page 37
AB T 0.200 AC T BASE METAL 0.080 AC T ...
Page 38
Part 5 Design Considerations 5.1 Thermal Design Considerations An estimation of the chip junction temperature, T Equation Where ambient temperature ° package junction-to-ambient thermal resistance °C ...
Page 39
Use the value obtained by the equation (T case determined by a thermocouple. The junction-to-case thermal resistances quoted in this data sheet are determined using the first definition on page 45. From a practical standpoint, that value is also ...
Page 40
Take special care to minimize noise levels on the VREF, V • Designs that utilize the TRST pin for JTAG port or OnCE module functionality (such as development or debugging systems) should allow a means to assert TRST whenever ...