LT1913EDD#PBF Linear Technology, LT1913EDD#PBF Datasheet - Page 17

LT1913EDD#PBF
Manufacturer Part Number
LT1913EDD#PBF
Description
IC REG STEP DOWN 3.5A 10-DFN
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Type
Step-Down (Buck)r
Datasheet
1.LT1913EDDPBF.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of LT1913EDD#PBF
Internal Switch(s)
Yes
Synchronous Rectifier
No
Number Of Outputs
1
Voltage - Output
0.79 ~ 25 V
Current - Output
3.5A
Frequency - Switching
200kHz ~ 2.4MHz
Voltage - Input
3.6 ~ 25 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
10-DFN
Primary Input Voltage
25V
No. Of Outputs
1
Output Voltage
25V
Output Current
3.5A
No. Of Pins
10
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To +125°C
Msl
MSL 1 - Unlimited
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Power - Output
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
the output is held high, then parasitic diodes inside the
LT1913 can pull large currents from the output through
the SW pin and the V
will run only when the input voltage is present and that
protects against a shorted or reversed input.
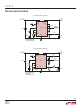
PCB Layout
For proper operation and minimum EMI, care must be
taken during printed circuit board layout. Figure 8 shows
the recommended component placement with trace,
ground plane and via locations. Note that large, switched
currents fl ow in the LT1913’s V
diode (D1) and the input capacitor (C1). The loop formed
by these components should be as small as possible. These
components, along with the inductor and output capacitor,
should be placed on the same side of the circuit board,
and their connections should be made on that layer. Place
a local, unbroken ground plane below these components.
The SW and BOOST nodes should be as small as possible.
Finally, keep the FB and V
traces will shield them from the SW and BOOST nodes.
V
IN
Figure 7. Diode D4 Prevents a Shorted Input from
Discharging a Backup Battery Tied to the Output. It Also
Protects the Circuit from a Reversed Input. The LT1913
Runs Only When the Input is Present
MBRS140
D4
V
RUN/SS
V
IN
C
LT1913
GND FB
IN
BOOST
pin. Figure 7 shows a circuit that
C
SW
nodes small so that the ground
IN
and SW pins, the catch
1913 F07
V
BACKUP
OUT
The Exposed Pad on the bottom of the package must be
soldered to ground so that the pad acts as a heat sink. To
keep thermal resistance low, extend the ground plane as
much as possible, and add thermal vias under and near
the LT1913 to additional ground planes within the circuit
board and on the bottom side.
Hot Plugging Safely
The small size, robustness and low impedance of ceramic
capacitors make them an attractive option for the input
bypass capacitor of LT1913 circuits. However, these capaci-
tors can cause problems if the LT1913 is plugged into a
live supply (see Linear Technology Application Note 88 for
a complete discussion). The low loss ceramic capacitor,
combined with stray inductance in series with the power
source, forms an under damped tank circuit, and the
voltage at the V
nominal input voltage, possibly exceeding the LT1913’s
rating and damaging the part. If the input supply is poorly
controlled or the user will be plugging the LT1913 into an
energized supply, the input network should be designed
Figure 8. A Good PCB Layout Ensures Proper, Low EMI Operation
VIAS TO LOCAL GROUND PLANE
VIAS TO V
D1
OUT
IN
pin of the LT1913 can ring to twice the
L1
C1
VIAS TO SYNC
V
OUT
GND
VIAS TO RUN/SS
VIAS TO PG
C2
R
R
PG
RT
VIAS TO V
OUTLINE OF LOCAL
GROUND PLANE
LT1913
C
R1
C
R
C
R2
IN
1913 F08
17
1913f