PIC10F200-I/P Microchip Technology, PIC10F200-I/P Datasheet - Page 15

PIC10F200-I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC10F200-I/P
Description
IC PIC MCU FLASH 256X12 8DIP
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® 10Fr
Datasheets
1.PIC10F200T-IOT.pdf
(96 pages)
2.PIC10F200T-IOT.pdf
(6 pages)
3.PIC10F200T-IOT.pdf
(18 pages)
4.PIC10F202-EP.pdf
(88 pages)
Specifications of PIC10F200-I/P
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Program Memory Size
384B (256 x 12)
Package / Case
8-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Core Processor
PIC
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
4MHz
Peripherals
POR, WDT
Number Of I /o
3
Ram Size
16 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2 V ~ 5.5 V
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Processor Series
PIC10F
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
16 B
Interface Type
USB
Maximum Clock Frequency
4 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
4
Number Of Timers
1
Operating Supply Voltage
2 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
3rd Party Development Tools
52715-96, 52716-328, 52717-734
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005, PG164120
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
For Use With
AC162059 - HEADER INTRFC MPLAB ICD2 8/14PINAC164037 - MODULE SKT 6L PROMATE II SOT23
Eeprom Size
-
Data Converters
-
Connectivity
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC10F200-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
1 200
Part Number:
PIC10F200-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
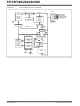
3.1
The clock is internally divided by four to generate four
non-overlapping quadrature clocks, namely Q1, Q2,
Q3 and Q4. Internally, the PC is incremented every Q1
and the instruction is fetched from program memory
and latched into the instruction register in Q4. It is
decoded and executed during the following Q1 through
Q4. The clocks and instruction execution flow is shown
in Figure 3-3 and Example 3-1.
FIGURE 3-3:
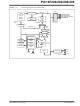
EXAMPLE 3-1:
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
1. MOVLW 03H
2. MOVWF GPIO
3. CALL
4. BSF
All instructions are single cycle, except for any program branches. These take two cycles, since the fetch instruction
is “flushed” from the pipeline, while the new instruction is being fetched and then executed.
Clocking Scheme/Instruction
Cycle
SUB_1
GPIO, BIT1
OSC1
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
PC
CLOCK/INSTRUCTION CYCLE
INSTRUCTION PIPELINE FLOW
Q1
Execute INST (PC – 1)
Fetch INST (PC)
Q2
Fetch 1
PC
Q3
Execute 1
Q4
Fetch 2
Q1
Execute INST (PC)
Fetch INST (PC + 1)
Execute 2
PIC10F200/202/204/206
Q2
Fetch 3
PC + 1
3.2
An instruction cycle consists of four Q cycles (Q1, Q2,
Q3 and Q4). The instruction fetch and execute are
pipelined such that fetch takes one instruction cycle,
while decode and execute take another instruction
cycle. However, due to the pipelining, each instruction
effectively executes in one cycle. If an instruction
causes the PC to change (e.g., GOTO), then two cycles
are required to complete the instruction (Example 3-1).
A fetch cycle begins with the PC incrementing in Q1.
In the execution cycle, the fetched instruction is latched
into the Instruction Register (IR) in cycle Q1. This
instruction is then decoded and executed during the
Q2, Q3 and Q4 cycles. Data memory is read during Q2
(operand read) and written during Q4 (destination
write).
Q3
Execute 3
Q4
Fetch 4
Instruction Flow/Pipelining
Q1
Fetch SUB_1 Execute SUB_1
Execute INST (PC + 1)
Fetch INST (PC + 2)
Q2
Flush
PC + 2
Q3
Q4
DS41239D-page 13
Internal
phase
clock