ATmega16M1 Automotive Atmel Corporation, ATmega16M1 Automotive Datasheet - Page 136

ATmega16M1 Automotive
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega16M1 Automotive
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Datasheets
1.AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(225 pages)
2.ATMEGA16M1_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(12 pages)
3.ATMEGA16M1_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(25 pages)
4.ATMEGA16M1_AUTOMOTIVE.pdf
(367 pages)
Specifications of ATmega16M1 Automotive
Flash (kbytes)
16 Kbytes
Pin Count
32
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
12
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
27
Ext Interrupts
27
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Uart
1
Can
1
Lin
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
11
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
125
Analog Comparators
4
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Dac Channels
1
Dac Resolution (bits)
10
Temp. Sensor
Yes
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
1
Eeprom (bytes)
512
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 150
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
2
Output Compare Channels
14
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
10
32khz Rtc
No
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
- AT90CAN128_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet
- ATMEGA16M1_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet #2
- ATMEGA16M1_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet #3
- ATMEGA16M1_AUTOMOTIVE PDF datasheet #4
- Current page: 136 of 367
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
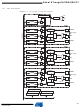
14. Power Stage Controller – (PSC) (only ATmega16/32/64M1)
14.1
14.2
14.3
136
Features
Overview
Accessing 16-bit Registers
Atmel ATmega16/32/64/M1/C1
The Power Stage Controller is a high performance waveform controller.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Many register and bit references in this section are written in general form.
The purpose of the Power Stage Controller (PSC) is to control an external power interface. It
has six outputs to drive for example a 3 half-bridge. This feature allows you to generate three
phase waveforms for applications such as Asynchronous or BLDC motor drives, lighting
systems...
The PSC also has 3 inputs, the purpose of which is to provide fast emergency stop capability.
The PSC outputs are programmable as “active high” or “active low”. All the timing diagrams in
the following examples are given in the “active high” polarity.
Some PSC registers are 16-bit registers. These registers can be accessed by the AVR CPU
via the 8-bit data bus. The 16-bit registers must be byte accessed using two read or write
operations. The PSC has a single 8-bit register for temporary storing of the high byte of the
16-bit access. The same temporary register is shared between all PSC 16-bit registers.
Accessing the low byte triggers the 16-bit read or write operation. When the low byte of a
16-bit register is written by the CPU, the high byte stored in the temporary register, and the low
byte written are both copied into the 16-bit register in the same clock cycle. When the low byte
of a 16-bit register is read by the CPU, the high byte of the 16-bit register is copied into the
temporary register in the same clock cycle as the low byte is read.
To do a 16-bit write, the high byte must be written before the low byte. For a 16-bit read, the
low byte must be read before the high byte.
• A lower case “n” replaces the PSC module number, in this case 0, 1 or 2. However, when
• A lower case “x” replaces the PSC part , in this case A or B. However, when using the
PWM waveform generation function with 6 complementary programmable outputs (able to
control 3 half-bridges)
Programmable dead time control
PWM up to 12 bit resolution
PWM clock frequency up to 64MHz (via PLL)
Programmable ADC trigger
Automatic Overlap protection
Failsafe emergency inputs - 3 (to force all outputs to high impedance or in inactive state - fuse
configurable)
Center aligned and edge aligned modes synchronization
using the register or bit defines in a program, the precise form must be used, i.e.,
POCR0SAH for accessing module 0 POCRnSAH register and so on.
register or bit defines in a program, the precise form must be used, i.e., OCR0SAH for
accessing part A OCR0SxH register and so on.
7647G–AVR–09/11
Related parts for ATmega16M1 Automotive
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
AM-FM Receiver IC U4255BM-M
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Monolithic Integrated Feature Phone Circuit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Multistandard Video-IF and Quasi Parallel Sound Processing
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
High-performance EE PLD
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
8-bit Flash Microcontroller
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
2-Wire Serial EEPROM
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: