UPD61052 NEC, UPD61052 Datasheet

UPD61052
Available stocks
Related parts for UPD61052
UPD61052 Summary of contents
Page 1
... The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Before using this document, please confirm that this is the latest version. Not all products and/or types are available in every country. Please check with an NEC Electronics sales representative for availability and additional information. Document No. ...
Page 2
APPLICATION D-VHS, DVD video recorder, HDD video recorder ORDERING INFORMATION Part Number µ PD61051GD-LML 208-pin plastic QFP (Fine pitch) (28×28) µ Note PD61051GD-LML-A 208-pin plastic QFP (Fine pitch) (28×28) µ PD61052GD-LML 208-pin plastic QFP (Fine pitch) (28×28) µ Note PD61052GD-LML-A ...
Page 3
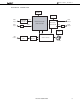
... PERIPHERAL CONNECTION Video BT.656 NTSC/PAL Input Decoder Audio PCM ADC Input 1394 1394 1394 In/Out PHY AV Link SDRAM SDRAM MPEG2 AV Encoder TS Decoder µPD61051/61052 MPEG Decoder Stream Interface TS Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 Video Output PCM Audio DAC Output Host CPU ...
Page 4
... This LSI deals with two kinds of methods to connect a system controller. Parallel Bus Interface BT.656 NTSC/PAL Decoder PCM Audio ADC 27 MHz STC Clock MPEG TS/PS Serial Bus Interface BT.656 NTSC/PAL Decoder PCM Audio ADC 27 MHz STC Clock MPEG TS/PS User Interface 4 64M SDRAM BT.656 µ ...
Page 5
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW) • 208-pin plastic QFP (Fine pitch) (28×28) µ PD61051GD-LML µ PD61051GD-LML-A µ PD61052GD-LML µ PD61052GD-LML DD2 AMCLK 2 GND 3 OALRCK 4 OABCK 5 OABD 6 IALRCK 7 IABCK 8 IABD 9 GND 10 ...
Page 6
PIN LIST AMCLK :Audio Main Clock CA0/FA0 to CA5/FA5 :Host CPU Address/ Instruction ROM Address CCS :Host CPU Chip Select CD0/FD0 to CD7/FD7 :Host CPU Data/ Instruction ROM Data CINT :Host CPU Interrupt CMODE0/CSCLK :Host CPU Mode/ SPI Clock CMODE1/CSDO ...
Page 7
... Stream Input Interface ........................................................................................................................ 10 1.6 Stream Output Interface ..................................................................................................................... 11 1.7 SDRAM Interface ................................................................................................................................. 11 1.8 Host CPU Interface.............................................................................................................................. 12 1.8.1 Parallel bus interface................................................................................................................. 12 1.8.2 Serial bus interface.................................................................................................................... 12 1.9 Clock, Reset......................................................................................................................................... 13 1.10 N-Wire................................................................................................................................................... 13 1.11 GPIO ..................................................................................................................................................... 14 1.12 Power Supply ...................................................................................................................................... 14 1.13 Recommended Connections of Unused Pins ................................................................................... 15 2. FEATURE OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................. 16 2.1 Video .................................................................................................................................................... 16 2.1.1 Encoding ................................................................................................................................... 16 2.1.2 Transcoding............................................................................................................................... 16 2.1.3 Input/output processing ............................................................................................................. 17 2.2 Audio .................................................................................................................................................... 19 2.2.1 Encoding ................................................................................................................................... 19 2.2.2 Transcoding (DEMUX, MUX) .................................................................................................... 19 2.2.3 Input/output processing ............................................................................................................. 19 2 ...
Page 8
Download interrupt register ....................................................................................................... 47 3.2.6 Interrupt register ........................................................................................................................ 48 3.2.7 Reset register ............................................................................................................................ 48 3.2.8 ROM access cycle register........................................................................................................ 49 3.2.9 Port setup register ..................................................................................................................... 49 4. SYSTEM INTERFACE PROCEDURE.......................................................................................... 50 4.1 Outline .................................................................................................................................................. 51 4.2 Firmware Download ...
Page 9
PIN FUNCTION Sharing pin is bold faced in name and explains the feature shown. 1.1 Video Input Interface The video input is based on the ITU-R BT.656 format. The horizontal synchronization signal, and the vertical synchronization signal, the field ...
Page 10
... Audio Input/output Interface After hardware reset, it becomes input. OALRCK, OABCK and OABD connect with 3 pull up resistance. Firmware controls input/output of those pins. Name IO Pin Number OALRCK IO 4 OABCK IO 5 OABD IO 6 AMCLK I 2 1.5 Stream Input Interface Stream input corresponds to MPEG TS/PS stream. When slave mode (MPEG2-TS input with using valid signal), data input is possible to select 8 bits parallel data or serial data mode ...
Page 11
Stream Output Interface This interface outputs MPEG TS/PS stream. When in master mode (MPEG2-TS output with using valid signal), data output is possible to select 8bits parallel data or serial data mode. In serial mode, data output from OS0. ...
Page 12
... Host CPU Interface It chooses a parallel bus connection and a serial bus connection by the setting of CMODE2. Name IO Pin Number CMODE2 I 158 1.8.1 Parallel bus interface Name IO Pin Number CA5 to CA0/ I 187, 185 to 181 FA5 to FA0 CD7 to CD0/ IO 172, 170 to FD7 to FD0 166, 164, 162 ...
Page 13
... I 34 PSTOP I 29 PWM O 40 RESET I 151 1.10 N-Wire IE Port for firmware of Internal CPU evaluation When not connecting an in-circuit emulator, take countermeasures against noise by pulling up the NDI pin to avoid the pin becoming low level. Name IO Pin Number NMOD I 178 NCLK I 174 NRST I ...
Page 14
... GPIO GPIO becomes input after hardware reset by the RESET pin and ALL RESET by the reset register. GPIO connect with 3 through the 10 kΩ pull up resistance. DD Name IO Pin Number GPIO0 IO 189 GPIO1 IO 190 GPIO2 IO 191 GPIO3 IO 192 GPIO4 IO 193 GPO5/OVHSYNC O 195 ...
Page 15
... Recommended Connections of Unused Pins Connect unused pins as follows. Name IVIN7 to IVIN0 IVCLK IVHSYNC IVVSYNC IVFLD OVOUT7, OVOUT6 OVOUT5 to OVOUT0/FA19 to FA14 OVCLK IALRCK IABCK IABD OALRCK OABCK OABD AMCLK ISREQ ISCLK/ISSTB ISSYNC ISVLD IS7 to IS0 OSREQ OSSYNC CA5 to CA0/FA5 to FA0 CD7 to CD0/FD7 to FD0 ...
Page 16
FEATURE OVERVIEW The functions and I/O interfaces are set using firmware. Supported functions differ depending on firmware. 2.1 Video This LSI can do flexible encoding and transcoding by using the firmware control of internal CPU and an exclusive use ...
Page 17
Input/output processing (1) Video input The video input format is ITU-R BT.656 (8-bit Y/Cb/Cr the 4:2:2 format) and 8-bit Y/Cb/Cr which deals with the 4:2:0 format. The horizontal synchronization signal, the vertical synchronization signal and the field index can ...
Page 18
TV method NTSC VBID Closed caption PAL Wide screen signal (6) Video output It converts an input video or a local-decoded video into picture size of 720 dots by 480/576 line and outputs with the ITU-R BT.656 format. Horizontal and ...
Page 19
Audio This LSI encodes the MPEG audio encoding and transcode with the internal DSP. 2.2.1 Encoding It encodes MPEG1 audio layer 2 or Dolby Digital Consumer Encoder (only the possible to bypass internal audio encode DSP, when the audio ...
Page 20
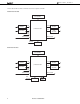
IALRCK Lch (OALRCK) IABCK (OABCK) IABD Don't care MSB (OABD) 16/32 IABCK (OABCK) IALRCK Lch (OALRCK) IABCK (OABCK) IABD MSB (OABD) Audio data 16/32 IABCK (OABCK) IALRCK Lch (OALRCK) IABCK (OABCK) IABD MSB (OABD) Audio data 32 IABCK (OABCK) 20 ...
Page 21
MSB First Right Justified Mode OALRCK Lch OABCK OABD MSB MSB 16/32 OABCK OALRCK Lch OABCK OABD MSB Audio data 16/32 OABCK Lch OALRCK OABCK OABD MSB Audio data 32 OABCK Figure 2-3. Audio Output MSB LSB MSB Audio ...
Page 22
MPEG System Processing This LSI multiplexes and/or de-multiplexes Audio and video streams based on MPEG2-TS/PS and MPEG1. By combining the multiplexer and de-multiplexer, it does the transcode which is accompanied by MPEG2-TS⇔MPEG2 PS conversion. 2.3.1 System time clock (1) ...
Page 23
Encoding and Transcoding system It can output the signal, which generates the pulse wide modulation (PWM) with comparing PCR/SCR of the stream and system time clock value, for making the reference clock of the system. Figure 2-5. System Time ...
Page 24
VBI data The user data stream, the wide screen signal, the closed caption, VBID and format of the video and the audio can be read from the host CPU interface. 2.3.4 Transcode The transcode is a combined multiplexer and ...
Page 25
... Parallel steam data interface This LSI connects to external device by the master mode or the slave mode. When parallel interface, the maximum stream input rate is 100 Mbps, the maximum stream output rate is 30 Mbps. The stream of MPEG encoding and transcode is limited to 15 Mbps on MPEG MP@ML. ...
Page 26
Figure 2-7. Parallel Stream Receiving Mode (2/2) (b) Example of Receiving MPEG2-PS, ES with Valid and Clock ISREQ ISVLD ISCLK No Valid IS7 to IS0 received data data ISSYNC (c) Example of Receiving MPEG2-PS, MPEG2-ES with a Strobe ISREQ ISSTB ...
Page 27
Master Mode Valid This is the MPEG2-TS dedicated output mode. The period of OSCLK can be selected from n times 37 ns (1/27 MHz) (3 ≤ n ≤ 255 integer). If using local decode or input ...
Page 28
Bytes Transfer Mode, Strobe In byte transfer mode, the transfer rate is determined by the handshake of OSREQ and OSSTB. Figure 2-9. Parallel Stream Transmission Mode (Transmission of MPEG2-PS, MPEG2-ES) (a) Example for Transmission of Strobe Mode One Byte ...
Page 29
Serial stream data interface This LSI is able to input a serial stream. Bit rate of serial input is limited less than parallel interface. Serial Stream Interface can transfer only MPEG2-TS stream. Maximum bit rate of stream input is ...
Page 30
First Byte of TS packet ISVLD ISCLK MSB Bit6 IS0 ISSYNC IS1/ISERR ISVLD ISCLK MSB IS0 ISSYNC IS1/ISERR "L" Remark Example for ISVLD, ISSYNC, ISERR active high, ISCLK active high edge 30 Figure 2-10. Serial Stream Input One packet More ...
Page 31
Stream Output OSCLK is fixed 27 MHz OSSYNC active at first byte in each packet. OSVLD is active of 1 packet continuously. Data is the MSB first outputs. ISSYNC becomes active among 1 byte at the head of the ...
Page 32
... Host CPU Interface The connection of the host CPU can select the eight bits parallel data interface and serial interface (SPI). Internal CPU sends and receives command status through the System Interface Register, which is in the host CPU interface unit. In addition, to control an internal DMA controller through the system interface register, it loads an instruction for internal CPU to the instruction RAM and the transfer of the large-volume data can be sent to the data area on SDRAM ...
Page 33
... Mbit SDRAM 32 bits µ The PD61051/61052 preserves the part of the parameter that is necessary to generate the stream, entry video image, a video stream, an audio stream, a stream header, user data, and the instruction of the firmware at this memory. This system uses only CAS latency = 3, burst length = 4. ...
Page 34
... Memory Connection Diagram Each memory connection is as follows. Figure 2-14. Memory Connection Diagram (1/2) µPD61051/61052 Bank A: SDRAM address = 0x xxxx xxxx xxxxB Bank B: SDRAM address = 1x xxxx xxxx xxxxB µPD61051/61052 Bank A: SDRAM address = 00 xxxx xxxx xxxxB Bank B: SDRAM address = 10 xxxx xxxx xxxxB Bank C: SDRAM address = 01 xxxx xxxx xxxxB ...
Page 35
... Figure 2-14. Memory Connection Diagram (2/2) (c) 64 Mbit SDRAM 128 Mbit SDRAM by 2 MA13 MA12 MA11 MA10 to MA0 D15 to D0 µPD61051/61052 MA13 A13 MA12 A12 MA11 A11 MA10 to MA0 A10 to A0 MD31 to MD16 MD15 to MD0 D15 to D0 Bank A: SDRAM address = 00 xxxx xxxx xxxxB ...
Page 36
Memory Map Firmware sets memory map such as video image area and usable work area. Firmware cabinet (temporal buffered area) is the area which firmware does not use. Video Image area size is changed NTSC or PAL. Each area ...
Page 37
Figure 2-15. Memory Map (2/2) (c) Example for 64 Mbit SDRAM 128 Mbit SDRAM by 2 Bank A Bank B 00000H Firmware Video Stream Video Stream Unused Header Video Image Area Firmware Unused Unused Instruction Pool Instruction ...
Page 38
SYSTEM INTERFACE REGISTER This LSI corresponds to the various operation modes in exchange instruction of internal CPU from SDRAM to instruction RAM (iRAM). This has 64 byte Registers. They are defined to common registers, interrupt registers and interrupt mask ...
Page 39
Register Mapping (General Mapping) Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 00H to 1FH 20H SI SSD SDI 21H 22H 23H 24H 25H 26H 27H 28H 29H 2AH 2BH 2CH 2DH 2EH 2FH 30H 31H 32H 33H 34H 35H 36H 37H to ...
Page 40
Register Functions 3.2.1 Common register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 00H to 1FH Each firmware defines these registers. These registers are used to communicate with host CPU and internal CPU. For the details of the register, refer to the application ...
Page 41
Data transfer register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 20H SI SSD SDI Bit Field 7 SI Host CPU→instruction RAM of internal CPU 0: Releasing of transfer, 1: Transfer 6 SSD Host CPU→SDRAM 0: Releasing of transfer, 1: Transfer 5 SDI ...
Page 42
Source address register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 21H 22H 23H It sets the address of the data to transfer. It becomes effective in case of transfer from SDRAM or instruction ROM. Until it releases a transfer mode after setting ...
Page 43
Destination address register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 24H 25H 26H It sets Destination address. It becomes effective in case of transfer to SDRAM or instruction RAM of internal CPU. It isn't possible to change until it cancels a transfer ...
Page 44
Transfer data counter register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 27H 28H 29H It sets the transfer data number of the bytes. In case of transfer between host CPU and SDRAM, it sets the number of the transfer bytes by 4 ...
Page 45
SDRAM read <1> Interrupt mask Host CPU sets mask bit to interrupt mask register (2CH to 2FH) for the interrupt that needs a data transfer. <2> Set source address Host CPU sets the address of SDRAM to the source address ...
Page 46
... Release of interrupt mask It releases the limitation on interrupt which is set by <1>. <11> In the case of an interrupt to internal CPU necessary Host CPU sets a data bank number and the number of the bytes to the address that defined with the firmware. It sets 01H to the 2AH address of the 46 µ ...
Page 47
Internal CPU interrupt register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 2AH Host CPU set interrupt to internal CPU. Internal CPU clears this bit after interrupt operation. The reset of the RESET pin or ALL RESET of the reset register initializes this ...
Page 48
Interrupt register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 31H 32H 33H 34H It is set for 1 when the interrupt factor occurs. The interrupt bit clears when host CPU writes 1 in the bit of the interrupt after the interrupt processing. ...
Page 49
... Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 35H It specifies the access cycle of the instruction ROM of internal CPU when connecting host CPU interface with the serial bus. The reset of the RESET pin or ALL RESET of the reset register initializes this address to 7H. Bit Field Reserved (Set 0) ...
Page 50
SYSTEM INTERFACE PROCEDURE The host CPU transfers the firmware of each operation mode to the instruction RAM of the internal CPU and works it. This LSI stores up firmware in SDRAM. Host CPU sets to load the firmware of ...
Page 51
... Outline An overview from the reset of the hardware to the setting of an operation mode is shown. Y Note This is not necessary in case that the SDRAM initialization firmware is not separated. Initialization Hardware reset SDRAM Note initialization Software reset of internal CPU Reset address (3EH)← 02H Instruction ...
Page 52
... The host CPU downloads the firmware at the instruction RAM for the internal CPU. When a host CPU is connected with the serial bus, the firmware can be downloaded from the external ROM for the download processing to speed up. In addition, it stores more than one piece of firmware in the instruction pool area of SDRAM and it can be replaced depending on the need, too ...
Page 53
External ROM to instruction RAM of internal CPU When the host CPU is a serial bus type, CPU transmits the instruction of a mode from external ROM to instruction RAM of Internal CPU. When transferring data continuously, transfer during ...
Page 54
Host CPU to SDRAM The host CPU can store firmware in the instruction pool area of SDRAM for the internal CPU. It stores more than one piece of firmware and it can be replaced depending on the need, too. ...
Page 55
External ROM to SDRAM The firmware for the internal CPU can be stored in the firmware cabinet of SDRAM from the external ROM. It stores more than one piece of firmware beforehand and it can be replaced according to ...
Page 56
SDRAM Write during Executing While encoding, the host CPU can transfer parameters to the internal CPU through SDRAM. The number of the transfer bytes is a 4-byte unit. SDRAM writing, during executing Mask Interrupt which requests data transfer Interrupt ...
Page 57
SDRAM Read during Executing While encoding, the host CPU reads parameters of usable work area of SDRAM. The maximum data of the reading once is 128 bytes. When reading is equal to or more than 128 byte data, execute ...
Page 58
SDRAM Initialization The host CPU transfers the firmware which makes SDRAM a standby condition to the instruction RAM of the internal CPU and executes it. 58 SDRAM initialization SDRAM initialize firmware to instruction RAM of internal CPU 100 µs ...
Page 59
Operation Mode Setting by Changing Firmware When changing a mode, host CPU transfers the instruction of each mode from SDRAM to the instruction RAM of the internal CPU and restarts. Mode setting Software reset of internal CPU Reset register ...
Page 60
Transfer Ending The host CPU confirms a transfer error when the instruction or data transfer ends. The host CPU clears transfer mode and interrupt registers. Transfer ending Interrupt register 0 (30H): 01H Transfer mode register (20H) ← 00H setting ...
Page 61
Transfer Error Handling 4.8.1 Transfer error handling the error handling of DMA-ERR which occurs when interrupting the transfers (the host CPU → the instruction RAM of internal CPU transfer, the host CPU → SDRAM transfer (SSD, ...
Page 62
Transfer error handling 2 This is a error handling of DMA-ERR which occurs when interrupting the transfers (SDRAM read during executing and SDRAM → instruction RAM of internal CPU transfer) Transfer error handling 2 Destination address register (24H to ...
Page 63
... Transfer error handling the error handling of DMA-ERR which occurs when transfer operation in case of host CPU serial connection with SPI. Transfer error handling 3 Transfer counter register (27H to 29H) ← 01H setting SDRAM → host CPU transfer Transfer mode register (20H) ← 01H setting Transfer data register (3FH) → ...
Page 64
EXAMPLE FOR COMMON REGISTER USAGE µ The PD61051, 61052 operates while the “command code register” “start”. When “command code register” becomes “start”, internal CPU reads parameter registers, then starts the operation. Additionally, internal register sets “status register”. ...
Page 65
Register Map Example Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 00H 01H 02H to 1FH Parameters (Defined by each firmware) 20H SI SSD SDI 21H 22H 23H 24H 25H 26H 27H 28H 29H 2AH 2BH 2CH to 2FH Interrupt Mask (Defined by ...
Page 66
Example of the Common Register Which A Firmware Defines 5.2.1 COMCODE: Command code register Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 00H The host CPU can change the state of operation to the command code register. The commands to operate in three ...
Page 67
Figure 5-2. Command Status Transition 001 : Stop Valid Command in Initial State: Standby Valid Command in Standby State: Start Valid Command in Operation State: Stop Hardware reset Initial State (000) 001 : Standby Standby State (001) 011 : Start ...
Page 68
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Absolute Maximum Ratings (T = 25°C) A Parameter Symbol Supply Voltage V V DD3 V V DD2 PV Input Voltage V Vs GND3 IN Output Voltage V Vs GND3 OUT Output Current I OUT Permissible Loss P ...
Page 69
Pin Capacitance (T = 25°C) A Parameter Symbol Input capacitance C I Output capacitance C O I/O capacitance +70° Characteristics (T A DD3 (1) System Parameter Symbol SCLK frequency f SCK SCLK high-level ...
Page 70
Reset input V DD3 V DD2 PV DD2 Frequency stabilization (±10% max. ) SCLK PSTOP RESET Caution Notes on power on/off • Apply power and V DD3 DD2 • difficult to apply the power ...
Page 71
IVCLK AMCLK STCLK SCLK PSTOP RESET t IVRES t AURES t STRES t STP4 t WSTP t RES Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 71 ...
Page 72
IVCLK AMCLK STCLK SCLK PSTOP ''L'' RESET 72 t IVRES t AURES t STRES t RESW Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 ...
Page 73
Video input interface Parameter Symbol IVCLK frequency f IVCKS IVCLK high-level width t VCKH IVCLK low-level width t VCKL IVIN7 to IVIN0 setup time t Vs rising edge of IVCLK IVDS IVIN7 to IVIN0 hold time t Vs rising ...
Page 74
Video output interface Parameter Symbol OVCLK frequency f OVCKS OVCLK high-level width t OVCKH OVCLK low-level width t OVCKL OVOUT7 to OVOUT0 hold t Vs rising edge of OVCLK OVHO time OVOUT7 to OVOUT0 delay t Vs rising edge ...
Page 75
Audio input interface Parameter Symbol Bit data-in setup time t Vs IABCK ACDS Bit data-in hold time t Vs IABCK ACDH LRCK-in setup time t Vs IABCK ACLS LRCK-in hold time t Vs IABCK ACLH IABCK t ACDS IABD ...
Page 76
Audio output interface Parameter Symbol Bit data-out hold time t Vs OABCK ACDHO Bit data-out delay time t Vs OABCK ACDD LRCK-out hold time t Vs OABCK ACLHO LRCK-out delay t Vs OABCK ACLD BCK-out duty ratio d BCK ...
Page 77
Stream input interface (a) Parallel stream input Valid mode Parameter Symbol ISCLK cycle t ISCcyc ISCLK low-level width t ISCLW ISCLK high-level width t ISCHW ISREQ output hold time t Vs active edge of ISCLK ISRQHO ISVLD setup time ...
Page 78
Strobe mode Parameter Symbol ISSTB low-level width t ISSTLW ISSTB high-level width t ISSTHW ISREQ output hold time t Vs active edge of ISSTB ISRQHO ISSYNC setup time t Vs active edge of ISSTB ISSS ISSYNC hold time t Vs ...
Page 79
Serial stream input Parameter Symbol ISCLK period t ISSCW ISCLK low-level width t ISSCLW ISCLK high-level width t ISSCHW ISVLD setup time t Vs active edge of ISCLK ISSVS ISVLD hold time t Vs active edge of ISCLK ISSVH ...
Page 80
Stream output interface (a) Parallel stream data output Valid and master mode Parameter Symbol OSCLK low-level width t Active rising edge OSCLW Active falling edge OSCLK high-level width t Active rising edge OSCHW Active falling edge OSVLD hold time ...
Page 81
Strobe and byte mode Parameter Symbol OSREQ high-level time t OSRHW OSSTB high-level width t Active rising edge OSSTHW Active falling edge OSSTB low-level width t Active rising edge OSSTLW Active falling edge OSREQ hold time t Vs active edge ...
Page 82
Serial stream data output Parameter Symbol OSCLK period t OSSCW OSCLK low-level width t OSSCLW OSCLK high-level width t OSSCHW OS0 delay time t Vs active edge of OSCLK OSSDD OS0 hold time t Vs active edge of OSCLK ...
Page 83
SDRAM interface Parameter Symbol MCLK cycle time t CK MCLK high-level width t CH MCLK low-level width t CL MD31 to MD0-out hold time t OH MD31 to MD0-out delay time t OD MD31 to MD0 low-Z output time ...
Page 84
Read timing (Manual pre-charge, burst length = 4, CAS latency = 3) 84 Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 ...
Page 85
Read timing (Auto pre-charge, burst length = 4, CAS latency = 3) Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 85 ...
Page 86
Write timing (Burst length = 4, CAS latency = 3) 86 Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 ...
Page 87
Host CPU interface (a) Parallel bus interface: Wait mode Parameter Symbol CCS↓ → CA5 to CA0 delay time t CAD CCS↓ → CWAIT delay time t CWAD1 CCS↓→ CWAIT release time t CRDY CA5 to CA0 → CRE↓ delay ...
Page 88
Parameter Symbol CWE↑ → CA5 to CA0 hold time t CWE↑ → CCS↑ hold time t CCS↑ → CD7 to CD0 hold time t CCS↑ → CWAIT release time t CWAIT release → CWE/CRE hold time t CWAIT release → ...
Page 89
Wait mode (Wait active low, read cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE t CAC CWE CWAIT Wait mode (Wait active low, write cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE t CAC CWAIT t ARD ...
Page 90
Wait mode (Wait active high, read cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE t CAC CWE CWAIT Wait mode (Wait active high, write cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE t CAC CWAIT 90 t ...
Page 91
CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE CWAIT CA5 to CA0 CCS t CCYC CD7 to CD0 t CCYC CRE t CCYC CWE CWAIT Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 t CCYC t CCYC t CCYC 91 ...
Page 92
Parallel bus interface: Ready mode Parameter Symbol CCS↓ → CA5 to CA0 delay time t CAD CCS↓ → CWAIT delay time t CWAD1 CCS↓ → CWAIT ready time t CRDY CA5 to CA0 → CRE↓ delay time t ARD ...
Page 93
Parameter Symbol CWE↑ → CWAIT release time t WWD2 CCS↑ → CWAIT release time t CWAD2 CWAIT ready → CWE/CRE hold t CWR time CWAIT ready → CA5 to CA0 hold t CWA time CWAIT ready → CCS↑ hold time ...
Page 94
Ready mode (Ready active high, read cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE t CAC CWE CWAIT Ready mode (Ready active high, write cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE t CAC CWAIT 94 t ...
Page 95
Ready mode (Ready active low, read cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE t CAC CWE CWAIT Ready mode (Ready active low, write cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE t CAC CWAIT t ARD ...
Page 96
CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE CWAIT CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE CWAIT 96 t CCYC t CCYC t CCYC t CCYC t CCYC t CCYC Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 ...
Page 97
Parallel bus interface: Fixed wait mode Parameter Symbol CCS↓ → CA5 to CA0 delay time t CAD CRE pulse width t RW CA5 to CA0 → CRE↓ delay time t ARD CCS↓ → CRE↓delay time t CRD CCS↓ → ...
Page 98
Fixed wait mode (Read cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE t CAC CWE Fixed wait mode (Write cycle) CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE t CAC 98 t ARD t t CAD CRD t ...
Page 99
CA5 to CA0 CCS CD7 to CD0 CRE CWE CA5 to CA0 CCS t CCYC CD7 to CD0 t CCYC CRE t CCYC CWE Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 t CCYC t CCYC t CCYC 99 ...
Page 100
Serial bus interface (a) Serial bus interface Parameter Symbol CCS → CSCLK delay time t CSCK CCS → CSDI delay time t CSDI CSDI setup time t CSDS CSDI hold time t CSDH CSDO hold time t CSDHO CSDO ...
Page 101
Write] CCS t CSCK CSCLK t CSDI CSDI CSDO xx t CSDS t CSDH [Data Read] CCS t CSCK CSCLK t CSDI CSDI CSDO xx t CSDS t CSDH ...
Page 102
PACKAGE DRAWING 208-PIN PLASTIC QFP (FINE PITCH) (28x28) 156 157 208 NOTE Each lead centerline is located within 0. its true position (T.P.) at maximum material condition. 102 A B 105 ...
Page 103
... The PD61051, 61052 should be soldered and mounted under the following recommended conditions. For soldering methods and conditions other than those recommended below, contact an NEC Electronics sales representative. For technical information, see the following website. Semiconductor Device Mount Manual (http://www.necel.com/pkg/en/mount/index.html) Table 8-1. Surface-Mounted Soldering Conditions µ ...
Page 104
... HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS FOR CMOS Note: No connection for CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction connection is provided to the input pins possible that an internal input level may be generated due to noise, etc., hence causing malfunction. CMOS devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of CMOS devices must be fixed high or low by using a pull-up or pull-down circuitry ...
Page 105
Data Sheet S15082EJ4V0DS µ PD61051, 61052 105 ...
Page 106
... NEC Electronics does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of third parties by or arising from the use of NEC Electronics products listed in this document or any other liability arising from the use of such products. No license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Electronics or others. • ...