ADE7752ARZ Analog Devices Inc, ADE7752ARZ Datasheet - Page 15

ADE7752ARZ
Manufacturer Part Number
ADE7752ARZ
Description
IC ENERGY METERING DETEC 24-SOIC
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.ADE7752AARZ-RL.pdf
(24 pages)
Specifications of ADE7752ARZ
Input Impedance
450 KOhm
Measurement Error
0.1%
Voltage - I/o High
2.4V
Voltage - I/o Low
0.8V
Current - Supply
6mA
Voltage - Supply
4.75 V ~ 5.25 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
24-SOIC (0.300", 7.50mm Width)
Meter Type
3 Phase
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ADE7752ARZ
Manufacturer:
ADI/亚德诺
Quantity:
20 000
PHASE
PHASE
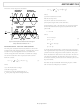
TYPICAL CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
CURRENT CHANNEL CONNECTION
Figure 19 shows a typical connection diagram for the current
channel (IA). A current transformer (CT) is the current trans-
ducer selected for this example. Notice the common-mode
voltage for the current channel is AGND and is derived by
center tapping the burden resistor to AGND. This provides the
complementary analog input signals for IAP and IAN. The CT
turns ratio and burden resistor Rb are selected to give a peak
differential voltage of ±500 mV at maximum load.
IP
VOLTAGE CHANNELS CONNECTION
Figure 20 shows two typical connections for the voltage
channel. The first option uses a potential transformer (PT) to
provide complete isolation from the main voltage. In the second
option, the ADE7752 is biased around the neutral wire, and a
resistor divider is used to provide a voltage signal proportional
to the line voltage. Adjusting the ratio of Ra, Rb, and VR is also
a convenient way of carrying out a gain calibration on the meter.
PHASE
NEUTRAL
NEUTRAL
NEUTRAL
Figure 20. Typical Connections for Voltage Channels
Figure 19. Typical Connection for Current Channels
Ra
VR
*
Rb
*
*
PT
*
CT
Ra >> Rf + VR;
AGND
±500mV
Cf
R
±500mV
b
*
Rf
Rf
Rb + VR = Rf
±500mV
Rf
Rf
Rf
Cf
Cf
Cf
Cf
Cf
IAP
IAN
VAP
VAP
VN
VN
Rev. C | Page 15 of 24
METER CONNECTIONS
In 3-phase service, two main power distribution services exist:
3-phase 4-wire or 3-phase 3-wire. The additional wire in the
3-phase 4-wire arrangement is the neutral wire. The voltage
lines have a phase difference of ±120° (±2π/3 radians) between
each other. See Equation 5.
where V
different phases.
The current inputs are represented by Equation 6.
where I
each phase and ϕ
the current and voltage channel of each phase.
The instantaneous powers can then be calculated as follows:
Then:
As shown in Equation 7, in the ADE7752, the real power calcu-
lation per phase is made when current and voltage inputs of one
phase are connected to the same channel (A, B, or C). Then the
summation of each individual real power calculation gives the
total real power information, P(t) = P
P
P
P
V
V
V
I
I
I
P
P
P
A
B
C
C
A
B
C
A
B
A
B
(t) = V
B
C
(t) = V
(t) = V
A
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
A
t
, I
( )
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
, V
B
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
=
, and I
B
=
B
V
V
V
, and V
B
B
A
C
2
2
2
2
B
C
A
2
( t) × I
B
(t) × I
(t) × I
2
×
×
I
×
×
I
×
I
×
A
A
C
B
C
I
I
V
V
, ϕ
I
V
B
C
×
×
×
represent the rms value of the current of
A
A
B
C
C
×
cos
cos
cos
B
B
×
A
C
×
×
(t)
B
×
, and ϕ
B
represent the voltage rms values of the
(t)
(t)
×
cos
cos
cos
cos
cos
cos
⎧
⎨
⎩
⎧
⎨
⎩
(
ω
ω
ω
( )
( )
( )
φ
φ
φ
⎛
⎜
⎝
l
( )
l
l
⎛
⎜
⎝
t
t
t
ω
B
C
ω
A
C
ω
+
+
+
l
l
t
represent the phase difference of
t
l
−
−
t
φ
−
π 2
4
+
+
3
3
V
V
A
ADE7752/ADE7752A
V
π
)
π 2
B
C
4
A
3
+
+
3
×
×
π
×
φ
⎞
⎟
⎠
φ
I
I
A
⎞
⎟
⎠
I
B
C
B
C
(t) + P
A
⎫
⎬
⎭
⎫
⎬
⎭
×
×
×
cos
cos
cos
B
⎛
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎜
⎝
(t) + P
B
(
2
2
2
ω
ω
ω
l
l
l
t
t
t
+
+
+
C
φ
(t).
π 4
π 8
3
3
A
)
+
+
φ
φ
C
B
(5)
(6)
⎞
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎟
⎠
(7)