MRF89XA-I/MQ Microchip Technology, MRF89XA-I/MQ Datasheet

MRF89XA-I/MQ
Specifications of MRF89XA-I/MQ
Available stocks
Related parts for MRF89XA-I/MQ
MRF89XA-I/MQ Summary of contents
Page 1
... Ultra-Low Power, Integrated ISM Band © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. MRF89XA Data Sheet Sub-GHz Transceiver Preliminary DS70622B ...
Page 2
... PICtail, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries. SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies. ...
Page 3
... Sports and performance monitoring • Wireless toy controls • Medical applications General Description The MRF89XA is a single chip, multi-channel FSK/OOK transceiver capable of operating in the 863-870 MHz and 902-928 MHz license-free ISM frequency bands, as well as the 950-960 MHz frequency band. The low-cost MRF89XA is optimized for very low power consumption ( Receiver mode) ...
Page 4
... MRF89XA uses several low-power mechanisms to reduce overall current consumption and extend battery life. Its small size and low power consumption makes the MRF89XA ideal for a wide variety of short range radio applications. The MRF89XA complies with European (ETSI EN 300-220 V2.3.1) and United States (FCC Part 15 ...
Page 5
... When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are using. Customer Notification System Register on our web site at www.microchip.com to receive the most current information on all of our products. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 5 ...
Page 6
... MRF89XA NOTES: DS70622B-page 6 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 7
... The MRF89XA supports a stable sensitivity and linearity characteristics for a wide supply range and is internally regulated. The frequency synthesizer of the MRF89XA is a fully integrated integer-N type PLL. The oscillator circuit provided on the MRF89XA device provides the reference clock for the PLL. The ...
Page 8
... FIGURE 1-1: MRF89XA SIMPLIFIED BLOCK DIAGRAM Reception Block First Stage LNA Mixers LO1 RX RFIO X LO1 TX I Second PA Stage Q Mixers Transmission Block For General Biasing Supply Block DVRS x Supply RSSI I Second Filtering/ Stage IF Gain Amplification Mixers Q LO2 RX LO2 TX I Modulation First (DDS, DACs, ...
Page 9
... FIGURE 1-2: MRF89XA TO MICROCONTROLLER INTERFACE (NODE) BLOCK DIAGRAM Antenna Matching Saw Circuitry Filter Block The interface between the MRF89XA and the MCU depends on the Data mode of operation. For more information refer to Section 3.8 “Data Note: Processing”. Loop Tank Filter Circuit Block ...
Page 10
... MRF89XA NOTES: DS70622B-page 10 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 11
... SPI, interrupts (IRQ0 and IRQ1), PLOCK, DATA and Chip Select pins for SPI are illustrated in Figure 2-1. On-chip regulators provide stable supply voltages to sensitive blocks and allow the MRF89XA to be used with supply voltages from 2.1 to 3.6V. Most blocks are supplied with a voltage below 1.4V. ...
Page 12
... MRF89XA FIGURE 2-1: DETAILED BLOCK DIAGRAM OF THE MRF89XA PARS PA RFIO LNA LO1 RX OSC1 Frequency Synthesizer XO OSC2 DS70622B-page 12 I LO2 LO1 LO2 TX Q RSSI OOK Demod FSK LO2 RX Demod LO1 RX I LO2 Generator I LO1 LO2 TX Q Preliminary Waveform Generator IRQ0 IRQ1 BitSync ...
Page 13
... Digital Input 13 TEST8 Digital I/O 14 CSCON Digital Input 15 CSDAT Digital Input 16 SDO Digital Output Serial data output interface from MRF89XA. 17 SDI Digital Input 18 SCK Digital Input 19 CLKOUT Digital Output Clock output. Output clock at reference frequency divided by a pro- 20 DATA Digital I/O ...
Page 14
... To provide stable sensitivity characteristics over a wide supply range, the MRF89XA is internally voltage regulated. This internal regulated power supply block structure is illustrated in Figure 2-2. The power supply bypassing is essential for better handling of signal surges and noise in the power line. To ensure correct operation of the regulator circuit, the decoupling capacitor connection (shown in Figure 2-2) is recommended ...
Page 15
... RFIO Antenna LNA © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. The PA and the LNA front-ends in the MRF89XA, which share the same Input/Output pin, are internally matched to approximately 50Ω. 2.4 Filters and Amplifiers Block 2.4.1 INTERPOLATION FILTER After digital-to-analog conversion during transmission, both I and Q signals are smoothed by interpolation filters ...
Page 16
... DS70622B-page 16 2.5 Frequency Synthesizer Block The frequency synthesizer of the MRF89XA is a fully integrated integer-N type PLL. The crystal oscillator provides the reference frequency for the PLL. The PLL AND circuit requires only a minimum of five external ...
Page 17
... LO VCO Output © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 2.5.3.1 The MRF89XA features a PLL lock detect indicator (PLOCK). This is useful for optimizing power consump- tion, by adjusting the synthesizer wake-up time. The lock status can also be read on the LSTSPLL bit from the FTPRIREG register (Register 2-15), and must be cleared by writing a ‘ ...
Page 18
... MRF89XA Operating Modes (Includes Power-Saving Mode) This section summarizes the settings for each operating mode of the MRF89XA to save power, based on the operations and available functionality. The timing requirements for switching between modes described in Section 5.3 “Switching Times and Procedures”. ...
Page 19
... Interrupt (IRQ0 and IRQ1) Pins The Interrupt Requests (IRQ0 and IRQ1) pins 21 and 22, respectively provide an interrupt signal to the host microcontroller from the MRF89XA. Interrupt requests are generated for the host microcontroller by pulling the IRQ0 (pin 21) or IRQ1 (pin 22) pins low or high based on the events and configuration settings of these interrupts ...
Page 20
... MRF89XA 2.9.1 TRANSMITTER ARCHITECTURE Figure 2-6 illustrates the transmitter architecture block diagram. The baseband I and Q signals are digitally generated by a DDS whose Digital-to-Analog Converters (DAC) followed by two anti-aliasing low-pass filters transform the digital signal into analog in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) components whose frequency is the selected frequency deviation (set by using the FDVAL< ...
Page 21
... Buffered mode. Image rejection is achieved by using a Note: SAW filter on the RF input. polyphase RSSI OOK Demod FSK LO2 RX Demod Baseband, IF2 in OOK Preliminary MRF89XA 100 MHz). The second Control Logic - Pattern Recognition - FIFO Handler BitSync - SPI Interface - Packet Handler DS70622B-page 21 ...
Page 22
... First down-conversion Image Frequency First down-conversion The SPI in the MRF89XA consists of the following two sub-blocks, as illustrated in Figure 2-11: the host • SPI CONFIG: This sub-block is used in all data operation modes to read and write the configuration registers which control all the parameters of the chip (operating mode, frequency and bit rate). • ...
Page 23
... Table 5-7. The SDO pin defaults to a high impedance (hi-Z) state when any of the CS pins are high (the MRF89XA is not selected). This pin has a tri-state buf- fer and uses a bus hold logic. As the device uses byte writes, any of the Chip Select (CS) pins should be pulled low for 8 bits ...
Page 24
... A1, the current content of A1 can be read by the µC. DS70622B-page A(2) A(1) A(0) stop D(7) D(6) D( D(7) D(6) D(5) (In)/(Out) refers to MRF89XA side Preliminary New value at address A1 D(4) D(3) D(2) D(1) D(0) Current value at address A1* D(4) D(3) D(2) D(1) D(0) HZ (input) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 25
... FIGURE 2-13: READ REGISTER SEQUENCE CSCON (In) SCK (In) SDI (In) start rw A(4) A(3) Address = A1 x SDO (Out (input) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc A(2) A(1) A(0) stop D(7) D(6) D(5) Preliminary MRF89XA Current value at address A1 D(4) D(3) D(2) D(1) D(0) HZ (input) DS70622B-page 25 ...
Page 26
... MRF89XA 2.11.2 SPI DATA Write Byte (before/during TX write bytes into the FIFO, the timing diagram illustrated in Figure 2-14 should be followed by the host microcontroller compulsory to toggle CSDAT back Note: high between each byte written. The byte is pushed into the FIFO on the rising edge of CSDAT ...
Page 27
... READ BYTES SEQUENCE (EXAMPLE DIAGRAM FOR 2 BYTES CSDAT (In) SCK (In) SDI (In First byte read D1(7) D1(6) D1(5) D1(4) D1(3) D1(2) D1(1) SDO (Out) HZ (input) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc D1(0) D2(7) D2(6) D2(5) D2(4) D2(3) D2(2) D2(1) D2(0) HZ (input) Preliminary MRF89XA Second byte read HZ (input) DS70622B-page 27 ...
Page 28
... Data TX/RX DS70622B-page 28 2.13 MRF89XAConfiguration/Control/ Status Registers The memory in the MRF89XA transceiver is implemented as static RAM and is accessible through the SPI port. The memory configuration of the MRF89XA is illustrated in Figure 2-17 and Figure 2-18. FIFO LSB 0x00 Transmit/Receive FIFO 0x40 SHIFT REGISTER (8 bits) ...
Page 29
... FIGURE 2-18: MRF89XA REGISTERS MEMORY MAP Register Name 0x00 GCONREG 0x01 DMODREG FDEVREG 0x02 BRSREG 0x03 0x04 FLTHREG 0x05 FIFOCREG 0x06 R1CREG 0x07 P1CREG 0x08 S1CREG 0x09 R2CREG 0x0A P2CREG 0x0B S2CREG 0x0C PACREG FTXRXIREG 0x0D 0x0E FTPRIREG 0x0F RSTHIREG The ...
Page 30
... MRF89XA TABLE 2-6: CONFIGURATION/CONTROL/STATUS REGISTER DESCRIPTION General Configuration Registers: Size – 13 Bytes, Start Address – 0x00 Register Register Address Name 0x00 GCONREG General Configuration Register 0x01 DMODREG Data and Modulation Configuration Register 0x02 FDEVREG Frequency Deviation Control Register 0x03 BRSREG Bit Rate Set Register ...
Page 31
... Node’s local address for filtering of received packets Packet format, size of the preamble, whitening, CRC on/off, address filtering of received packets, CRC status FIFO auto-clear (if CRC failed), FIFO access Preliminary MRF89XA Related Control Functions Related Control Functions Related Control Functions Related Control Functions Related Control Functions DS70622B-page 31 ...
Page 32
... MRF89XA 2.14 General Configuration Registers 2.14.1 GENERAL CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-1: GCONREG: GENERAL CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0X00) (POR:0X28) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-1 CMOD<2:0> bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-5 CMOD<2:0>: Chip Mode bits These bits select the mode of operation of the transceiver. ...
Page 33
... Data Operation DMODE1 Mode Continuous 0 (default mode) Buffer 0 Packet 0/1) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W-1 OOKTYP<1:0> DMODE1 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) (1) DMODE0 0 1 Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 IFGAIN<1:0> bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 33 ...
Page 34
... MRF89XA 2.14.3 FREQUENCY DEVIATION CONTROL REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-3: FDEVREG: FREQUENCY DEVIATION CONTROL REGISTER (ADDRESS:0X02) (POR:0X03) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-0 FDVAL<7:0>: Frequency Deviation Value bits The bits indicate single side frequency deviation (in bit value) in FSK Transmit mode. ...
Page 35
... Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 FTOVAL<7:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 FTINT<5:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-1 R/W-1 bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 35 ...
Page 36
... MRF89XA 2.14.7 R1 COUNTER SET REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-7: R1CREG: R1 COUNTER SET REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x06) (POR:0x77) R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-0 R1CVAL<7:0>: R1 Value bits These bits indicate the value in R1 counter to generate carrier frequencies in FSK mode. ...
Page 37
... Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-0 S1CVAL<7:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-1 R2CVAL<7:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-1 R/W-0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 37 ...
Page 38
... MRF89XA 2.14.11 P2 COUNTER SET REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-11: P2CREG: P2 COUNTER SET REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x0A) (POR:0x62) R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-0 P2CVAL<7:0>: P2 Value bits These bits indicate the value in P2 counter to generate carrier frequencies in FSK mode. ...
Page 39
... Reserved: Reserved bits; do not use 000 = Reserved (default) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-1 R/W-1 r PARC<1:0> — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary MRF89XA r r — — bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 39 ...
Page 40
... MRF89XA 2.15 Interrupt Configuration Registers 2.15.1 FIFO TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE INTERRUPT REQUEST CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-14: FTXRXIREG: FIFO TRANSMIT AND RECEIVE INTERRUPT REQUEST CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x0D) (POR:0x00) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 IRQ0RXS<1:0> IRQ1RXS<1:0> bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ...
Page 41
... No FIFO Overrun occurred Writing a ‘1’ for this bit clears flag and FIFO. Note 1: This mode is also available in Stand-by mode. 2: PLREADY = Payload ready 3: ADRSMATCH = Address Match © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Continuous Mode (default): Buffer Mode or 1x Packet Mode: Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 41 ...
Page 42
... MRF89XA 2.15.2 FIFO TRANSMIT PLL AND RSSI INTERRUPT REQUEST CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-15: FTPRIREG: FIFO TRANSMIT PLL AND RSSI INTERRUPT REQUEST CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x0E) (POR:0x01) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 FIFOFM FIFOFSC TXDONE bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ...
Page 43
... The PLL lock detect flag is mapped to the PLOCK pin (pin 23), and pin High-Z pin Note 1: Setting this bit to ‘0’ disables the RSSI IRQ source. It can be left enabled at any time, and the user can choose to map this interrupt to IRQ0/IRQ1 or not. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 43 ...
Page 44
... MRF89XA 2.15.3 RSSI THRESHOLD INTERRUPT REQUEST REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-16: RSTHIREG: RSSI THRESHOLD INTERRUPT REQUEST CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x0F) (POR:0x00) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-0 RTIVAL<7:0>: RSSI Threshold for Interrupt Value bits These bits indicate the RSSI threshold value for interrupt request RTIVAL< ...
Page 45
... Note © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared – 100 kHz (default MHz/12.8 MHz BUTFILV)/8 = 12.8 MHz. xtal Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 BUTFILV<3:0> bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 45 ...
Page 46
... MRF89XA 2.16.2 POLYPHASE FILTER CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-18: PFCREG: POLYPHASE FILTER CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x11) (POR:0x38) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-1 POLCFV<3:0> bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-4 POLCFV<3:0>: Polyphase Centre Frequency Value bits These bits indicate the center frequency of the polyphase filter (typically recommended to 100 kHz). ...
Page 47
... These bits indicate the number of errors tolerated in the SYNC word recognition Errors Errors Errors Errors (default) bit 0 Reserved: Reserved bit; do not use 0 = Reserved (default) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-0 SYNCWSZ<1:0> SYNCTEN<1:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 r — bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 47 ...
Page 48
... MRF89XA 2.16.4 RESERVED REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-20: RESVREG: RESERVED REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x13) (POR:0x07 — — — bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-0 Reserved: Reserved bits; do not use 00000111 = Reserved (default) 2.16.5 RSSI STATUS READ REGISTER ...
Page 49
... These bits set the cut-off frequency of the averaging for the average mode of the OOK threshold in the demodulator. ( BR/32.π Reserved; do not use 01 = Reserved; do not use BR/8.π (default) c © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 OOKTHPV<2:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared (1) Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 R/W-0 OOKATHC<1:0> bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 49 ...
Page 50
... MRF89XA 2.17 Sync Word Configuration Registers 2.17.1 SYNC VALUE FIRST BYTE SET REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-23: SYNCV31REG: SYNC VALUE FIRST BYTE CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x16) (POR:0x00) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-0 SYNCV< ...
Page 51
... Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 SYNCV<15:8> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 SYNCV<7:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Bit is unknown R/W-0 R/W-0 bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 51 ...
Page 52
... MRF89XA 2.18 Transmitter Configuration Registers 2.18.1 TRANSMIT PARAMTER CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-27: TXCONREG: TRANSMIT PARAMETER CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x1A) (POR:0x7C) R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 TXIPOLFV<3:0> bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7-4 TXIPOLFV<3:0>: Transmission Interpolation Filter Cut Off Frequency Value bits These bits control the cut off frequency of the interpolation filter in the transmission path. TXIPOLFV< ...
Page 53
... Reserved<1:0>: Reserved bits; do not use 00 = Reserved (default) © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 CLKOFREQ<4:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared = 427 kHz (default Preliminary MRF89XA r r — — bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 53 ...
Page 54
... MRF89XA 2.20 Packet Configuration Registers 2.20.1 PAYLOAD CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-29: PLOADREG: PAYLOAD CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0x1C) (POR:0x00) R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 MCHSTREN bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7 MCHSTREN: Manchester Encoding/Decoding Enable bit 1 = Enabled ...
Page 55
... This bit checks the status/result of the CRC of the current packet (read-only Not OK © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-0 WHITEON CHKCRCEN ADDFIL<1:0> Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary MRF89XA R/W-0 R/W-0 STSCRCEN bit Bit is unknown DS70622B-page 55 ...
Page 56
... MRF89XA 2.20.4 FIFO CRC CONFIGURATION REGISTER DETAILS REGISTER 2-32: FCRCREG: FIFO CRC CONFIGURATION REGISTER (ADDRESS:0xIE) (POR:0x00) R/W-0 R/W-0 r ACFCRC FRWAXS — bit Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set r = Reserved bit 7 ACFCRC: Auto Clear FIFO CRC bit This bit when enabled auto clears FIFO if CRC failed for the current packet. ...
Page 57
TABLE 2-8: DETAILED CONFIGURATION/CONTROL/STATUS REGISTER MAP Register Function/ Register Register Name Bit 7 Parameter Address Type General 0x00 GCONREG 0x01 DMODREG 0x02 FDEVREG 0x03 BRSREG Reserved 0x04 FLTHREG 0x05 FIFOCREG 0x06 R1CREG 0x07 P1CREG 0x08 S1CREG 0x09 R2CREG 0x0A P2CREG ...
Page 58
... Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 58 ...
Page 59
... FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION The functional block diagram of the MRF89XA is illustrated in Figure 3-1. The functional operations of individual blocks are explained in subsequent sections. FIGURE 3-1: MRF89XA FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM PARS PA RFIO LNA LO1 RX OSC1 Frequency Synthesizer XO OSC2 © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Waveform ...
Page 60
... DS70622B-page 60 3.1.2 MANUAL RESET A manual reset of the MRF89XA is possible even for applications in which V disconnected. The TEST8 pin should be pulled high for 100 u (micro) and then released. The user should then wait 5 ms before using the chip. The pin is driven with ...
Page 61
... GCONREG (Register 2-1) • CLKOUTREG (Register 2-28). 3.2.4 PHASE-LOCKED LOOP (PLL) The frequency synthesizer of the MRF89XA is a fully integrated integer-N type PLL. The PLL circuit requires only five external components for the PLL loop filter and the VCO tank circuit. ...
Page 62
... OOK signal is represented by Equation 3-2. bits EQUATION 3- ook ook tx range is Consequently, in Receive mode, due to the low intermediate frequency (Low-IF) architecture of the MRF89XA, the frequency should be configured ensure the correct low-IF receiver baseband center frequency, IF2, as shown in Equation 3-3. EQUATION 3- ook ook described in Section 3.4.4 “ ...
Page 63
... The MRF89XA is set to Transmit mode when the CMOD<2:0> bits (GCONREG<7:5>) are set to ‘100’ (see Register 2-1). The transmitter chain in the MRF89XA is based on the same double-conversion architecture and uses the same intermediate frequencies as the receiver chain. The frequency synthesizer is based on an integer-N type PLL, having bandwidth of 15k Hz ...
Page 64
... FTXRXIREG (Register 2-14 µs • FTPRIREG (Register 2-15) During the Transmit mode of MRF89XA, the Shift reg- ister takes bytes from the FIFO and outputs them seri- ally (MSb first) at the programmed bit rate to the modulator. When the transmitter is enabled, it starts sending out data from the Shift register with respect to the set bit rate ...
Page 65
... Receiver The MRF89XA is set to Receive mode when the CMOD<2:0> bits (GCONREG<7:5>) are set to ‘011’ (see Register 2-1). The receiver is based on the superheterodyne architecture. The front-end is composed of an LNA and a mixer whose gains are constant. The mixer down-converts the RF signal to an intermediate ...
Page 66
... MRF89XA 3.4.4 CHANNEL FILTERS The second mixer stages are followed by the channel select filters. The channel select filters have a strong influence on the noise bandwidth and selectivity of the receiver and hence its sensitivity. Each filter comprises a passive and an active section. 3.4.4.1 Passive Filter ...
Page 67
... Table 4-2 in Section 4.6 “Crystal Specification and Selection Guidelines” suggests filter settings in FSK mode along with the corresponding passive filter band- for any o width and the accepted tolerance on the crystal reference. bits drifts Butterworth Filter BW, FSK Val BUTFILV<3:0> [d] Preliminary MRF89XA Actual Theoretical DS70622B-page 67 ...
Page 68
... MRF89XA 3.4.6 CHANNEL FILTERS SETTING IN OOK MODE The center frequency always set to 100 kHz. The o chart in Figure 3-8 illustrates the receiver bandwidth when the BUTFILV<3:0> bits (FILCREG<3:0>) are changed when the polyphase filter is activated. Table 4-2 in Section 4.6 “Crystal Specification and Selection Guidelines” ...
Page 69
... IF_Gain = 00 3.4.7.4 RSSI IRQ Source The MRF89XA can be used to detect a RSSI level above a preconfigured threshold. The threshold is set using RTIVAL<7:0> bits (RSTHIREG<7:0>) and the IRQ status stored in the RIRQS bit (FTPRIREG<2>), which is cleared by writing a ‘1’. FIGURE 3-10: RSSI IRQ TIMINGS ...
Page 70
... Synchronizer to recover the timing information. The user can use the raw, unsynchronized, output of the FSK demodulator in Continuous mode. The FSK demodulator of the MRF89XA operates effec- tively for FSK signals with a modulation index greater than or equal to two, as shown in Equation 3-13. FIGURE 3-11: ...
Page 71
... FTOVAL<7:0> bits is below the noise floor of the receiver chain. Conversely, if the output sig- nal on DATA is a logic ‘1’, the value due to the FTOVAL<7:0> bits is several dB above the noise floor. Set MRF89XA in OOK RX mode Adjust Bit Rate, Channel filter BW Default OOKTHSV<2:0> setting No input signal ...
Page 72
... MRF89XA 3.4.10.2 Optimizing OOK Demodulator Response for Fast Fading Signals A sudden drop in signal strength can cause the bit error rate to increase. For applications, where the expected signal drop can be estimated, the OOK demodulator parameters set by the OOKTHSV<2:0> and OOK- THPV<2:0> bits (OOKCREG< ...
Page 73
... Subsequent data transitions will preserve this centering. This has two implications: • If the Bit Rates of Transmitter and Receiver are known to be the same, the MRF89XA will be able to receive an infinite unbalanced sequence (all ‘0’s or all ‘1’s) with no restriction. ...
Page 74
... FSIZE<1:0> bits (FIFOCREG<7:6>). 3.6.2 INTERRUPT SOURCES AND FLAGS The MRF89XA generates an interrupt request for the host microcontroller by pulling the IRQ0 or IRQ1 pins low or high based on the events and configuration set- tings of these interrupts. All interrupt sources and flags ...
Page 75
... FILCREG (Register 2-17) • PFCREG (Register 2-18) • SYNCREG (Register 2-19) Number of • RSTSREG (Register 2-21) bytes in FIFO • OOKCREG (Register 2-22) • FCRCREG (Register 2-32) Preliminary MRF89XA STATUS OF FIFO WHEN SWITCHING BETWEEN DIFFERENT MODES OF THE CHIP FIFO Comments Status Cleared ...
Page 76
... The packet handler is the block used in Packet mode. Its functionality is described in Section 3.11 “Packet Mode ”. 3.7.3 CONTROL The control block configures and controls the behavior of the MRF89XA according to the settings programmed in the configuration registers. 3.7.4 SYNC REGISTERS The registers associated with SYNC are: • GCONREG (Register 2-1) • ...
Page 77
... Buffered Packet © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 3.8.2 DATA OPERATION MODES The MRF89XA has three different data operation modes which can be selected by the user or programmer: • Continuous mode: Each bit transmitted or received is accessed in real time at the DATA pin. This mode may be used if adequate external sig- nal processing is available. • ...
Page 78
... The setup and hold times are shown in gray in the Figure 3-18. The use of DCLK is compulsory in FSK and optional in OOK. DS70622B-page 78 MRF89XA Control T_DATA T_DATA 3.9.2 RX PROCESSING If the bit synchronizer is disabled, the raw demodulator output is made directly available on the DATA pin and no DCLK signal is provided ...
Page 79
... Output Continuous Output Continuous Output Continuous Output Continuous Output Data Mode Interrupt Type Continuous Output Continuous Output Continuous Output Continuous Output Preliminary MRF89XA Interrupt Source Sync Pattern RSSI – – DCLK DCLK DCLK DCLK Interrupt Source – – DCLK DCLK DS70622B-page 79 ...
Page 80
... V through a 100 kΩ resistor. DD The CSDAT pin (pin15), which is unused Note: in Continuous mode, should be pulled- through a 100 kΩ resistor. DD Table 2-4, details the MRF89XA pin con- figuration and chip mode. FIGURE 3-20: HOST MCU CONNECTIONS IN CONTINUOUS MODE MRF89XA DATA IRQ0 ...
Page 81
... Datapath © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 3.10.1 TX PROCESSING After entering TX in Buffered mode, the MRF89XA expects the host microcontroller to write to the FIFO, through the SPI data interface, all the data bytes to be transmitted (preamble, Sync word, payload). Actual transmission of the first byte will start either ...
Page 82
... XXX (from SR) 3.10.2 RX PROCESSING After entering RX in Buffered mode, the MRF89XA requires the host microcontroller to get received data from the FIFO. The FIFO will start being filled with received bytes either when a Sync word has been detected (in this case only the bytes following the Sync word are filled into the FIFO) or when the FIFOFSC bit (FPPRIREG< ...
Page 83
... DD The DATA pin (pin 20), which is unused in Note: Buffered mode, should be pulled- through a 100 kΩ resistor. Table 2-4, DD provides details about the MRF89XA pin configuration and chip mode. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. RX Interrupt Data Mode Interrupt Type Buffered Output ...
Page 84
... MRF89XA TABLE 3-10: CONFIGURATION REGISTERS RELATED TO DATA PROCESSING (ONLY) IN BUFFERED MODE Register Name Register Bits DMODREG DMODE0, DMODE1 FIFOCREG FSIZE<1:0> FIFOCREG FTINT<5:0> FTXRXIREG IRQ0RXS<1:0> FTXRXIREG IRQ1RXS<1:0> FTXRXIREG IRQ1TX FTPRIREG IRQ0TXST FTPRIREG FIFOFM FTPRIREG FIFOFSC SYNCREG SYNCREN SYNCREG SYNCWSZ<1:0> SYNCREG SYNCTEN<1:0> SYNCV31REG SYNCV< ...
Page 85
... NRZ data to/from the (de)modulator is not directly accessed by the host microcontroller but is stored in the FIFO and accessed through the SPI data interface. The MRF89XA’s packet handler also performs several packet oriented tasks such as Preamble and Sync word generation, CRC calculation/check, DC scram- ...
Page 86
... MRF89XA 3.11.0.1 Packet Format Two packet formats are supported: Fixed length and Variable length, which are selected by the PKTLENF bit (PKTCREG<7>). The maximum size of the payload is limited by the size of the FIFO selected (16, 32 bytes). 3.11.0.2 Fixed Length Packet Format In applications where the packet length is fixed in advance, this mode of operation may be useful to min- imize RF overhead (no length byte field is required) ...
Page 87
... Optional Address byte (Node ID) • Message data • Optional 2-bytes CRC checksum The length byte is not included in the CRC Note: calculation. Optional DC free data coding CRC checksum calculation Length Length Address Message 0 to (FIFO size - 1) bytes byte byte Payload/FIFO Preliminary MRF89XA CRC 2-bytes DS70622B-page 87 ...
Page 88
... Stand-by mode to get payload). The FIFO must be empty for a new packet reception to start. 3.11.3 PACKET FILTERING MRF89XA packet handler offers several mechanisms for packet filtering ensuring that only useful packets are made available to the host microcontroller, significantly reducing system power consumption and software complexity ...
Page 89
... FIFO. The CRC is based on the CCITT polynomial as illus- trated in Figure 3-28. This implementation also detects errors due to leading and trailing zeros. CRC Polynomial = Preliminary MRF89XA stored in the STSCRCEN bit DS70622B-page 89 ...
Page 90
... MRF89XA 3.11.4 DC-FREE DATA MECHANISMS The payload to be transmitted may contain long sequences of ‘1’s and ‘0’s, which introduces a DC bias in the transmitted signal, causing a non-uniform power distribution spectrum. The radio signal produced has a non-uniform power distribution over the occupied chan- nel bandwidth ...
Page 91
... Packet Output FIFOFULL Packet Output Packet Output FIFO_THRESHOLD FIFO_THRESHOLD Data Mode Interrupt Type Packet Output Packet Output Packet Output Packet Output Preliminary MRF89XA Whitened data Stand-by Interrupt Source Source — — FIFOEMPTY — (2) — FIFOFULL RSSI — Interrupt Source FIFO_THRESHOLD FIFOEMPTY ...
Page 92
... V DD The DATA pin (pin 20), which is unused in Note: Packet mode, should be pulled- through a 100 kΩ resistor. Table 2-4, pro- vides details about MRF89XA pin configu- ration and chip mode. TABLE 3-13: CONFIGURATION REGISTERS RELATED TO DATA PROCESSING (ONLY) IN PACKET MODE Register Name Register Bits ...
Page 93
... RSTSREG (Register 2-21) • OOKCREG (Register 2-22) • SYNCV31REG (Register 2-23) • SYNCV23REG (Register 2-24) • SYNCV15REG (Register 2-25) • SYNCV07REG (Register 2-26) • PLOADREG (Register 2-29) • NADDSREG (Register 2-30) • PKTCREG (Register 2-31) • FCRCREG (Register 2-32) Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 93 ...
Page 94
... Reset. After initialization, the other features of the MRF89XA device can be configured based on the application. Accessing a register is implied as a com- mand to the MRF89XA device through the SPI port. The steps to initialize the MRF89XA using the control registers are as follows the GCONREG register: a) Set the Chip Mode (CMOD< ...
Page 95
... Switching from Stand-by to Synthesizer mode, the PLL will lock in less than 0.5 ms. PLL lock can be monitored on the PLOCK pin (pin 23) of the MRF89XA. The radio can then be switched to either Transmit or Receive mode. When switching from any other mode back to Sleep mode, the device will drop to its Sleep mode current in less than 1 ms ...
Page 96
... EXAMPLE 3-1: TO PUT THE MRF89XA INTO SLEEP MODE Set CMOD<2:0> (GCONREG<2:0> The MRF89XA device can wake up from any interrupt activity. For Wake-up mode perform any one the following task: • Enter in TX/RX mode • Enable CLKOUT • Set the INT pin ...
Page 97
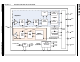
... APPLICATION DETAILS 4.1 Application Schematic An application circuit schematic of the MRF89XA with a matching circuit of the SAW filter and antenna is illus- trated in Figure 4-1. This application design (that is, schematics and BOM) can be replicated in the final application board for optimum performance. FIGURE 4-1: APPLICATION CIRCUIT SCHEMATIC © ...
Page 98
... RF out- puts are of open-collector type. 4.2 Antenna Components The MRF89XA is single-ended and has an unbalanced input/output impedance close to 30-j25. Therefore, it only requires a matching circuit to the SAW filter and antenna. C11, C12, and L6, L1, C4, and C5 are tuned to provide that impedance (30+j25) to the RFIO pin (pin 31) ...
Page 99
... FIGURE 4-3: 915 MHz SAW FILTER PLOT 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 -50 -60 -70 -80 400 600 800 © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 1000 1200 1400 Frequency [MHz] 1000 1200 1400 Frequency [MHz] Preliminary MRF89XA 1600 1800 2000 1600 1800 2000 DS70622B-page 99 ...
Page 100
... Note: for an optimized PA load setting. DS70622B-page 100 4.4.1 OPTIMUM LOAD IMPEDANCE As the PA and the LNA front-ends in the MRF89XA share the same input/output pin, they are internally matched to approximately 50Ω. Figure 4-4illustrates optimum load impedance of RFIO through an imped- ance chart. Pmax-1dB circle Max Power Zopt = 30 + j25Ω ...
Page 101
... OFF and PARS is tied to ground. The RF choke induc- tor is then used to bias the LNA. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 0.047 µF 100 nH 1Ω 1% SAW DC block Low-pass and DC block FIGURE 4-6: PARS RFIO To Antenna Preliminary MRF89XA Antenna port FRONT-END DESCRIPTION PA Regulator (1.8V LNA DS70622B-page 101 ...
Page 102
... Selection Guidelines Table 4-2 lists the crystal resonator specification for the crystal reference oscillator circuit of the MRF89XA. This specification covers the full range of operation of the MRF89XA and is used in the application schematic (for more information, see Section 4.7 “Bill of Materi- als”). Minimum ...
Page 103
... MRF89XA 4.7 Bill of Materials TABLE 4-3: MRF89XA APPLICATION SCHEMATIC BILL OF MATERIALS FOR 868 MHz Designator Value C1 0.047 uF Capacitor, Ceramic, 10V, +/-10%, X7R, SMT 0402 C2 0.22 uF Capacitor, Ceramic, 16V, +/-10%, X7R, SMT 0402 Capacitor, Ceramic, 6.3V, +/-10%, X5R, SMT 0603 Capacitor, Ceramic, 50V, +/-5%, UHI-Q NP0, SMT C5 1 ...
Page 104
... MRF89XA TABLE 4-4: MRF89XA APPLICATION SCHEMATIC BILL OF MATERIALS FOR 915 MHZ Designator Value C1 0.047 680 pF C10 0.01 uF C11 1.0 pF C12 0.9 pF FL1 TA0281A 100 ohm R2 100K ohm R3 6.8K ohm ohm U1 MRF89XA X1 12.800 MHz DS70622B-page 104 Description Capacitor, Ceramic, 10V, +/-10%, X7R, ...
Page 105
... Power supply bypassing is necessary. Poor bypass- ing contributes to conducted interference, which can cause noise and spurious signals to couple into the RF sections, significantly reducing the performance. Signal/Power/RF and Common Ground Dielectric Constant = 4.5 Signal/Power/RF and Common Ground Preliminary MRF89XA of the chip and for bias DD DS70622B-page 105 ...
Page 106
... MRF89XA FIGURE 4-9: FOUR BASIC COPPER FR4 LAYERS DS70622B-page 106 Signal Layout Dielectric Constant = 4.5 RF Ground Dielectric Constant = 4.5 Power Line Routing Dielectric Constant = 4.5 Ground Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 107
... This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any other conditions above those indicated in the operation listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. (except RFIO and V SS (1) ............................................................................................... -0.3V to 3.7V ).......................................................................................... - Preliminary MRF89XA ) ....... -0. 0.3V DS70622B-page 107 ...
Page 108
... MRF89XA 5.1 ESD Notice The MRF89XA is a high-performance radio frequency device, it satisfies: • Class II of the JEDEC standard JESD22-A114-B (Human Body Model KV, except on all of the RF pins where it satisfies Class 1A. • Class III of the JEDEC standard JESD22-C101C (Charged Device Model) on all pins. ...
Page 109
... Preliminary MRF89XA Unit Condition V — V — µ µ 3 — Unit Condition MHz Programmable but requires ...
Page 110
... MRF89XA TABLE 5-5: RECEIVER AC CHARACTERISTICS Symbol Parameter RSF Sensitivity (FSK) RSO Sensitivity (OOK) CCR Co-Channel Rejection ACR Adjacent Channel Rejection BI Blocking Immunity RXBWF Receiver Bandwidth in FSK (2) Mode RXBWU Receiver Bandwidth in OOK (2) Mode ITP3 Input Third Order Intercept Point TSRWF Receiver Wake-up Time ...
Page 111
... MHz, unless otherwise specified. DD Preliminary MRF89XA Unit Condition Maximum power setting. Minimum power setting. offset at the transmitter output. dBc At any offset between 200 kHz and 600 kHz, unmodulated carrier kHz. dev ...
Page 112
... MRF89XA 5.3 Switching Times and Procedures As an ultra-low power device, the MRF89XA can be configured for low minimum average power consump- tion. To minimize consumption the following optimized transitions between modes are shown. 5.3.1 OPTIMIZED RECEIVE CYCLE The lowest-power RX cycle is shown in Figure 5-1. ...
Page 113
... Microchip Technology Inc. TX Time Wait TSTR Wait TSFS Set MRF89XA in TX mode Packet mode starts its operation Set MRF89XA in FS mode Wait for PLL settling Preliminary MRF89XA MRF89XA can be put in Any other mode Data transmission can start in Continuous and Buffered modes DS70622B-page 113 ...
Page 114
... DS70622B-page 114 IDD IDDT Wait TSTWF Wait TS HOP 1. Set R2/P2/S2 2. Set MRF89XA in FS mode, change Frequency Band Select bits (FBS<1:0>) if needed, then switch from R1/P1/S1 to R2/P2/S2 Preliminary Time MRF89XA is now ready for data transmission Set MRF89XA back in TX mode © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 115
... Microchip Technology Inc. Wait TSRWF MRF89XA is now ready for data reception Wait TS HOP Set MRF89XA back in RX mode 1. Set R2/P2/S2 2. Set MRF89XA in FS mode, change Frequency Band Select bits (FBS<1:0>), then switch from R1/P1/S1 to R2/P2/S2 Preliminary MRF89XA Time DS70622B-page 115 ...
Page 116
... IDD IDDT 16 mA typ. @1 dBm IDDR 3.0 mA typ. Wait TSTWF MRF89XA mode DS70622B-page 116 Wait TSRWF Set MRF89XA in RX mode MRF89XA is now ready for data transmission Set MRF89XA in TX mode Preliminary Time MRF89XA is ready to receive data © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 117
... MHz and 915 MHz for each filter. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 865 866 867 Frequency [MHz] 910 912 914 916 918 Frequency [MHz] Sensitivity SAW Ripple Preliminary MRF89XA 14.0 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0.0 -2.0 868 869 870 14.0 12.0 10 ...
Page 118
... MRF89XA 5.4.2 SENSITIVITY VS. LO DRIFT FIGURE 5-8: FSK SENSITIVITY LOSS VS. LO DRIFT -25 -20 -15 -10 FIGURE 5-9: OOK SENSITIVITY LOSS VS. LO DRIFT -100 -80 -60 -40 In FSK mode, the default filter setting (“A3” at address 0x16) is kept, leading to f Note: 0x16, leading to ( – ...
Page 119
... FIGURE 5-11: OOK SENSITIVITY CHANGE VS 1.0 0 -1.0 -2.0 -3.0 -4.0 -5.0 -6.0 © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 150 200 of Active Filter [kHz 100 150 200 f -f [kHz Preliminary MRF89XA 250 300 250 300 350 DS70622B-page 119 ...
Page 120
... MRF89XA 5.4.4 SENSITIVITY STABILITY OVER TEMPERATURE AND VOLTAGE FIGURE 5-12: SENSITIVITY STABILITY 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 2.10 2.40 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 -2.0 -2.5 The sensitivity performance is very stable over the V Note: DS70622B-page 120 2.70 3.00 3.30 V [V] DD range, and the effect of high temperature is minimal. ...
Page 121
... FIGURE 5-14: OOK SENSITIVITY VS. BR 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 1.5 4 -0.5 -1.0 -1.5 -2.0 -2.5 © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc Bit Rate [kbps] 6.5 9 11.5 Bit Rate [kbps] Preliminary MRF89XA 75 100 14 16.5 DS70622B-page 121 ...
Page 122
... MRF89XA 5.4.6 ADJACENT CHANNEL REJECTION FIGURE 5-15: ACR IN FSK MODE -1000 -800 -600 -400 FIGURE 5-16: ACR IN OOK MODE -300 -200 In FSK mode, the unwanted signal is unmodulated (as described in the EN 300-220). Co-channel rejection (CCR, offset = 0 kHz) is Note: positive due to the DC cancellation process of the zero-IF architecture. In OOK mode, the polyphase filter efficiency is limited, thus limiting the adjacent channel rejection at 2xFo distance ...
Page 123
... Microchip Technology Inc. 865 866 867 Frequency [MHz] P SAW Ripple OUT 910 912 914 916 918 920 Frequency [MHz] P SAW Ripple OUT Preliminary MRF89XA 4.0 2.0 0.0 -2.0 -4.0 -6.0 -8.0 868 869 870 4.0 2.0 0.0 -2.0 -4.0 -6.0 -8.0 922 ...
Page 124
... MRF89XA 5.4.8 P AND I VS. PA SETTING OUT DD FIGURE 5-19: P AND I OUT DD 12.0 8.0 4.0 0.0 -4.0 -8.0 -12.0 01 FIGURE 5-20: P AND I OUT DD 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0.0 -2.0 -4.0 -6.0 -8.0 -10.0 -12.0 0123 +10 dBm typical. Output power is achievable, evan at SAW filter’s output. ...
Page 125
... The output power is not sensitive to the supply voltage, and it decreases slightly when temperature rises. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. 2.7 3.0 3.3 V [V] DD Preliminary MRF89XA 3.6 85ºC 25ºC -40ºC 0ºC DS70622B-page 125 ...
Page 126
... MRF89XA 5.4.10 TRANSMITTER SPECTRAL PURITY FIGURE 5-22: 869 MHz SPECTRAL PURITY DC-1 GHz FIGURE 5-23: 869 MHz SPECTRAL PURITY 1-6 GHz DS70622B-page 126 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 127
... The OOK bit rate ranges form 1.56 to 16.7 kbps. For the lowest bit rates, a channel spacing around 200 kHz is achievable. FIGURE 5-24: OOK SPECTRUM – 2 kbps FIGURE 5-25: OOK SPECTRUM – 8 kbps © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 127 ...
Page 128
... MRF89XA FIGURE 5-26: OOK SPECTRUM – 16.7 kbps DS70622B-page 128 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 129
... FIGURE 5-27: FSK – 1.56 KBPS – ±33 kHz The default configuration of the MRF89XA yields the bandwidth visible on Figure 5-28. FIGURE 5-28: FSK – 25 KBPS – ±50 kHz Figure 5-28 illustrates the maximal bit rate and frequency deviation that can fit in the 868 to 868 ...
Page 130
... MRF89XA FIGURE 5-29: FSK – 40 KBPS – ±40 kHz DS70622B-page 130 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 131
... Figure 5-32 provides graphs for I vs. Temperature DD and © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. The MRF89XA can meet these constraints while transmitting at the maximum output power of the device, typically 10 dBm. The built-in whitening process details are described in Section 3.11.4.2 “Data Whitening”. Preliminary MRF89XA ...
Page 132
FIGURE 5-32: I vs. Temperature and V DD Sleep Mode Current 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 2.1 2.4 2.7 3 VDD [V] FS Mode Current 2.00 1.80 1.60 1.40 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 2.1 2.4 ...
Page 133
... PACKAGING INFORMATION 6.1 Package Details This section provides the technical details of the packages. © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary MRF89XA DS70622B-page 133 ...
Page 134
... MRF89XA NOTES: DS70622B-page 134 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 135
... Filter Setting Address 16 Programmed Hex kHz C1 150 C1 150 A0 125 A0 125 A0 125 A0 125 A0 125 Preliminary MRF89XA Maximum Drift Actual kHz ± ppm 306 62 214 53 158 37 137 41 116 Maximum Drift Actual kHz ± ppm 154 41 154 46 129 22 129 23 ...
Page 136
... MRF89XA APPENDIX B: REVISION HISTORY Revision A (January 2010) This is the initial version of this document. Revision B (June 2010) Updates have been incorporated throughout the document, which required extensive revisions to all chapters. This version also includes minor typographical and formatting changes throughout the data sheet text. ...
Page 137
... Local sales offices are also available to help customers. A listing of sales offices and locations is included in the back of this document. Technical support is available through the web site at: http://support.microchip.com Preliminary MRF89XA MRF89XA contact their distributor, DS70622B-page 137 ...
Page 138
... Telephone: (_______) _________ - _________ Application (optional): Would you like a reply? Y Device: MRF89XA Questions: 1. What are the best features of this document? 2. How does this document meet your hardware and software development needs you find the organization of this document easy to follow? If not, why? 4 ...
Page 139
... INDEX A Absolute Maximum Ratings .............................................. 107 Architecture Description ...................................................... 20 B Bit Synchronizer .................................................................... 7 Block Diagrams Detailed....................................................................... 12 MRF89XA Simplified Functional ................................... 8 Power Supply.............................................................. 14 C Channel Filters .................................................................... 16 CLKOUT Output (CLKOUT Pin) ......................................... 16 Configuration Control/Status Register Map ........................ 57 Configuration/Control/Status Register Description ............. 30 Customer Change Notification Service ............................. 137 Customer Support ............................................................. 137 D DATA Pin ............................................................................ 19 Digital Pin Configuration vs ...
Page 140
... MRF89XA SYNC Value Second Byte Configuration Register (SYNCV23REG)............. 50 SYNC Value Third Byte Configuration Register (SYNCV15REG)............. 51 Transmit Parameter Configuration Register TXCONREG) ...................................................... 52 Revision History ................................................................ 136 S Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) ......................................... 22 SPI Config ........................................................................... 24 SPI Data.............................................................................. 26 SPI Interface Overview and Host Microcontroller Connections ................................................................ 23 Suggested PA Biasing and Matching.................................. 15 Super-Heterodyne Architecture ...
Page 141
... MRF89XA: Ultra Low-Power, Integrated ISM Band Sub-GHz Transceiver Temperature I = -40ºC to +85ºC (Industrial) Range Package MQ = QFN (Quad Flat, No Lead Tape and Reel © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. Example: XXX a) MRF89XA-I/MQ: Industrial temperature, QFN package. Pattern b) MRF89XAT-I/MQ: Industrial temperature, QFN package, tape and reel. Preliminary MRF89XA . DS70622B-page 141 ...
Page 142
... Taiwan - Kaohsiung Tel: 886-7-536-4818 Fax: 886-7-536-4803 Taiwan - Taipei Tel: 886-2-2500-6610 Fax: 886-2-2508-0102 Thailand - Bangkok Tel: 66-2-694-1351 Fax: 66-2-694-1350 Preliminary © 2010 Microchip Technology Inc. EUROPE Austria - Wels Tel: 43-7242-2244-39 Fax: 43-7242-2244-393 Denmark - Copenhagen Tel: 45-4450-2828 Fax: 45-4485-2829 France - Paris Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 ...