AFS250-FGG256 Actel, AFS250-FGG256 Datasheet - Page 28

AFS250-FGG256
Manufacturer Part Number
AFS250-FGG256
Description
FPGA - Field Programmable Gate Array 250K System Gates
Manufacturer
Actel
Datasheet
1.AFS600-PQG208.pdf
(330 pages)
Specifications of AFS250-FGG256
Processor Series
AFS250
Core
IP Core
Maximum Operating Frequency
1098.9 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
114
Data Ram Size
36864
Supply Voltage (max)
1.575 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
Development Tools By Supplier
AFS-Eval-Kit, AFS-BRD600, FlashPro 3, FlashPro Lite, Silicon-Explorer II, Silicon-Sculptor 3, SI-EX-TCA
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Supply Voltage (min)
1.425 V
Number Of Gates
250 K
Package / Case
FPBGA-256
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
AFS250-FGG256
Manufacturer:
Actel
Quantity:
135
Company:
Part Number:
AFS250-FGG256
Manufacturer:
ACTEL
Quantity:
6 800
Company:
Part Number:
AFS250-FGG256I
Manufacturer:
Microsemi SoC
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 28 of 330
- Download datasheet (13Mb)
Device Architecture
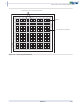
Figure 2-11 • Overview of Fusion VersaNet Global Network
2- 12
Global Pads
Chip (main)
Spine-Selection
Bottom Spine
Quadrant Global Pads
Tree MUX
Top Spine
Global Resources (VersaNets)
Fusion devices offer powerful and flexible control of circuit timing through the use of analog circuitry.
Each chip has six CCCs. The west CCC also contains a PLL core. In the two larger devices (AFS600 and
AFS1500), the west and the east CCCs each contain a PLL. The PLLs include delay lines, a phase
shifter (0°, 90°, 180°, 270°), and clock multipliers/dividers. Each CCC has all the circuitry needed for the
selection and interconnection of inputs to the VersaNet global network. The east and west CCCs each
have access to three VersaNet global lines on each side of the chip (six lines total). The CCCs at the four
corners each have access to three quadrant global lines on each quadrant of the chip.
Advantages of the VersaNet Approach
One of the architectural benefits of Fusion is the set of powerful and low-delay VersaNet global networks.
Fusion offers six chip (main) global networks that are distributed from the center of the FPGA array
(Figure
four chip quadrants. Each core VersaTile has access to nine global network resources: three quadrant
and six chip (main) global networks. There are a total of 18 global networks on the device. Each of these
networks contains spines and ribs that reach all VersaTiles in all quadrants
This flexible VersaNet global network architecture allows users to map up to 180 different
internal/external clocks in a Fusion device. Details on the VersaNet networks are given in
page
design requirements. User applications that are clock-resource-intensive can easily route external or
gated internal clocks using VersaNet global routing networks. Designers can also drastically reduce
delay penalties and minimize resource usage by mapping critical, high-fanout nets to the VersaNet
global network.
2-13. The flexibility of the Fusion VersaNet global network allows the designer to address several
2-11). In addition, Fusion devices have three regional globals (quadrant globals) in each of the
Pad Ring
R e visio n 1
High-Performance
VersaNet Global Network
(Figure 2-12 on page
Global Ribs
Global Spine
Main (chip)
Global Network
Global
Pads
Table 2-4 on
2-13).
Related parts for AFS250-FGG256
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
FPGA 256/I°/Fusion Voltage: 1.5, 1.8, 2.5, 3.3 Mixed Voltage
Manufacturer:
Actel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
FPGA - Field Programmable Gate Array 250K System Gates
Manufacturer:
Actel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU, MPU & DSP Development Tools Silicon Sculptor Programming Mod
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
MCU, MPU & DSP Development Tools InSystem Programming ProASICPLUS Devices
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators PQ160 Module
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators Axcelerator Adap Module Kit
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators Evaluation
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators AFDX Solutions
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators SILICON SCULPTOR ADAPTER MODULE
Manufacturer:
Actel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators Axcelerator Adap Module Kit
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators Evaluation
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators Silicon Sculptor Software
Manufacturer:
Actel

Part Number:
Description:
Programming Socket Adapters & Emulators InSystem Programming ProASICPLUS Devices
Manufacturer:
Actel