PCA9691BS/1 NXP Semiconductors, PCA9691BS/1 Datasheet
PCA9691BS/1
Specifications of PCA9691BS/1
Related parts for PCA9691BS/1
PCA9691BS/1 Summary of contents
Page 1
PCA9691 8-bit A/D and D/A converter Rev. 02 — 27 January 2010 1. General description The PCA9691 is a single chip, single supply, low power, 8-bit CMOS device with four analog inputs, one analog output and a serial I address ...
Page 2
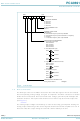
... NXP Semiconductors 3. Ordering information Table 1. Type number Package PCA9691BS PCA9691TS PCA9691T 4. Marking Table 2. Type number PCA9691BS PCA9691TS PCA9691T 5. Block diagram SCL SDA EXT OSC AIN0 AIN1 AIN2 AIN3 AOUT Fig 1. PCA9691_2 Product data sheet Ordering information Name Description HVQFN16 plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; ...
Page 3
... NXP Semiconductors 6. Pinning information 6.1 Pinning Fig 2. Fig 3. Fig 4. PCA9691_2 Product data sheet terminal 1 index area 1 AIN2 AIN3 Transparent top view For mechanical details, see Figure 25. Pin configuration for HVQFN16 (PCA9691BS) AIN0 1 2 AIN1 3 AIN2 AIN3 4 PCA9691TS Top view. For mechanical details, see ...
Page 4
... NXP Semiconductors 6.2 Pin description Table 3. Pin description Symbol Pin HVQFN16 TSSOP16 (PCA9691BS) (PCA9691TS) AIN0 15 1 AIN1 16 2 AIN2 1 3 AIN3 [ SDA 7 9 SCL 8 10 OSC 9 11 EXT 10 12 AGND 11 13 VREF 12 14 AOUT [1] The die paddle (exposed pad) is connected Functional description 7 ...
Page 5
... NXP Semiconductors 7.1.1 Address map Table 4. Pin SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SCL SCL SCL SCL SCL SCL SCL SCL SCL PCA9691_2 Product data sheet PCA9691 address map Bit SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA SDA ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors Table 4. Pin SCL SCL SDA SDA SDA SDA SCL SCL SDA SCL SCL SCL SDA SDA 7.2 Control byte The second byte sent to a PCA9691 is stored in its control register and is required to control the PCA9691 function. The upper nibble of the control register is used for enabling the analog output, and for programming the analog inputs as single-ended or differential inputs ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors The selection of a non-existing input channel results in the highest available channel number being allocated. Therefore, if the auto-increment flag is set, the next selected channel is always channel 0. After power-on all bits of the control register are reset to logic 0. The DAC and the oscillator are disabled for power saving ...
Page 8
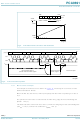
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 6. 7.3 D/A conversion The third byte sent to a PCA9691 is stored in the DAC data register and is converted to the corresponding analog voltage using the on-chip DAC. This DAC consists of a resistor divider chain connected to the external reference voltage (pin VREF) with 256 taps and selection switches ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors In order to release the DAC for a successive approximation A/D conversion cycle, the unity gain amplifier is equipped with a sample and hold circuit. This circuit holds the output voltage while executing the A/D conversion. The formula for the output voltage supplied to the analog output pin AOUT is shown in Figure 8 ...
Page 10
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 8. protocol S ADDRESS SCL 1 2 SDA V AOUT high-impedance state of previous value held in DAC register Fig 9. D/A conversion sequence 7.3.1 Worst case example An example of the worst case is shown in between 8T When the I 9 μs. The previous AOUT value is valid at least until the rising edge of the acknowledge bit ≥ ...
Page 11
... NXP Semiconductors The new AOUT value is valid, at the latest, after 8.0 μs so before the rising edge of the 8th bit of the next transferred byte. Therefore, at the full speed of the I output is valid under all circumstances between the rising edges of the 8th bit and the acknowledge bit ...
Page 12
... NXP Semiconductors The first byte transmitted in a read cycle contains the conversion result code of the previous read cycle. After a Power-On Reset (POR) condition the first byte read is 80h. The protocol The actual speed of the I Fig 12. A/D conversion characteristics of single-ended inputs PCA9691_2 ...
Page 13
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 13. A/D conversion characteristics of differential inputs 7.5 Reference voltage For the D/A and A/D conversion either a stable external voltage reference or the supply voltage has to be applied to the resistor divider chain (pins VREF and AGND). Pin AGND has to be connected to the system analog ground and may have a DC off-set with reference low frequency may be applied to pins VREF and AGND ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors It is recommended that if the I frequency by half (see the definition of the control byte in If pin EXT is connected to V state allowing to feed an external clock signal to the OSC input. The frequency of the external clock must be in the specified range. 7.7 Characteristics of the I ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors 7.7.3 System configuration A device which sends data to the bus is a transmitter, a device which receives data from the bus is a receiver. The device which initiates and terminates a transfer is the master; and the devices which are addressed by the master are the slaves (see ...
Page 16
... NXP Semiconductors 2 7.7.5 I C-bus protocol After a start condition a valid hardware address has to be sent to a PCA9691 device. The read/write bit defines the direction of the following single or multiple byte data transfer. For the format and the timing of the start condition (S), the stop condition (P) and the ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors Table 5. In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol tot ESD stg T amb [1] Pass level; Human Body Model (HBM), according to [2] Pass level; Machine Model (MM), according to [3] Pass level; latch-up testing according to [4] According to the NXP store and transport requirements (see stored at a temperature of +8 ° ...
Page 18
... NXP Semiconductors Table 6. Static characteristic Symbol Parameter Reference inputs: pins VREF and AGND V voltage on pin VREF VREF V voltage on pin AGND AGND I input leakage current LI R reference resistance ref Oscillator: pin OSC f internal oscillator frequency pin EXT is LOW osc(int) f external oscillator ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors 50 Z AOUT (Ω Output impedance near negative power rail ( ° amb DD Fig 22. Output impedance of analog output buffer (near power rails) 10.2 Dynamic characteristics 2 Table 7. I C-bus characteristics (see Figure 23). DD Symbol Parameter f SCL clock frequency SCL t bus free time ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors 2 Table 7. I C-bus characteristics (see Figure 23). DD Symbol Parameter t fall time of both SDA f and SCL signals t rise time of both r SDA and SCL signals t spike pulse width w(spike) [1] The minimum SCL clock frequency is limited by the bus time-out feature which resets the serial bus interface if either the SDA or SCL is held LOW for a minimum ...
Page 21
... NXP Semiconductors Table 5 pF; unless otherwise specified. L Symbol Parameter Analog output V AOUT I LO Accuracy s(DAC) f c(DAC) α sup(n) [1] The linearity error is assured if the internal frequency is changed by setting bit 7 and bit 3 of the control byte to logic 1 (see [2] The time from the start of AOUT to a change of Table 9 ...
Page 22
... NXP Semiconductors [1] The linearity error is assured if the internal frequency is changed by setting bit 7 and bit 3 of the control byte to logic 1 (see 11. Application information Inputs must be connected to V connected to pins AGND or VREF. In order to prevent excessive ground and supply noise and to minimize crosstalk of the digital-to-analog signal paths the printed-circuit board layout must be designed very carefully ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors 12. Package outline HVQFN16: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads; 16 terminals; body 0.85 mm terminal 1 index area terminal 1 index area DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) (1) A UNIT max. 0.05 0. 0.2 0.00 0.23 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors TSSOP16: plastic thin shrink small outline package; 16 leads; body width 4 pin 1 index 1 DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) A UNIT max. 0.15 0.95 mm 1.1 0.25 0.05 0.80 Notes 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included. 2. Plastic interlead protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 25
... NXP Semiconductors SO16: plastic small outline package; 16 leads; body width 7 pin 1 index 1 e DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions) A UNIT max. 0.3 2.45 mm 2.65 0.25 0.1 2.25 0.012 0.096 inches 0.1 0.01 0.004 0.089 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm (0.006 inch) maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 26
... NXP Semiconductors 13. Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 13.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering is one of the most common methods through which packages are attached to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), to form electrical circuits ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors 13.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process window for a mix of large and small components on one board • ...
Page 28
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 28. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 14. Abbreviations Table 12. Acronym CMOS DAC DC HBM LSB MM MSB MSL PCB POR SCL SDA SMD 15. References [1] AN10365 — Surface mount reflow soldering description ...
Page 29
... NXP Semiconductors [2] IEC 60134 — Rating systems for electronic tubes and valves and analogous semiconductor devices [3] IEC 61340-5 — Protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena [4] IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020D — Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification for Nonhermetic Solid State Surface Mount Devices [5] JESD22-A114 — Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Sensitivity Testing Human Body ...
Page 30
... Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document, including without limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without notice ...
Page 31
... NXP Semiconductors 19. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 4 Marking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 5 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 6 Pinning information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 6.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 6.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 7 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 7.1 Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 7.1.1 Address map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 7.2 Control byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 7.3 D/A conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 7.3.1 Worst case example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 7 ...