MF5CWM National Semiconductor, MF5CWM Datasheet - Page 13
MF5CWM
Manufacturer Part Number
MF5CWM
Description
IC FILTER MONO SW CAP SO14
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MF5CWM.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of MF5CWM
Filter Type
Universal Switched Capacitor
Frequency - Cutoff Or Center
30kHz
Number Of Filters
1
Max-order
2nd
Voltage - Supply
8 V ~ 14 V
Mounting Type
*
Package / Case
*
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
*MF5CWM
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MF5CWM
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
18c ) The passive resistor divider with a bypass capacitor is
3 0 Applications Information
For a cutoff frequency of 200 Hz the external clock can be
either 10 kHz with pin 9 connected to V
with pin 9 tied to A
Logic Level Shift pin (7) determines the logic threshold for
the clock input The threshold is approximately 2V higher
than the voltage applied to pin 7 Therefore when pin 7 is
grounded the clock logic threshold will be 2V making it
compatible with 0–5 volt TTL logic levels and
CMOS levels Pin 7 should be connected to a clean low-im-
pedance (less than 1000 ) voltage source
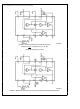
The complete circuit of the design example is shown for a
100 1 clock ratio in Figure 16
3 2 SINGLE SUPPLY OPERATION
The MF5 can also operate with a single-ended power sup-
ply Figure 17 shows the example filter with a single-ended
power supply V
supply (8 to 14 volts) and V
A
This half-supply point should be very ‘‘clean’’ as any noise
appearing on it will be treated as an input to the filter It can
be derived from the supply voltage with a pair of resistors
and a bypass capacitor ( Figure 18a ) or a low-impedance
half-supply voltage can be made using a three-terminal volt-
age regulator or an operational amplifier ( Figures 18b and
sufficient for many applications provided that the time con-
stant is long enough to reject any power supply noise It is
also important that the half-supply reference present a low
impedance to the clock frequency so at very low clock fre-
quencies the regulator or op-amp approaches may be pref-
erable because they will require smaller capacitors to filter
the clock frequency The main power supply voltage should
be clean (preferably regulated) and bypassed with 0 1 F
3 3 DYNAMIC CONSIDERATIONS
The maximum signal handling capability of the MF5 like
that of any active filter is limited by the power supply volt-
ages used The amplifiers in the MF5 are able to swing to
within about 1 volt of the supplies so the input signals must
be kept small enough that none of the outputs will exceed
GND
(a) Resistive Divider with
pin must be tied to V
Decoupling Capaciter
a
is again connected to the positive power
GND
or V
FIGURE 18 Three Ways of Generating
TL H 5066– 27
a
b
b
2 for single supply operation
is connected to ground The
(100 1) The voltage on the
a
(50 1) or 20 kHz
(Continued)
g
(b) Voltage Regulator
5 volt
13
Figures 7 through 15 are equations labeled ‘‘circuit dynam-
V
these limits If the MF5 is operating on
ple the outputs will clip at about 8V
voltage multiplied by the filter gain should therefore be less
than 8V
Note that if the filter has high Q the gain at the lowpass or
highpass outputs will be much greater than the nominal filter
gain ( Figure 6 ) As an example a lowpass filter with a Q of
10 will have a 20 dB peak in its amplitude response at f
the nominal gain of the filter H
f
be less than 800 mV
volt supplies
Also note that one output can have a reasonable small volt-
age on it while another is saturated This is most likely for a
circuit such as the notch in Mode 1 ( Figure 7 ) The notch
output will be very small at f
apply a large signal to the input However the bandpass will
have its maximum gain at f
output clips the performance at the other outputs will be
degraded so avoid overdriving any filter section even ones
whose outputs are not being directly used Accompanying
ics’’ which relate the Q and the gains at the various outputs
These should be consulted to determine peak circuit gains
and maximum allowable signals for a given application
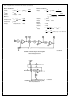
3 4 OFFSET VOLTAGE
The MF5’s switched capacitor integrators have a higher
equivalent input offset voltage than would be found in a
typical continuous-time active filter integrator Figure 19
shows an equivalent circuit of the MF5 from which the out-
put dc offsets can be calculated Typical values for these
offsets are
V
V
V
The dc offset at the BP output is equal to the input offset of
the lowpass integrator (V
puts depend on the mode of operation and the resistor ra-
tios as described in the following expressions
o
2
os1
os2
os3
a
will be 10 The maximum input signal at f
for Single-supply Operation
TL H 5066 – 28
e b
e a
e
p-p
opamp offset
185mV
115mV
50 1
50 1
p-p
e
when the circuit is operated on
os3
g
o
(c) Operational Amplifier
5mV
and can clip if overdriven If one
) The offsets at the other out-
o
OLP
so it might appear safe to
with Divider
is equal to 1 the gain at
p-p
The maximum input
g
b
a
5 volts for exam-
o
310mV
240mV
must therefore
TL H 5066 – 29
100 1
100 1
o
g
If
5