MF5CWM National Semiconductor, MF5CWM Datasheet - Page 4
MF5CWM
Manufacturer Part Number
MF5CWM
Description
IC FILTER MONO SW CAP SO14
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MF5CWM.pdf
(16 pages)
Specifications of MF5CWM
Filter Type
Universal Switched Capacitor
Frequency - Cutoff Or Center
30kHz
Number Of Filters
1
Max-order
2nd
Voltage - Supply
8 V ~ 14 V
Mounting Type
*
Package / Case
*
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
*MF5CWM
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
MF5CWM
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
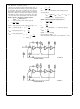
Pin Description
LP(14) BP(1)
N AP HP(2)
INV1(3)
S1(4)
SA(5)
50 100(9)
AGND(11)
Typical Performance Characteristics
Deviation of
The second order lowpass bandpass
and notch allpass highpass outputs The
LP and BP outputs can typically sink 1 mA
and source 3 mA The N AP HP output
can typically sink 1 5 mA and source 3
mA Each output typically swings to within
1V of each supply
The inverting input of the summing op
amp of the filter This is a high impedance
input but the non-inverting input is
internally tied to AGND making INV1
behave like a summing junction (low
impedance current input)
S1 is a signal input pin used in the allpass
filter configurations (see modes 4 and 5)
The pin should be driven with a source
impedance of less than 1 k
driven with a signal it should be tied to
AGND (mid-supply)
This pin activates a switch that connects
one of the inputs of the filter’s second
summer to either AGND (SA tied to V
or to the lowpass (LP) output (SA tied to
V
configuring the filter in its various modes
of operation
This pin is used to set the internal clock to
center frequency ratio (f
filter By tying the pin to V
ratio of about 50 1 (typically 50 11
0 2%) is obtained Tying the 50 100 pin to
either AGND or V
ratio to about 100 1 (typically 100 04
0 2%)
This is the analog ground pin This pin
should be connected to the system
ground for dual supply operation or biased
to mid-supply for single supply operation
For a further discussion of mid-supply
biasing techniques see the Applications
Information (Section 3 2) For optimum
filter performance a ‘‘clean’’ ground must
be provided
a
) This offers the flexibility needed for
F
CLK
F
o
vs Nominal Q
b
will set the f
CLK
a
an f
f
o
If S1 is not
) of the
CLK
CLK
g
f
f
g
Deviation of
b
o
o
)
4
V
CLK(8)
L Sh(7)
INV2(12)
Vo2(13)
F
a
CLK
F
o
(6) V
vs Nominal Q
b
(10)
These are the positive and negative
supply pins The MF5 will operate over a
total supply range of 8V to 14V
Decoupling the supply pins with 0 1 F
capacitors is highly recommended
This is the clock input for the filter CMOS
or TTL logic level clocks can be
accomodated by setting the L Sh pin to
the levels described in the L Sh pin
description For optimum filter
performance a 50% duty cycle clock is
recommended for clock frequencies
greater than 200 kHz This gives each op
amp the maximum amount of time to
settle to a new sampled input
This pin allows the MF5 to accommodate
either CMOS or TTL logic level clocks For
dual supply operation (i e
or TTL logic level clock can be accepted if
the L Sh pin is tied to mid-supply (AGND)
which should be the system ground
For single supply operation the L Sh pin
should be tied to mid-supply (AGND) for a
CMOS logic level clock The mid-supply
bias should be a very low impedance
node See Applications Information for
biasing techniques For a TTL logic level
clock the L Sh pin should be tied to V
which should be the system ground
This is the inverting input of the
uncommitted op amp This is a very high
impedance input but the non-inverting
input is internally tied to AGND making
INV2 behave like a summing junction
(low-impedance current input)
This is the output of the uncommitted op
amp It will typically sink 1 5 mA and
source 3 0 mA It will typically swing to
within 1V of each supply
OPAMP Output Voltage
Swing vs Temperature
g
5V) a CMOS
TL H 5066 – 3
b