NHE6300ESB Intel Corporation, NHE6300ESB Datasheet

NHE6300ESB
Specifications of NHE6300ESB
Available stocks
Related parts for NHE6300ESB
NHE6300ESB Summary of contents
Page 1
Intel® 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Datasheet November 2007 ® Notice: The Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available ...
Page 2
... Dads, PC Parents, PDCharm, Pentium, Pentium II Xeon, Pentium III Xeon, Performance at Your Command, RemoteExpress, SmartDie, Solutions960, Sound Mark, StorageExpress, The Computer Inside., The Journey Inside, TokenExpress, VoiceBrick, VTune, and Xircom are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others. ...
Page 3
ICH ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Product Features • 8-Bit Hub Interface — 266 Mbyte/s maximum throughput — Parallel Termination scheme for longer trace lengths — Supports Lower Voltages as per Hub Interface 1.5 spec • ...
Page 4
USB — Includes one EHCI USB2 host controllers, a total of four ports (shared with the UHCI ports) — Two UHCI Host Controllers for a total of four ports (shared with EHCI ports) — New: supports a USB 2.0 ...
Page 5
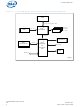
ICH System Block Diagrams Figure 1. Workstation/PC Model Graphics GBE FWH / SIO GBE / SCSI Legacy Peripherals USB 2.0 SM Bus November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US CPU AGP ® Intel 875P MCH HL 1.5 Hublink 1.5 ...
Page 6
Figure 2. Low to Mid-Range Communication Appliance Model (Diskless) GBE GBE / 2D Graphics SM Bus ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 6 CPU Processor System Bus ® Intel HL 1.5 875P MCH Hublink ® Intel PCI-X 6300ESB I/O ...
Page 7
ICH Figure 3. Value Server, Ultra-Dense Server and Low-End Server Blade GBE GBE 2D Graphics USB 2.0 SM Bus BMC November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US CPU Processor System Bus ® Intel HL 1.5 E7210 MCH Hublink 1.5 ...
Page 8
Contents 1 Introduction ............................................................................................................49 1.1 About This Document .........................................................................................49 ® 2 Intel 6300ESB ICH and System Clock Domains .....................................................53 3 Signal Description....................................................................................................55 3.1 Hub Interface to Host Controller ..........................................................................55 3.2 Firmware Hub Interface ......................................................................................56 3.3 PCI Interface.....................................................................................................57 3.4 PCI-X Interface ...
Page 9
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 5.2.1.5 SYNC Time-Out ...................................................................... 100 5.2.1.6 SYNC Error Indication .............................................................. 100 5.2.1.7 LFRAME# Usage ..................................................................... 101 5.2.1.8 I/O Cycles.............................................................................. 102 5.2.1.9 Bus Master Cycles ................................................................... 102 5.2.1.10 LPC Power Management........................................................... 102 5.2.1.11 Configuration and Intel 5.3 ...
Page 10
Normal End of Interrupt ........................................................... 119 5.6.4.10 Automatic End of Interrupt Mode ............................................... 119 5.6.5 Masking Interrupts................................................................................ 119 5.6.5.1 Masking on an Individual Interrupt Request ................................ 119 5.6.5.2 Special Mask Mode .................................................................. 119 5.6.6 Steering PCI Interrupts.......................................................................... 119 5.6.7 ...
Page 11
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 5.11.6.3 STPCLK# Implementation Notes ............................................... 154 5.11.7 Sleep States ........................................................................................ 155 5.11.7.1 Sleep State Overview .............................................................. 155 5.11.7.2 Initiating Sleep State............................................................... 155 5.11.7.3 Exiting Sleep States ................................................................ 156 5.11.7.4 Sx-G3-Sx, Handling Power Failures ........................................... 157 5.11.8 ...
Page 12
IDE Port Decode...................................................................... 179 5.14.2.3 IDE Legacy Mode and Native Mode ............................................ 179 5.14.2.4 PIO IDE Timing Modes ............................................................. 180 5.14.2.5 IORDY Masking ....................................................................... 181 5.14.2.6 PIO 32-Bit IDE Data Port Accesses............................................. 181 5.14.2.7 PIO IDE Data Port Prefetching ...
Page 13
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 5.17.5.3 Packet Field Formats ............................................................... 208 5.17.5.4 Address Fields ........................................................................ 210 5.17.5.5 Frame Number Field ................................................................ 211 5.17.5.6 Data Field .............................................................................. 211 5.17.5.7 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)................................................ 211 5.17.6 Packet Formats .................................................................................... 211 5.17.6.1 Token Packets ...
Page 14
Interrupts/SMI# ................................................................................... 250 5.19.6 SMBALERT#......................................................................................... 251 5.19.7 SMBus CRC Generation and Checking ...................................................... 251 5.19.8 SMBus Slave Interface........................................................................... 251 5.19.8.1 Format of Slave Write Cycle...................................................... 252 5.19.8.2 Format of Read Command ........................................................ 254 5.19.8.3 Format of Host Notify Command................................................ ...
Page 15
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 7.1.5 Offset 08h: RID—Revision Identification Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) .............................................................................. 291 7.1.6 Offset 0Ah: SCC—Sub-Class Code Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) .................. 291 7.1.7 Offset 0Bh: BCC—Base-Class Code Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) .............................................................................. 291 7.1.8 Offset 0Dh: PMLT—Primary Master Latency Timer Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) ...
Page 16
Offset 06 - 07h: PCISTA—PCI Device Status (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ................................................................................ 314 8.1.5 Offset 08h: RID—Revision ID Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0)........................... 315 8.1.6 Offset 09h: PI—Programming Interface (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ......................... 315 8.1.7 Offset 0Ah: SCC—Sub-Class Code Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ................................................................................ 315 ...
Page 17
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 8.1.37 Offset F4: ETR1—PCI-X Extended Features Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ................................................................................ 345 8.1.38 Offset F8h: Manufacturer’s ID ................................................................ 345 8.2 DMA I/O Registers ........................................................................................... 346 8.2.1 DMABASE_CA—DMA Base and Current Address Registers .......................... 348 8.2.2 DMABASE_CC—DMA Base ...
Page 18
COPROC_ERR—Coprocessor Error Register ............................................... 383 8.7.5 RST_CNT—Reset Control Register ........................................................... 383 8.8 Power Management Registers (D31:F0) .............................................................. 384 8.8.1 Power Management PCI Configuration Registers (D31:F0) .......................... 384 8.8.1.1 Offset A0h: GEN_PMCON_1—General PM Configuration 1 Register (PM—D31:F0) ......................................................................... 385 8.8.1.2 ...
Page 19
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 8.10.4 Offset GPIOBASE + 0Ch: GP_LVL—GPIO Level for Input or Output Register.. 427 8.10.5 Offset GPIOBASE + 18h: GPO_BLINK—GPO Blink Enable Register ............... 429 8.10.6 Offset GPIOBASE + 2Ch: GPI_INV—GPIO Signal Invert Register ................. 430 8.10.7 ...
Page 20
Offset 06 - 07h: STA—Device Status Register (USB—D29:F0/F1) ................................................................................ 464 10.1.5 Offset 08h: RID—Revision Identification Register (USB—D29:F0/F1) ................................................................................ 464 10.1.6 Offset 09h: PI—Programming Interface (USB—D29:F0/F1)......................... 465 10.1.7 Offset 0Ah: SCC—Sub Class Code Register (USB—D29:F0/F1) ................................................................................ 465 10.1.8 Offset 0Bh: ...
Page 21
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 11.1.19 Offset 59h: Next Item Pointer #2 ........................................................... 496 11.1.20 Offset 5Ah - 5Bh: Debug Port Base Offset................................................ 496 11.1.21 Offset 60h: Serial Bus Release Number ................................................... 496 11.1.22 Offset 61h: Frame Length Adjustment..................................................... 496 11.1.23 ...
Page 22
Offset 20 - 23h: SMB_BASE—SMBUS Base Address Register (SMBUS—D31:F3) .................................................................... 531 12.1.10Offset 2Ch - 2Dh: SVID—Subsystem Vendor ID (SMBUS—D31:F2/F4)............................................................................ 531 12.1.11Offset 2Eh - 2Fh: SID—Subsystem ID (SMBUS—D31:F2/F4)....................... 532 12.1.12Offset 3Ch: INTR_LN—Interrupt Line Register (SMBUS—D31:F3) ................................................................................ 532 12.1.13Offset 3Dh: INTR_PN—Interrupt ...
Page 23
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 13.1.15 Offset 2E - 2Fh: SID—Subsystem ID Register (Audio—D31:F5) .................................................................................. 559 13.1.16 Offset 34h: CAP_PTR—Capabilities Pointer (Audio—D31:F5) .................................................................................. 560 13.1.17 Offset 3Ch: INTR_LN—Interrupt Line Register (Audio—D31:F5) .................................................................................. 560 13.1.18 Offset 3Dh: INTR_PN—Interrupt Pin Register (Audio—D31:F5) .................................................................................. ...
Page 24
PID—PCI Power Management Capability ID Register (Modem— D31:F6)590 14.1.18Offset 52h: PC—Power Management Capabilities Register (Modem—D31:F6) 591 14.1.19Offset 54h: PCS—Power Management Control and Status Register (Modem— D31:F6)591 14.2 AC’97 Modem I/O Space (D31:F6) ..................................................................... 593 14.2.1 x_BDBAR—Buffer Descriptor List ...
Page 25
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 16.5.3 Reload Sequence.................................................................................. 630 16.5.4 Low Power State .................................................................................. 630 17 APIC1 Configuration Registers (D29:F5)631 17.1 APIC1 Configuration Registers (D29:F5) ............................................................. 631 17.1.1 Offset 00 - 03h: VID_DID—Vendor/ID Register (APIC1—D29:F5).................................................................................. 632 17.1.2 Offset 04 - 05h: ...
Page 26
Offset 00: ID—Identifiers ......................................................... 654 18.6.1.3 Offset 04: CMD—Command ...................................................... 655 18.6.1.4 Offset 06: PSTS—Primary Status ............................................... 656 18.6.1.5 Offset 08: RID—Revision ID...................................................... 658 18.6.1.6 Offset 09: CC—Class Code ........................................................ 659 18.6.1.7 Offset 0C: CLS—Cache Line Size ............................................... 659 ...
Page 27
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 18.8.2 Attributes ............................................................................................ 691 18.8.3 Special Notes for Burst Transactions ....................................................... 692 18.8.4 Device Select Timing ............................................................................ 692 18.8.5 Wait States ......................................................................................... 692 18.8.6 Split Transactions ................................................................................. 693 18.8.6.1 Completer Attributes ............................................................... 693 18.8.6.2 Requirements for ...
Page 28
Internal Register Descriptions ................................................... 710 19.5.1.4 FIFO Operation ....................................................................... 723 19.6 Logical Device 7 (07H): Port 60/64 Emulation...................................................... 724 19.6.1 Feature List ......................................................................................... 724 19.6.2 Overview ............................................................................................. 724 19.6.2.1 Port 60H Emulation (SCR60) ..................................................... 725 19.6.2.2 Port 64H Emulation ...
Page 29
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 20.1.19 Offset 40 - 41h: IDE_TIMP—Primary IDE Timing Register (SATA–D31:F2).................................................................................... 748 20.1.20 IDE_TIMS—Secondary IDE Timing Register (SATA–D31:F2) ....................... 750 20.1.21 Offset 44h: SIDETIM—Slave IDE Timing Register (SATA–D31:F2).................................................................................... 750 20.1.22 Offset 48h: SDMA_CNT—Synchronous DMA Control Register (SATA–D31:F2) ...
Page 30
Test Mode Description ...................................................................................... 825 23.2 Tri-State Mode ................................................................................................ 826 23.3 XOR Chain Mode.............................................................................................. 826 23.3.1 XOR Chain Testability Algorithm Example................................................. 826 Index ..................................................................................................................... 835 ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 30 ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—Contents November 2007 ...
Page 31
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH Figures 1 Workstation/PC Model.................................................................................................5 2 Low to Mid-Range Communication Appliance Model (Diskless) .......................................... 6 3 Value Server, Ultra-Dense Server and Low-End Server Blade ........................................... 7 4 Conceptual System Clock Diagram ............................................................................. 54 5 Power Plane Usage ...
Page 32
Ultra ATA Mode (Pausing a DMA Burst) ...................................................................... 819 55 Ultra ATA Mode (Terminating a DMA Burst) ................................................................ 820 56 USB Rise and Fall Times .......................................................................................... 820 57 USB Jitter .............................................................................................................. 821 58 USB EOP Width ...................................................................................................... 821 59 ...
Page 33
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH Tables 1 Industry Specifications.............................................................................................. 49 ® 2 Intel 6300ESB ICH Clock Domains............................................................................ 53 3 Hub Interface Signals ............................................................................................... 55 4 Firmware Hub Interface Signals ................................................................................. 56 5 PCI Interface Signals ................................................................................................ 57 6 PCI-X Interface Signals ...
Page 34
Interrupt Message Address Format ........................................................................... 134 55 Interrupt Message Data Format ................................................................................ 135 56 Stop Frame Explanation .......................................................................................... 137 57 Data Frame Format................................................................................................. 137 58 Configuration Bits Reset By RTCRST# Assertion.......................................................... 140 59 INIT# Going Active ................................................................................................. 141 60 ...
Page 35
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 109 Read Policies for Periodic DMA ................................................................................. 224 110 Write Policies for Periodic DMA ................................................................................. 225 111 Read Policies for Asynchronous DMA ......................................................................... 226 112 Write Policies for Asynchronous DMA ........................................................................ 227 113 Effect of Resets ...
Page 36
Offset 22 - 23h: MEMLIM—Memory Limit Register 165 Offset 24h - 25h: PREF_MEM_BASE—Prefetchable Memory Base Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) 298 166 Offset 26h-27h: PREF_MEM_MLT—Prefetchable Memory Limit Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) 299 167 Offset 30 - 31h: IOBASE_HI—I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register (HUB-PCI—D30:F0) ...
Page 37
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 216 Offset F2h: FUNC_DIS—Function Disable Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ............................ 343 217 Offset F4: ETR1—PCI-X Extended Features Register (LPC I/F—D31:F0) ......................... 345 218 Offset F8h: Manufacturer’s ID 219 DMABASE_CA—DMA Base and Current Address Registers ............................................ 346 220 ...
Page 38
Power Management PCI Configuration Registers 272 Offset A0h: GEN_PMCON_1—General PM Configuration 1 Register (PM—D31:F0) ............ 385 273 Offset A2h: GEN_PMCON_2—General PM Configuration 2 Register (PM—D31:F0) ............ 386 274 Offset A4h: GEN_PMCON_3—General PM Configuration 3 Register (PM—D31:F0) ............ 387 275 ...
Page 39
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 324 Offset 02 - 03h: DID—Device ID Register (LPC I/F—D31:F1) ....................................... 436 325 Offset 04h - 05h: CMD—Command Register (IDE—D31:F1) ......................................... 437 326 Offset 06 - 07h: STS—Device Status Register (IDE—D31:F1) ....................................... 438 327 Offset 08h: ...
Page 40
Offset Base + (04 - 05h): USBINTR—Interrupt Enable Register..................................... 479 375 Offset Base + (06 - 07h): FRNUM—Frame Number Register ......................................... 481 376 Offset Base + (08 - 0Bh): FRBASEADD—Frame List Base Address ................................. 481 377 Offset Base + ...
Page 41
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 428 Offset 06 - 07h: STA—Device Status Register (SMBUS—D31:F3) .................................. 529 429 Offset 08h: RID—Revision ID Register (SMBUS—D31:F3) ............................................ 529 430 Offset 09h: PI—Programming Interface (SMBUS—D31:F3) .......................................... 530 431 Offset 0Ah: SCC—Sub Class Code Register (SMBUS—D31:F3)...................................... ...
Page 42
Offset 54h: PCS—Power Management Control and Status Register (Audio—D31:F5) ........ 563 ® 483 Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Audio Mixer Register Configuration .......................... 565 484 Native Audio Bus Master Control Registers ................................................................. 566 485 x_BDBAR—Buffer Descriptor Base Address Register ...
Page 43
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 537 Memory Mapped Registers....................................................................................... 618 538 Offset 00h: VID—Vendor Identification Register ......................................................... 618 539 Offset 02h: DID—Device Identification Register.......................................................... 619 540 Offset 04 - 05h: COM—Command Register ................................................................ 619 541 Offset 06h - 07h: DS—Device Status ...
Page 44
Offset 0E: HTYPE—Header Type ............................................................................... 660 593 Offset 18: BNUM—Bus Numbers ............................................................................... 661 594 Offset 1B: SLT—Secondary Latency Timer.................................................................. 661 595 Offset 1C: IOBL—I/O Base and Limit ......................................................................... 662 596 Offset 1E: SSTS—Secondary Status .......................................................................... 663 597 Offset 20: ...
Page 45
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH 646 Line Status Register (LSR) ...................................................................................... 718 647 Modem Control Register (MCR) ................................................................................ 720 648 Modem Status Register (MSR) ................................................................................. 721 649 Scratch Pad Register (SCR) ..................................................................................... 722 650 Divisor Latch Register Low (DLL) .............................................................................. 722 ...
Page 46
Offset Index 54h - 57h: SER0—SATA SError Register Port 0 (SATA–D31:F2) .................. 763 698 Offset Index 64h - 67h: SER1—SATA SError Register Port 1 (SATA–D31:F2) .................. 763 699 Offset E0h - E3h: BFCS—BIST FIS Control/Status Register (SATA–D31:F2) .................... 763 ...
Page 47
Contents—Intel 6300ESB ICH Revision History Date Revision • Included Specification Changes from specification update, version 011 • Included Specifications Clarifications from specification update, version 011 November 004 • Included Documentation Changes from specification update, version 2007 ...
Page 48
Date Revision • Included changes from previous spec updates • Updated Section 22.1 December 003 • Updated Section 22.2 2004 • Updated DC Characteristics Section 22.3 • -Updated AC Characteristics Section 22.4 • Clarified WDT Reload register bit details; listed ...
Page 49
ICH Introduction 1.1 About This Document This datasheet is intended for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and BIOS vendors creating products based on the Intel manual assumes a working knowledge of the vocabulary and principles of USB, IDE, ...
Page 50
This document contains these chapters: Chapter 1, “Introduction” on manual organization. Chapter 3, “Signal Description” ICH signal. Signals are arranged according to interface. Details are provided about the drive characteristics (Input/Output, Open Drain, etc.) of all signals. Chapter 2, “Intel® ...
Page 51
ICH Chapter 13, “AC’97 Audio Controller Registers (D31:F5)” of all registers that reside in the audio controller. This controller resides at Device 31, Function 5 (D31:F5). Note that this section of the EDS does not include the ...
Page 52
Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 52 This page intentionally left blank. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—1 November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US ...
Page 53
ICH ® Intel 6300ESB ICH and System Clock Domains Warning:This section is provided for background purposes and should not be considered by implementers and validators as part of the behavioral definition ® of the Intel 6300ESB ICH. ...
Page 54
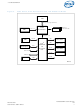
Figure 4. Conceptual System Clock Diagram ® Intel 6300ESB ICH 32 kHz XTAL ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub MHz 33 MHz Clock 14.31818 MHz Gen. 48 MHz 100 MHz Diff. Pair 12.288 MHz AC’97 Codec(s) SUSCLK# ...
Page 55
ICH Signal Description This section provides a detailed description of each signal. The signals are arranged in functional groups according to their associated interface. The “#” symbol at the end of the signal name indicates that the ...
Page 56
Table 3. Hub Interface Signals HIREF HI_VSWING NOTES: 1. The Hub Interface signals are all in a separate power plane, called the Hub Interface plane. 2. During the S3, S4, and S5 states, power to the Hub Interface is assumed ...
Page 57
ICH 3.3 PCI Interface Table 5. PCI Interface Signals (Sheet Signal Type Name AD[31:0] I/O C/ I/O BE[3:0]# DEVSEL# I/O FRAME# I/O IRDY# I/O November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Description PCI Address/Data: AD[31:0] signals ...
Page 58
Table 5. PCI Interface Signals (Sheet Signal Type Name TRDY# I/O STOP# I/O PAR I/O PERR# I/O REQ[0:3]# I GNT[0:3]# O PCICLK I ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 58 Description Target Ready: TRDY# indicates the ...
Page 59
ICH Table 5. PCI Interface Signals (Sheet Signal Type Name PLOCK# I/O SERR# I/OD PME# I/OD November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Description PCI Lock: Indicates an exclusive bus operation and may require multiple ® ...
Page 60
PCI-X Interface Table 6. PCI-X Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type PXAD[31:0] I/O PXAD[63:32 I/O ] PXC/ I/O BE#[3:0] PXC/ I/O BE#[7:4] PXDEVSEL# I/O ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 60 Description PCI-X Address/Data: These signals ...
Page 61
ICH Table 6. PCI-X Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type PXFRAME# I/O PXIRDY# I/O PXTRDY# I/O PXSTOP# I/O PXPAR I/O November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Description Cycle Frame: The current Initiator drives PXFRAME# to indicate ...
Page 62
Table 6. PCI-X Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type PXPERR# I/O PXREQ[1:0] # PXREQ[2]# /GPIO[0] PXREQ[3]# / GPIO[1] PXGNT[1:0] # PXGNT[2]# / GPIO[16] PXGNT[3]# / GPIO[17] PXPCLKI PXPCLKO[4: 0] PXPCICLK PXRCOMP I/O RASERR# OD PXPCIRST# PXPLOCK# I/O ® ...
Page 63
ICH Table 6. PCI-X Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type PXSERR# I/OD PME# I/OD PXM66EN PXPCIXCAP PXPAR64 I/O PXREQ64# I/O PXACK64# I/O PCIXSBRST # November 2007 Order Number: 300641-004US Description System Error: PXSERR# may be ...
Page 64
SATA Interface Table 7. SATA Interface Signals Name Type SATA0TXP SATA0TXN SATA0RXP SATA0RXN SATA1TXP SATA1TXN SATA1RXP SATA1RXN SATACLKP, SATACLKN SATALED# SATARBIASP SATARBIASN 3.6 IDE Interface Table 8. IDE Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type PDCS1#, SDCS1# PDCS3#, ...
Page 65
ICH Table 8. IDE Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type PDDACK#, SDDACK# PDIOR# / (PDWSTB / PRDMARDY#) SDIOR# / (SDWSTB / SRDMARDY#) PDIOW# / (PDSTOP) SDIOW# / (SDSTOP) PIORDY / (PDRSTB / PWDMARDY#) SIORDY / ...
Page 66
LPC I/F Table 9. LPC Interface Signals Typ Name e LAD[3:0] I/O / FWH[3:0] LFRAME# / I/O FWH[4] LDRQ[1 NOTE: All LPC/FWH signals are in the core well 3.8 Interrupt Interface Table 10. Interrupt Signals (Sheet 1 ...
Page 67
ICH Table 10. Interrupt Signals (Sheet Name Type PIRQ[H:E]# / GPIO[5:2] IRQ[14-15] PXIRQ[3:0]# / GPIO[36:33] NOTE: The Interrupt signals are 5V tolerant except for PXIRQ [3:0]# / GPIO[36:33] 3.9 USB Interface Table 11. USB ...
Page 68
Power Management Interface Table 12. Power Management Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type THRM# THRMTRIP # SLP_S3# SLP_S4# SLP_S5# PWROK PWRBTN# RI# SYS_RESET # RSMRST# NOTE: These signals are all in the RESUME well, except THRM# which ...
Page 69
ICH Table 12. Power Management Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type SUS_STAT# / LPCPD# SUSCLK VRMPWRG D NOTE: These signals are all in the RESUME well, except THRM# which is in the core well; PWROK ...
Page 70
Table 13. CPU Interface Signals (Sheet Name Type IGNNE# INIT# INTR NMI SMI# STPCLK# RCIN# A20GATE NOTES: 1. The CPU I/F signals (except RCIN#, A20GATE, and FERR#) are on a separate power well. This saves the external ...
Page 71
ICH 3.12 SMBus Interface Table 14. SM Bus Interface Signals Name Type SMBDATA I/OD SMBCLK I/OD SMBALERT I #/ GPIO[11] NOTE: The SMBus I/F signals are all in the RESUME well. 3.13 System Management Interface Table 15. ...
Page 72
Other Clocks Table 17. Other Clocks Name Type CLK14 I CLK48 I HICLK I 3.16 Miscellaneous Signals Table 18. Miscellaneous Signals Typ Name SPKR RTCRST# WDT_TOUT# / GPIO[32] ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 72 Description Oscillator Clock: ...
Page 73
ICH 3.17 AC’97 Link Table 19. AC’97 Link Signals Name AC_RST# AC_SYNC AC_BIT_CLK AC_SDOUT AC_SDIN[2:0] NOTES: 1. These signals are in the RESUME well, except AC_SYNC, AC_BIT_CLK, and AC_SDATA_OUT, which are in the core well. 2. See ...
Page 74
Table 20. Universal Asynchronous Receive and Transmit (UART0, 1) (Sheet Signal Name Type SIU0_DSR SIU1_DSR SIU0_DCD SIU1_DCD SIU0_RI# SIU1_RI# SIU0_DTR# SIU1_DTR# SIU0_RTS# SIU1_RTS# 3.19 General Purpose I/O Note: Alternative signal definition is for pin strap selected feature ...
Page 75
ICH Table 21. General Purpose I/O Signals (Sheet Signal Name GPIO[0]/ PXREQ[2]# GPIO[1]/ PXREQ[3]# GPIO[5:2]/ PIRQ[H:E]# GPIO[6] GPIO[7] GPIO[8] GPIO[9:10] GPIO[11] GPIO[12:13] GPIO[14:15] GPIO[16] GPIO[17] GPIO[18] GPIO[19] GPIO[20] GPIO[21] GPIO[23] GPIO[24] GPIO[25] GPIO[26] GPIO[27:28] ...
Page 76
Table 21. General Purpose I/O Signals (Sheet Signal Name GPIO[40:43] GPIO[44:55] GPIO[56:57] GPIO[58:63] NOTES: 1. GPIO[0:7], GPIO[16:21, 23], and GPIO[32:55] are in the core well. 2. GPIO[8:15] and GPIO[24:31] are in the suspend well. 3. Core-well GPIO ...
Page 77
ICH Table 22. Power and Ground Signals (Sheet Name VccPLL V_CPU_IO Vss 3.21 Pin Straps 3.21.1 Functional Straps The following signals are used for static configuration. They are sampled at various reset points to ...
Page 78
Revision and Device ID Table Table 24. Revision and Device ID Table Device Description Function D30,F0 Hub to PCI Bridge D31,F0 LPC Bridge D31,F1 D31,F2 SATA Controller D31, F3 SMBus Controller D31, F5 AC’97 Audio D31, F6 AC’97 Modem ...
Page 79
ICH ® Intel 6300ESB ICH Power Planes and Pin States 4.1 Power Planes ® Table 25. Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub Power Planes Plane Main I/O (3.3 V) Main Logic (1.5 V) Resume I/O (3.3 V Standby) ...
Page 80
Figure 5. Power Plane Usage Model ATX Power Supply 4.2 Integrated Pull-Ups and Pull-Downs Table 26. Integrated Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors Signal AC_BITCLK AC_RST# AC_SDIN[2:0] AC_SDOUT AC_SYNC DPRSLPVR EE_DIN EE_DOUT GNT[B:A]# / GNT[5]# / GPIO[17:16] LAD[3:0]# / FWH[3:0]# LDRQ[1:0] PME# ...
Page 81
ICH Table 26. Integrated Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors Signal PDDREQ / SDDREQ SPKR USB[3:0] [P,N] NOTES: 1. Simulation data shows that these resistor values may range from 10 KΩ KΩ. 2. Simulation data shows that ...
Page 82
Note: The signal levels are the same in S4 and S5. ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 82 The power plane is off, so the Intel driving. ® Intel 6300ESB ICH—4 ® 6300ESB ICH is not November 2007 ...
Page 83
ICH 4.5 Power Planes for Input Signals Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type H1PD[7:0] I/O H1PSTRBS I/O H1PSTRBF I/O H1REQM I H1REQI ...
Page 84
Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type PXPAR64 I/O PXPAR I/O PXPERR# I/O PXREQ[0]# I PXREQ[3:2]#/ I GPIO[1:0] PXGNT[0:1]# O PXGNT[3]#/GPIO[17] O PXGNT[2]#/GPIO[16] O PCICLK I ...
Page 85
ICH Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type PME# I/OD LAD[3:0] I/O LFRAME# I LDRQ[0]#, I/O LDRQ[1]# USBP[3:0]P/N, I/O OC[3:0]# I USBRBIASP O ...
Page 86
Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type PDD[15:0], I/O SDD[15:0] PDDREQ, I SDDREQ PDDACK#, O SDDACK# PDIOR# / (PDWSTB / PRDMARDY#) O SDIOR# / (SDWSTB / ...
Page 87
ICH Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type AC_SDATA_OUT O AC_SDATA_IN[2:0] I/O THRM# I THRMTRIP# I SLP_S3# O SLP_S4# O SLP_S5# O SYS_RESET# ...
Page 88
Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type RCIN# I A20GATE I SMBDATA I/OD SMBCLK I/OD SMBALERT#/ I GPIO[11] INTRUDER# I SMLINK[1:0] I/OD RTCX1 Special RTCX2 Special ...
Page 89
ICH Table 28. Power Plane and States for Output and I/O Signal for Desktop Configurations (Sheet Signal Name Type GPIO[43:37] I/O GPIO[57:56] OD UART_CLK I SIU0_RXD I SIU1_RXD I/O SIU0_TXD I/O SIU1_TXD I/O SIU0_CTS# ...
Page 90
Table 29. Power Plane for Input Signals for Desktop Configurations Signal Name Power Well A20GATE AC_BIT_CLK AC_SDIN[2:0] Resume I/O APICCLK CLK14 CLK48 CLK66 FERR# INTRUDER# IRQ[15:14] LDRQ[0]# LDRQ[1]# OC[5:0]# Resume I/O PCICLK PDDREQ PIORDY PME# Resume I/O PWRBTN# Resume I/O ...
Page 91
ICH Functional Description 5.1 Hub Interface to PCI Bridge (D30:F0) The Hub Interface to PCI Bridge resides in PCI Device 30, Function 0 on bus #0. This portion of the Intel PCI and the Hub Interface. The ...
Page 92
This will result in overrun or underrun, causing reduced quality of the isochronous data, such as audio. Note: PCI configuration write cycles, initiated by the processor, with the following characteristics will be converted to a Special Cycle with ...
Page 93
ICH Figure 6. Primary Device Status Register Error Reporting Logic Master Abort Mode (D30:3Eh.5) HL-to-PCI Posted Write Master Aborts P_SERR_EN (D30:04h.8) Delayed Transaction Timeout SERR_DTT_EN (D30.3Eh.1) Legacy PCI SERR signal SERR# Enable (D30:3Eh.1) SERR_RTA_EN (D30:90h.2) RX TARGET ...
Page 94
Figure 7. Secondary Status Register Error Reporting Logic SERR# Enable (D31:F0.04h.8) South PCI Delayed Transaction Timeout SERR_DTT_EN (D31:88h.1) Receive DO_SERR message from HL MCHSERR_STS (TCOBASE+04h.bit 12) SERR_RTA_EN (D31:88h.2) ® Intel 6300ESB I/O Controller Hub DS 94 AND ERROR from XL-Unit ...
Page 95
ICH Figure 8. NMI# Generation Logic IOCHK from SERIRQ Logic PCI_SERR_STS (Port 61.2) Pre-latch S_SSE Pre-latch P_SSE S_SSE for PCI-X Pre-latch USBe_SSE HubLink Parity Error Detected D30_P_PER (D30:04h.6) PCI Parity Error Detected D30_S_PER (D30:3Eh.0) South PCI Parity ...
Page 96
Standard PCI Bus Configuration Mechanism The PCI Bus defines a slot based “configuration space” that allows each device to contain up to eight functions with each function containing up to 256, 8-bit configuration registers. The PCI specification defines two ...
Page 97
ICH 5.1.7 PCI Dual Address Cycle (DAC) Support ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH supports DAC format on PCI for cycles from PCI initiators to main memory. This allows PCI masters to generate an address ...
Page 98
LPC Cycle Types ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH implements all of the cycle types described in the Low Pin Count Interface Specification, Revision 1.0. ® by the Intel 6300ESB ICH. Table 31. LPC Cycle Types Supported Cycle Type Memory ...
Page 99
ICH 5.2.1.2 Cycle Type/Direction (CYCTYPE + DIR) ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH will always drive bit 0 of this field to zero. Peripherals running bus master cycles must also drive bit The following table ...
Page 100
Table 35. SYNC Bit Definition (Sheet Bits[3:0] Long Wait: Part indicating wait-states, and many wait-states will be added. This 0110 encoding driven by the Intel the Short Wait (0101). Ready More (Used only by peripheral for DMA ...
Page 101
ICH Upon recognizing the SYNC field indicating an error, the Intel this the same as IOCHK# going active on the ISA bus. 5.2.1.7 LFRAME# Usage Start of Cycle For Memory, I/O, and DMA cycles, the Intel clock ...
Page 102
I/O Cycles For I/O cycles targeting registers specified in the Intel ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH performs I/O cycles as defined in the LPC spec. These will be 8-bit transfers. When the processor attempts a 16-bit or 32-bit transfer, ...
Page 103
ICH Bus Master Device Mapping and START Fields Bus Masters must have a unique START field. In the case of the Intel which supports two LPC bus masters, it will drive 0010 for the START field for ...
Page 104
Channel Priority For priority resolution, the DMA consists of two logical channel groups: channels 0–3 and channels 4–7. Each group may be in either fixed or rotate mode, as determined by the DMA Command Register. See information. DMA I/O ...
Page 105
ICH 5.3.4 Summary of DMA Transfer Sizes Table 39 lists each of the DMA device transfer sizes. The column labeled “Current Byte/ Word Count Register” indicates that the register contents represents either the number of bytes to ...
Page 106
Software Commands There are three additional special software commands that the DMA controller may execute. The three software commands are: 1. Clear Byte Pointer Flip-Flop 2. Master Clear 3. Clear Mask Register They do not depend on any specific ...
Page 107
ICH LDRQ# is synchronous with LCLK (PCI clock). As shown in uses the following serial encoding sequence: • Peripheral starts the sequence by asserting LDRQ# low (start bit). LDRQ# is high during idle conditions. • The next ...
Page 108
General Flow of DMA Transfers Arbitration for DMA channels is performed through the 8237 within the host. Once the host has won arbitration on behalf of a DMA channel assigned to LPC, it asserts LFRAME# on the LPC I/F ...
Page 109
ICH The DMA agent uses a SYNC encoding on each byte of data being transferred, which indicates to the Intel more bytes are requested. To indicate the last byte of transfer, the peripheral uses a SYNC value ...
Page 110
The peripheral must not assume that the host will be able to perform transfer sizes that are larger than the size allowed for the DMA channel, and be willing to accept a SIZE field that is smaller than what it ...
Page 111
ICH 1. Write a control word to select a counter. 2. Write an initial count for that counter. 3. Load the least and/or most significant bytes (as required by Control Word bits the 16-bit ...
Page 112
With the simple read and counter latch command methods, the count must be read according to the programmed format; specifically, when the counter is programmed for two byte counts, two bytes must be read. The two bytes do not have ...
Page 113
ICH 5.5.5.3 Read Back Command The Read Back command, written to port 43h, latches the count value, programmed mode, and current states of the OUT pin and Null Count flag of the selected counter or counters. The ...
Page 114
Table 41. Interrupt Controller Core Connections (Sheet 8259 8259 Input Slave ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH cascades the slave controller onto the master controller through master controller interrupt input ...
Page 115
ICH 5.6.1.2 Acknowledging Interrupts The processor generates an interrupt acknowledge cycle which is translated by the host bridge into a PCI Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle to the Intel translates this command into two internal INTA# pulses expected by ...
Page 116
The base address for each 8259 initialization command word is a fixed location in the I/ O memory space: 20h for the master controller, and A0h for the slave controller. 5.6.2.1 ICW1 An I/O write to the master or slave ...
Page 117
ICH • OCW3 is sets up ISR/IRR reads, enables/disables the special mask mode (SMM), and enables/disables polled interrupt mode. 5.6.4 Modes of Operation 5.6.4.1 Fully Nested Mode In this mode, interrupt requests are ordered in priority from ...
Page 118
In this mode, internal status is updated by software control during OCW2. However independent of the EOI command. Priority changes may be executed during an EOI command by using the Rotate on Specific EOI Command in OCW2 (R=1, ...
Page 119
ICH 5.6.4.9 Normal End of Interrupt In Normal EOI, software writes an EOI command before leaving the interrupt service routine to mark the interrupt as completed. There are two forms of EOI commands: Specific and Non-Specific. When ...
Page 120
The Intel an active high level to the PIC. When a PCI interrupt is routed onto the PIC, the selected IRQ may no longer be used by an ISA device (through SERIRQ). However, active low non-ISA interrupts may ...
Page 121
ICH 5.7 Advanced Interrupt Controller (APIC) (D29:F5) There are two APICs in the Intel 5). APIC0’s direct registers are assigned with base address FEC0xxxxH; however, only primary (legacy) PCI devices can write to these registers. APIC1’s direct ...
Page 122
Boot Interrupt ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH’s APIC1 contains a capability to logically OR several of its interrupt inputs together to generate a single interrupt through PIC. This is necessary for systems that do not support the APIC, and ...
Page 123
ICH 5.7.4 Interrupt Mapping Only level-triggered interrupts can be shared. PCI interrupts (PIRQs and PXIRQs) are inherently shared on the board; these should, therefore, be programmed as level- triggered. The following tables show the mapping of the ...
Page 124
APIC Bus Functional Description Table 45. APIC Interrupt Mapping, APIC0 Agent Via IRQ # SERIRQ Yes Yes 4 Yes 5 Yes 6 Yes 7 Yes Yes 10 Yes 11 Yes ...
Page 125
ICH Table 46. APIC Interrupt Mapping, APIC1 Agent IRQ # Via SERIRQ ...
Page 126
When the Intel 6300ESB ICH detects a bus idle condition on the APIC Bus, and it has an interrupt to send over the APIC bus, it drives a start cycle to begin arbitration, by driving bit ...
Page 127
ICH message, the I/O APIC resets the Remote IRR bit for that interrupt. When the interrupt signal is still active after the IRR bit is reset, the I/O APIC will treat new interrupt. Table ...
Page 128
Short Message Short messages are used for the delivery of Fixed, NMI, SMI, Reset, ExtINT and Lowest Priority with Focus processor interrupts. The Delivery Mode bits (M2–M0) specify the message. All short messages take 21 cycles including the idle cycle. ...
Page 129
ICH Table 51. APIC Bus Status Cycle Definition Delivery Mode Fixed, EOI NMI, SMM, Reset, ExtINT Lowest Priority Remote Read Lowest Priority without Focus Processor (FP) Message This message format is used to deliver an interrupt in ...
Page 130
Table 52. Lowest Priority Message (Without Focus Processor) Cycle Bit ARBID 6 NOT(DM) 7 NOT(M1) 8 NOT(L) 9 NOT(V7) 10 NOT(V5) 11 NOT(V3) 12 NOT(V1) 13 NOT(D7) 14 NOT(D5) 15 NOT(D3) 16 NOT(D1) 17 ...
Page 131
ICH Remote Read Message Remote read message is used when a local APIC wishes to read the register in another local APIC. The I/O APIC in the Intel this cycle. The message format is same as short ...
Page 132
Table 53. Remote Read Message (Sheet Cycle Bit NOTE: Cycle 21 through 36 contain the remote register data. The status information in cycle 37 specifies when the data is valid ...
Page 133
ICH Since they are edge triggered, the interrupts that are allocated to the PCI bus for this scheme may not be shared with any other interrupt (such as the standard PCI PIRQ[A:D], those received via SERIRQ#, or ...
Page 134
Edge-Triggered Operation In this case, the “Assert Message” is sent when there is an inactive-to-active edge on the interrupt. 5.7.7.3 Level-Triggered Operation In this case, the “Assert Message” is sent when there is an inactive-to-active edge on the interrupt. ...
Page 135
ICH Table 54. Interrupt Message Address Format (Sheet Bit Redirection Hint: This bit is used by the processor host bridge to allow the interrupt message to be redirected The message will be ...
Page 136
T - Turn-around Phase. Signal released ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH supports a message for 21 serial interrupts. These represent the 15 ISA interrupts (IRQ0-1, 2-15), the four PCI interrupts, and the control signals SMI# and IOCHK#. The serial ...
Page 137
ICH 5.8.3 Stop Frame After all data frames, a Stop Frame is driven by the Intel signal is driven low by the Intel clocks is determined by the SERIRQ configuration register. The number of clocks determines the ...
Page 138
Table 57. Data Frame Format (Sheet Data Frame Interrupt # 9 IRQ8 10 IRQ9 11 IRQ10 12 IRQ11 13 IRQ12 14 IRQ13 15 IRQ14 16 IRQ15 17 IOCHCK# 18 PCI INTA# 19 PCI INTB# 20 PCI INTC# ...
Page 139
ICH ® Note: The Intel 6300ESB ICH supports the ability to generate an SMI# based on a century rollover. See Section 5.9.1.4, “Century Rollover” rollover. ® Note: The Intel 6300ESB ICH does not implement month/year alarms. 5.9.1.1 ...
Page 140
Clearing Battery-Backed RTC RAM Clearing CMOS RAM in an Intel jumper on RTCRST# or GPI, or using SAFEMODE strap. Implementations should not attempt to clear CMOS by using a jumper to pull VccRTC low. Using RTCRST# to clear CMOS: ...
Page 141
ICH 5.10 Processor Interface (D31:F0) ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH interfaces to the processor with a variety of signals • Standard Outputs to the processor: A20M#, SMI#, NMI, INIT#, INTR, STPCLK#, IGNNE#, CPUSLP# • The FERR# input ...
Page 142
Table 59. INIT# Going Active (Sheet Cause of INIT# Going Active PORTCF9 write, where RST_CPU (bit 2) was a 0 and SYS_RST(bit 1) transitions from RCIN# input signal goes low. RCIN# is expected to ...
Page 143
ICH 5.10.1.4 NMI Non-Maskable Interrupts (NMIs) may be generated by several sources, as described in Table 60. Table 60. NMI Sources Cause of NMI SERR# goes active (either internally, externally through SERR# signal, or through a message ...
Page 144
Because the S1 state will have the STPCLK# signal active, the STPCLK# signal can be connected to both processors. However, for ACPI implementations, the BIOS must indicate that the 6300ESB only supports the C1 state for dual-processor designs. In going ...
Page 145
ICH 5.11 Power Management (D31:F0) 5.11.1 Features • ACPI Power and Thermal Management Support — Processor THRMTRIP# emergency shutdown — ACPI 24-Bit Timer — Software initiated throttling of processor performance for Thermal and Power Reduction — Hardware ...
Page 146
Intel 6300ESB ICH Power States and Transition Rules Table 62 shows the power states defined for Intel state names generally match the corresponding ACPI states. Table 62. General Power States for Systems Using Intel State/ Substates Full On: ...
Page 147
ICH Table 63 shows the transitions rules among the various states. Note that transitions among the various states may appear to temporarily transition through intermediate states. For example, in going from S0 to S1, it may appear ...
Page 148
System Power Planes The system has several independent power planes. These power planes can be shut off and the voltage set to a zero volt level. The power planes and their control signals are listed in Table 64. Table ...
Page 149
ICH 5.11.5 SMI#/SCI Generation Upon any SMI# event, the Intel which will cause it to enter SMM space. SMI# remains active until the EOS bit is set. When the EOS bit (bit 1) is set, SMI# will ...
Page 150
Table 66. Causes of SMI# (Sheet Cause PME# Internal EHCI wake (PME_B0) Power Button Press RTC Alarm Ring Indicate AC’97 wakes USB #1 wakes USB #2 wakes USB #3 wakes THRM# pin active (based on THRM#_POL) ACPI ...
Page 151
ICH Table 66. Causes of SMI# (Sheet Cause Device Monitors matches an address in its range SMBus Host Controller SMBus Slave SMI message SMBus SMBALERT# signal active SMBus Host Notify message received Access to ...
Page 152
Dynamic Processor Clock Control ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH has extensive control for dynamically starting and stopping system clocks. The clock control is used for transitions among the various S0/Cx states, and processor throttling. Each dynamic clock control method ...
Page 153
ICH ® 5. The Intel 6300ESB ICH waits at least 180 PCI clocks (240 ns) after deasserting STPCLK# and then starts using the FERR# signal for an indication of a floating point error. The ...
Page 154
The Host controller must post Stop-Grant cycles in such a way that the processor gets an indication of the end of the special cycle prior to the Intel observing the Stop-Grant cycle. This ensures that the STPCLK# signals stays ...
Page 155
ICH Other Implementation Notes: • When STPCLK# goes active due to a Level read, it must go active prior to the completion of the associated I/O read. This is to ensure that the STPCLK# is recognized by ...
Page 156
Table 69. Sleep Types Sleep Type The Intel S1 assert CPUSLP# signal. This will lower the processor’s power consumption. No snooping is possible in this state. The Intel S3 power to non-critical circuits. Power will only be retained to devices ...
Page 157
ICH Table 70. Causes of Wake Events (Sheet Cause Power Button GPI[0:n] USB RI# AC’97 Secondary PME# SMBALERT# SMBus Slave Message PME_B0 (internal USB EHCI controller) NOTE: When in the S5 state due to ...
Page 158
Table 71. Transitions Due to Power Failure State at Power Failure S0, S1 5.11.8 Thermal Management ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH has mechanisms to assist with managing thermal problems in the system. 5.11.8.1 THRM# Signal The THRM# ...
Page 159
ICH Note: There is a small window where the Intel more throttling period after THRM# goes inactive. This is due to a sampling delay on THRM# (the signal is still active internally, but has just gone inactive ...
Page 160
Table 72. Transitions Due to Power Button Present State S0/Cx PWRBTN# goes low S1-S5 PWRBTN# goes low G3 PWRBTN# pressed PWRBTN# held low S0-S4 for at least four consecutive seconds Power Button Override Function When PWRBTN# is observed active for ...
Page 161
ICH Table 73. Transitions Due to RI# Signal Present State S0 RI# Active S1-S5 RI# Active NOTE: Filtering/Debounce on RI# will not be done in the Intel or external. 5.11.9.3 PME# - PCI Power Management Event The ...
Page 162
When the processor is running extremely hot and is heating up possible (although very unlikely) that components around it, such as the Intel longer executing cycles properly. Therefore, when THRMTRIP# fires and the Intel 6300ESB ICH is relying ...
Page 163
ICH 5.11.10.1Write Only Registers with Read Paths in ALT Access Mode The registers described in Table 76 have read paths in ALT access mode. The access number field in the table indicates which register will be returned ...
Page 164
Table 74. Write Only Registers with Read Paths in ALT Access Mode (Sheet Restore Data # I/O of Acces Add DMA Chan 0-3 Command 2 DMA Chan 0-3 Request DMA Chan 0 ...
Page 165
ICH Table 75. PIC Reserved Bits Return Values PIC Reserved Bits ICW2(2:0) ICW4(7:5) ICW4(3:2) ICW4(0) OCW2(4:3) OCW3(7) OCW3(5) OCW3(4:3) 5.11.10.3Read-Only Registers with Write Paths in ALT Access Mode The registers described in Software will restore these values ...
Page 166
Traditional designs have a reset button logically ANDs with the PWROK signal from the power supply and the processor’s voltage regulator module. When this is done ® with the Intel ICH treats this internally as though the RSMRST# signal ...
Page 167
ICH 5.11.11.4Controlling Leakage and Power Consumption during Low- Power States To control leakage in the system, various signals will tri-state or go low during some low-power states. General principles: • All signals going to powered down planes ...
Page 168
Legacy Power Management Theory of Operation 5.11.13.1Overview Instead of relying on ACPI software, legacy power management uses BIOS and various hardware mechanisms. The Intel legacy power management compared with previous component generations. The scheme relies on the concept of ...
Page 169
ICH • Used only after first timeout occurs. • Second timeout allows for system “reset and reboot” when a hardware error is detected. Various system states are preserved through this special reset to allow for possible error ...
Page 170
TCO Theory of Operation 5.12.3.1 Overview The System Management functions are designed to allow the system to diagnose failing subsystems. The intent of this logic is that some of the system management functionality be provided without the aid of ...
Page 171
ICH b. Write to the TCO_RLD register to reload the timer to make sure the TCO timer does not reach 0 again. c. Attempt to recover. May need to periodically reload the TCO timer. The exact recovery ...
Page 172
Heartbeat and Event Reporting through SMLink/ SMbus SMLink signals are implemented on the Intel compatible mode. Heartbeat and event reporting are accomplished via the SMLink signals. 5.12.4.1 Overview 5.12.4.1.1 TCO Compatible Mode ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH may function ...
Page 173
ICH When a triggering event occurs while a message is already being generated and sent, the new event may not appear in the current message. If not, then a second message will be generated, with the SEQ[3:0] ...
Page 174
The following rules/steps apply when the system state and the policy is for ® the Intel 6300ESB ICH to not reboot the system after a hardware lockup: 1. Upon detecting the lockup the SECOND_TO_STS bit will ...
Page 175
ICH The following rules will apply when the system (S1-S4) state: ® 1. The Intel 6300ESB ICH will send a Heartbeat message every Heartbeat Period (30-32 seconds). 2. When an event occurs prior ...
Page 176
General Purpose I/O 5.13.1 GPIO Mapping Table 79. GPIO Implementation (Sheet Alternate GPIO Type Function Input GPI[0] PXREQ[2]# Only Input GPI[1] PXREQ[3]# Only Input GPI[2:5] PIRQ[E:H]# Only Input GPI[6] Unmuxed Only Input GPI[7] Unmuxed Only Input ...
Page 177
ICH Table 79. GPIO Implementation (Sheet Alternate GPIO Type Function Outpu GPO[16] PXGNT[2]# t Only Outpu GPO[17] PXGNT[3]# t Only Outpu GPO[18] Unmuxed t Only Outpu GPO[19] Unmuxed t Only Outpu GPO[20 Unmuxed t ...
Page 178
Power Wells Some GPIOs exist in the resume power plane. Care must be taken to make sure GPIO signals are not driven high into powered-down planes. ® Some Intel 6300ESB ICH GPIOs may be connected to pins on devices ...
Page 179
ICH Ultra ATA/33: DMA protocol that redefines signals on the IDE cable to allow both host and target throttling of data and transfer rates Mbytes/s. Ultra ATA/66: DMA protocol that redefines signals on ...
Page 180
Note: The Data Register (I/O Offset 00h) should be accessed using 16-bit or 32-bit I/O instructions. All other registers should be accessed using 8-bit I/O instructions. Note: These registers are implemented in the IDE device. Therefore, accesses to these I/O ...
Page 181
ICH Shutdown latency is incurred after outstanding scheduled IDE data port transactions (either a non-empty write post buffer or an outstanding read prefetch cycles) have completed and before other transactions may proceed. It provides hold time on ...
Page 182
Bus Master Function ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH may act as a PCI Bus master on behalf of an IDE slave device. Two PCI Bus master channels are provided, one channel for each IDE connector (primary and secondary). By ...
Page 183
ICH 5.14.3.2 Line Buffer A single line buffer exists for the Intel buffer is not shared with any other function. The buffer is maintained in either the read state or the write state. Memory writes are typically ...
Page 184
When switching the IDE controller to native mode, the IDE Interrupt Pin Register will be masked (see (IDE—D31:F1)”). When an interrupt occurs while the masking is in place and the interrupt is still active when the masking ends, the ...
Page 185
ICH Table 82. Interrupt/Active Bit Interaction Definition Interrup Active 5.14.3.6 Error Conditions IDE devices are sector based mass storage devices. The drivers handle errors on a sector basis; ...
Page 186
Ultra ATA/33 Protocol Ultra ATA/33 is enabled through configuration register 48h in Device 31:Function 1 for each IDE device. The IDE signal protocols are significantly different under this mode than for the 8237 mode. These differences allow the following ...
Page 187
ICH All other signals on the IDE connector retain their functional definitions during Ultra ATA/33 operation. 5.14.4.2 Operation Initial setup programming consists of enabling and performing the proper configuration ® of the Intel 6300ESB ICH and the ...
Page 188
ICH will drive the CRC value onto the DD[15:0] signals then latched by the IDE device on deassertion of DDACK#. The IDE device compares the Intel 6300ESB ICH CRC value to its own and reports an error ...
Page 189
ICH 5.15 SATA Host Controller (D31:F2) 5.15.1 Overview ® The Intel 6300ESB ICH SATA controller features two sets of interface signals that may be independently enabled, tri-stated or driven low. Each interface is supported by an independent ...
Page 190
Power State Mappings The following PCI power management states for devices are supported by the Intel 6300ESB ICH SATA Controller: D0 – working D3 – very deep sleep. This state is split into two sub-states, D3 PCI configuration accesses) ...
Page 191
ICH 5.15.4.2 Power State Transitions 5.15.4.2.1 Partial and Slumber State Entry/Exit The partial and slumber states save interface power when the interface is idle. It would be most analogous to PCI CLKRUN# (in power savings, not in ...
Page 192
SATA Interrupts The following table summarizes interrupt behavior for MSI and wire-modes. In the table “bits” refers to the 4 possible interrupt bits in I/O space, which are: BMISP.PRDIS (offset 02h, bit 7), BMISP.I (offset 02h, bit 2), BMISS.PRDIS ...
Page 193
ICH 5.16.2 Timer Accuracy 1. The timers are accurate over any 1 ms period to within 0.005% of the time specified in the timer resolution fields. 2. Within any 100 ms period, the timer will report a ...
Page 194
All three timers support non-periodic mode. Periodic Mode Timer 0 is the only timer that supports periodic mode. When Timer 0 is set up for ...
Page 195
ICH 5.16.5 Enabling the Timers The BIOS or OS PnP code should route the interrupts. This includes the Legacy Rout bit, Interrupt Rout bit (for each timer), interrupt type (to select the edge or level type for ...
Page 196
When a 32-bit processor does not want to halt the timer, it may use the 64-bit timer as a 32-bit timer by setting the TIMERn_32MODE_CNF bit. This will cause the timer to behave as a 32-bit timer. The upper 32 ...
Page 197
ICH 5.17.2.2 Transfer Descriptors (TD) Transfer Descriptors (TDs) express the characteristics of the transaction requested on USB by a client. TDs are always aligned on 16-byte boundaries, and the elements of the TD are shown in a ...
Page 198
Table 88. TD Control and Status (Sheet Bit 31:30 Reserved. Short Packet Detect (SPD): When a packet has this bit set to 1 and the packet is an input packet queue; and successfully completes ...
Page 199
ICH Table 88. TD Control and Status (Sheet Bit Active: For Intel “Data Transfers to/from Main 0 = When the transaction associated with this descriptor is completed, the Intel 6300ESB ICH sets this bit ...
Page 200
Table 88. TD Control and Status (Sheet Bit Bus Turn Around Time-out (BTTO This bit is set the Intel that a bus time-out condition was detected for this USB transaction. This ...