DSPIC30F4012 Microchip Technology Inc., DSPIC30F4012 Datasheet

DSPIC30F4012
Available stocks
Related parts for DSPIC30F4012
DSPIC30F4012 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Data Sheet High-Performance, 16-Bit Digital Signal Controllers DS70135E ...
Page 2
... Company’s quality system processes and procedures are for its PIC MCUs and dsPIC DSCs, K EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified. ® L ® code hopping devices, Serial EE OQ © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 3
... All DSP instructions are single cycle • ±16-bit, single-cycle shift © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Peripheral Features: • High-current sink/source I/O pins: 25 mA/25 mA • Timer module with programmable prescaler: - Five 16-bit timers/counters; optionally pair 16-bit timers into 32-bit timer modules • ...
Page 4
... Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) dsPIC30F Motor Control and Power Conversion Family* Program SRAM Device Pins Mem. Bytes/ Bytes Instructions dsPIC30F2010 28 12K/4K 512 dsPIC30F3010 28 24K/8K 1024 dsPIC30F4012 28 48K/16K 2048 dsPIC30F3011 40/44 24K/8K 1024 dsPIC30F4011 40/44 48K/16K 2048 dsPIC30F5015 64 66K/22K 2048 dsPIC30F6010 80 144K/48K 8192 * This table provides a summary of the dsPIC30F6010 peripheral features ...
Page 5
... EMUC3/AN1/V AN2/SS1/CN4/RB2 AN3/INDX/CN5/RB3 AN4/QEA/IC7/CN6/RB4 AN5/QEB/IC8/CN7/RB5 OSC2/CLKO/RC15 EMUD1/SOSCI/T2CK/U1ATX/CN1/RC13 EMUC1/SOSCO/T1CK/U1ARX/CN0/RC14 EMUD2/OC2/IC2/INT2/RD1 44-Pin TQFP PGC/EMUC/U1RX/SDI1/SDA/RF2 U2TX/CN18/RF5 U2RX/CN17/RF4 C1TX/RF1 C1RX/RF0 PWM3H/RE5 PWM3L/RE4 PWM2H/RE3 PWM2L/RE2 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 MCLR +/CN2/RB0 REF SS -/CN3/RB1 3 38 PWM1L/RE0 REF 4 37 PWM1H/RE1 5 36 ...
Page 6
... QFN PGC/EMUC/U1RX/SDI1/SDA/RF2 U2TX/CN18/RF5 U2RX/CN17/RF4 C1TX/RF1 C1RX/RF0 PWM3H/RE5 PWM3L/RE4 PWM2H/RE3 DS70135E-page dsPIC30F4011 OSC2/CLKO/RC15 OSC1/CLKI AN8/RB8 AN7/RB7 AN6/OCFA/RB6 AN5/QEB/IC8/CN7/RB5 AN4/QEA/IC7/CN6/RB4 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 7
... PWM3H/RE5 SS OSC1/CLKI PGC/EMUC/U1RX/SDI1/SDA/C1RX/RF2 PGD/EMUD/U1TX/SDO1/SCL/C1TX/RF3 FLTA/INT0/SCK1/OCFA/RE8 EMUC2/OC1/IC1/INT1/RD0 dsPIC30F4012 OSC2/CLKO/RC15 32 OSC1/CLKI AN5/QEB/IC8/CN7/RB5 23 AN4/QEA/IC7/CN6/RB4 DS70135E-page 5 ...
Page 8
... When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are using. Customer Notification System Register on our web site at www.microchip.com to receive the most current information on all of our products. DS70135E-page 6 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 9
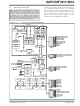
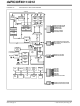
... This document contains device-specific information for the dsPIC30F4011/4012 devices. The dsPIC30F devices contain extensive Digital Signal Processor (DSP) functionality within a high-performance, 16-bit microcontroller (MCU) architecture. Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2 show device block diagrams for the dsPIC30F4011 and dsPIC30F4012 devices. X Data Bus ...
Page 10
... FIGURE 1-2: dsPIC30F4012 BLOCK DIAGRAM Y Data Bus Interrupt PSV & Table Controller Data Access 8 24 Control Block 24 24 PCH PCL PCU Program Counter Stack Loop Address Latch Control Control Logic Logic Program Memory (48 Kbytes) Data EEPROM (1 Kbyte) 16 Data Latch ROM Latch ...
Page 11
... ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Description Analog input channels. AN0 and AN1 are also used for device programming data and clock inputs, respectively. Positive supply for analog module. Ground reference for analog module. ...
Page 12
... UART1 alternate transmit. UART2 receive. UART2 transmit. Positive supply for logic and I/O pins. Ground reference for logic and I/O pins. Analog voltage reference (high) input. Analog voltage reference (low) input. Analog = C™ Analog input Output Power © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 13
... Multiple functions may exist on one port pin. When multiplexing occurs, the peripheral module’s functional requirements may force an override of the data direction of the port pin. TABLE 1-2: dsPIC30F4012 I/O PIN DESCRIPTIONS Pin Buffer Pin Name Type Type ...
Page 14
... TABLE 1-2: dsPIC30F4012 I/O PIN DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Buffer Pin Name Type Type OSC1 I ST/CMOS OSC2 I/O — PGD I/O ST PGC I ST RB0-RB5 I/O ST RC13-RC15 8I/O 8ST RD0-RD1 I/O ST RE0-RE5, I/O ST RE8 RF2-RF3 I/O ST SCK1 I/O ST SDI1 I ST SDO1 O — SS1 I/O ST SCL I/O ST SDA I/O ST SOSCO O — SOSCI I ST/CMOS T1CK I ST T2CK ...
Page 15
... Moreover, only the lower 16 bits of each instruction word can be accessed using this method. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 • SWWLinear indirect access of 32K word pages within program space is also possible, using any working register via table read and write instruc- tions ...
Page 16
... The upper byte of the SR register contains the DSP Adder/Subtracter Status bits, the DO Loop Active bit (DA) and the Digit Carry (DC) Status bit. 2.2.3 PROGRAM COUNTER The Program Counter is 23 bits wide. Bit 0 is always clear; therefore, the PC can address instruction words. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 17
... ACCB PC22 0 7 TABPAG TBLPAG Data Table Page Address 7 0 PSVPAG PSVPAG 22 DOSTART OAB SAB DA SRH © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 D15 D0 W0/WREG W10 W11 W12/DSP Offset W13/DSP Write-Back W14/Frame Pointer W15/Stack Pointer SPLIM ...
Page 18
... A block diagram of the DSP engine is shown in Figure 2-2. TABLE 2-2: Instruction CLR ED EDAC MAC MOVSAC MPY MPY.N MSC selection DSP INSTRUCTION SUMMARY Algebraic Operation – – change – – © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 19
... FIGURE 2-2: DSP ENGINE BLOCK DIAGRAM 40 Carry/Borrow Out Carry/Borrow In © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 40-bit Accumulator A 40-bit Accumulator B Saturate Adder Negate Barrel 16 Shifter 40 Sign-Extend 17-bit Multiplier/Scaler 16 16 To/From W Array Round u Logic Zero Backfill DS70135E-page 17 ...
Page 20
... Overflow Trap Flag Enable bit (OVATE, OVBTE) in the INTCON1 register (refer to Section 5.0 “Inter- rupts”) is set. This allows the user to take immediate action, for example, to correct system gain. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 21
... No saturation operation is performed and the accumulator is allowed to overflow (destroying its sign). If the COVTE bit in the INTCON1 register is set, a catastrophic overflow can initiate a trap exception. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 2.4.2.2 Accumulator ‘Write-Back’ The MAC class of instructions (with the exception of MPY, MPY ...
Page 22
... DSP shift operations and a 16-bit result for MCU shift operations. Data from the X bus is pre- sented to the barrel shifter between bit positions for right shifts, and bit positions for left shifts. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 23
... TBLRD/TBLWT, which use TBLPAG<7> to determine user or configura- tion space access. In Table 3-1, read/write instructions, bit 23 allows access to the Device ID, the User ID and the Configuration bits; otherwise, bit 23 is always clear. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 FIGURE 3-1: PROGRAM SPACE MEMORY MAP FOR dsPIC30F4011/4012 Reset – ...
Page 24
... Note: Program Space Visibility cannot be used to access bits <23:16> word in program memory. DS70135E-page 22 Program Space Address <23> <22:16> 0 TBLPAG<7:0> TBLPAG<7:0> 0 PSVPAG<7:0> 23 bits Program Counter Select bits 15 bits EA 8 bits 16 bits 24-bit EA <15> <14:1> <0> PC<22:1> 0 Data EA<15:0> Data EA<15:0> Data EA<14:0> 0 Byte Select © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 25
... Program Memory ‘Phantom’ Byte (read as ‘0’). © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 A set of table instructions is provided to move byte or word-sized data to and from program space (see Figure 3-3 and Figure 3-4). 1. TBLRDL: Table Read Low Word: Read the lsw of the program address; ...
Page 26
... Execution prior to exiting the loop due to an interrupt - Execution upon re-entering the loop after an interrupt is serviced • Any other iteration of the REPEAT loop allows the instruction, accessing data using PSV, to execute in a single cycle Visibility Page register, © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 27
... The data space memory is split into two blocks, X and Y data space. A key element of this architecture is that Y space is a subset of X space, and is fully contained within X space. In order to provide an apparent linear addressing space, X and Y spaces have contiguous addresses. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Program Space 0x0000 (1) PSVPAG ...
Page 28
... Optionally Mapped into Program Memory 0xFFFF DS70135E-page 26 16 bits Address MSB LSB 0x0000 SFR Space 0x07FE 0x0800 X Data RAM (X) 0x0BFE 0x0C00 Y Data RAM (Y) 0x0FFE 0x1000 0x8000 X Data Unimplemented (X) 0xFFFE LSB 4096 Bytes Near Data Space © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 29
... FIGURE 3-7: DATA SPACE FOR MCU AND DSP (MAC CLASS) INSTRUCTIONS EXAMPLE SFR SPACE (Y SPACE) Non-MAC Class Ops (Read/Write) MAC Class Ops (Write) Indirect EA using any W © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 SFR SPACE UNUSED Y SPACE UNUSED UNUSED MAC Class Ops Read-Only ...
Page 30
... Fault. FIGURE 3-8: 15 0001 Byte 1 0x0000 Byte 3 0003 0x0000 Byte 5 0005 0x0000 ® DATA ALIGNMENT MSB LSB 0000 Byte 0 Byte 2 0002 Byte 4 0004 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 31
... Note push during exception processing concatenates the SRL register to the MSB of the PC prior to the push. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 There is a Stack Pointer Limit register (SPLIM) associ- ated with the Stack Pointer. SPLIM is uninitialized at Reset the case for the Stack Pointer, SPLIM<0> ...
Page 32
TABLE 3-3: CORE REGISTER MAP Address SFR Name Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 (Home) W0 0000 W1 0002 W2 0004 W3 0006 W4 0008 W5 000A W6 000C W7 000E W8 0010 W9 0012 W10 0014 W11 ...
Page 33
TABLE 3-3: CORE REGISTER MAP (CONTINUED) Address SFR Name Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 (Home) XMODEND 004A YMODSRT 004C YMODEND 004E XBREV 0050 BREN DISICNT 0052 — — Legend uninitialized bit Note: Refer to the ...
Page 34
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 32 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 35
... Register Indirect Register Indirect Post-Modified Register Indirect Pre-Modified Register Indirect with Register Offset The sum of Wn and Wb forms the EA. Register Indirect with Literal Offset © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 4.1.1 FILE REGISTER INSTRUCTIONS Most file register instructions use a 13-bit address field (f) to directly address data present in the first 8192 bytes of data memory (near data space) ...
Page 36
... The only exception to the usage restrictions is for buff- ers which have a power-of-2 length. As these buffers satisfy the start and end address criteria, they may operate in a Bidirectional mode (i.e., address boundary checks will be performed on both the lower and upper address boundaries). © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 37
... Byte Address 0x1100 0x1163 Start Addr = 0x1100 End Addr = 0x1163 Length = 0x0032 words © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 4.2.2 W ADDRESS REGISTER SELECTION The Modulo and Bit-Reversed Addressing Control reg- ister, MODCON<15:0>, contains enable flags as well register field to specify the W Address registers. ...
Page 38
... Bit-Reversed Pointer. Sequential Address Bit Locations Swapped Left-to-Right Around Center of Binary Value Bit-Reversed Address Pivot Point XB = 0x0008 for a 16-Word Bit-Reversed Buffer N bytes, should not be enabled © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 39
... Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Bit-Reversed Address Decimal ...
Page 40
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 38 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 41
... The INTCON2 register controls the external interrupt request signal behavior and the use of the AIVT. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Note: Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt condition occurs, regardless of the state of ...
Page 42
... Reserved 35 43 Reserved 36 44 Reserved 37 45 Reserved 38 46 Reserved 39 47 PWM – PWM Period Match 40 48 QEI – QEI Interrupt 41 49 Reserved 42 50 Reserved 43 51 FLTA – PWM Fault Reserved 45-53 53-61 Reserved Lowest Natural Order Priority © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 43
... A momentary dip in the power supply to the device has been detected which may result in malfunction. • Trap Lockout: Occurrence of multiple trap conditions simultaneously will cause a Reset. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 5.3 Traps Traps can be considered as non-maskable interrupts, indicating a software or hardware error which adhere to a predefined priority, as shown in Figure 5-1 ...
Page 44
... Address Error Trap Vector Math Error Trap Vector Reserved Vector AIVT Reserved Vector Reserved Vector Interrupt 0 Vector Interrupt 1 Vector — — — Interrupt 52 Vector Interrupt 53 Vector © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. 0x000000 0x000002 0x000004 0x000014 0x00007E 0x000080 0x000082 0x000084 0x000094 0x0000FE ...
Page 45
... The RETFIE (return from interrupt) instruction will unstack the program counter and STATUS registers to return the processor to its state prior to the interrupt sequence. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 5.5 Alternate Interrupt Vector Table In program memory, the Interrupt Vector Table (IVT) is followed by the Alternate Interrupt Vector Table (AIVT), as shown in Figure 5-1 ...
Page 46
TABLE 5-2: INTERRUPT CONTROLLER REGISTER MAP SFR ADR Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Name INTCON1 0080 NSTDIS — — — — INTCON2 0082 ALTIVT DISI — — — IFS0 0084 CNIF MI2CIF SI2CIF NVMIF ADIF ...
Page 47
... Using NVMADR Addressing Using Table Instruction User/Configuration Space Select © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 6.2 Run-Time Self-Programming (RTSP) RTSP is accomplished using TBLRD (table read) and TBLWT (table write) instructions. With RTSP, the user may erase program memory, 32 instructions (96 bytes time, and can write program memory data, 32 instructions (96 bytes time ...
Page 48
... NVMKEY register. Refer to Section 6.6 “Programming Operations” for further details. Note: The user can also directly write to the NVMADR and NVMADRU registers to specify a program memory address for erasing or programming. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 49
... MOV #0xAA,W1 MOV W1 NVMKEY , BSET NVMCON,#WR NOP NOP © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 4. Write 32 instruction words of data from data RAM “image” into the program Flash write latches. 5. Program 32 instruction words into program Flash. a) Setup NVMCON register for multi-word, program Flash, program and set WREN bit. ...
Page 50
... Write PM low word into program latch ; Write PM high byte into program latch ; Block all interrupts with priority <7 ; for next 5 instructions ; Write the 0x55 key ; ; Write the 0xAA key ; Start the erase sequence ; Insert two NOPs after the erase ; command is asserted © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 51
TABLE 6-1: NVM REGISTER MAP File Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 NVMCON 0760 WR WREN WRERR NVMADR 0762 NVMADRU 0764 — — — NVMKEY 0766 — — — Legend: ...
Page 52
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 50 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 53
... EEPROM write/erase operation. Attempting to read the data EEPROM while a programming or erase operation is in progress results in unspecified data. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Control bit, WR, initiates write operations, similar to program Flash writes. This bit cannot be cleared, only set, in software ...
Page 54
... Block all interrupts with priority <7 ; for next 5 instructions ; ; Write the 0x55 key ; ; Write the 0xAA key ; Initiate erase sequence ; Block all interrupts with priority <7 ; for next 5 instructions ; ; Write the 0x55 key ; ; Write the 0xAA key ; Initiate erase sequence © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 55
... NOP ; Write cycle will complete in 2mS. CPU is not stalled for the Data Write Cycle ; User can poll WR bit, use NVMIF or Timer IRQ to determine write complete © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The write will not initiate if the above sequence is not exactly followed (write 0x55 to NVMKEY, write 0xAA to NVMCON, then set WR bit) for each word ...
Page 56
... The NVMADR captures last table access address. ; Select data EEPROM for multi word op ; Operate Key to allow program operation ; Block all interrupts with priority <7 ; for next 5 instructions ; Write the 0x55 key ; Write the 0xAA key ; Start write cycle © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 57
... This should be used in applications where excessive writes can stress bits near the specification limit. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 7.5 Protection Against Spurious Write There are conditions when the device may not want to write to the data EEPROM memory ...
Page 58
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 56 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 59
... WR TRIS WR LAT + WR PORT Read LAT Read PORT © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Any bit and its associated data and control registers that are not valid for a particular device will be disabled. That means the corresponding LATx and TRISx registers and the port pin will read as zeros. ...
Page 60
... Typically this instruction would be a NOP will be OL EXAMPLE 8-1: MOV 0xFF00 Configure PORTB<15:8> MOV W0, TRISBB ; and PORTB<7:0> as outputs NOP BTSS PORTB, #13 ; Next Instruction I/O Cell I/O Pad Input Data PORT WRITE/READ EXAMPLE ; as inputs ; Delay 1 cycle © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 61
TABLE 8-1: dsPIC30F4011 PORT REGISTER MAP SFR Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Name TRISB 02C6 — — — — PORTB 02C8 — — — — LATB 02CA — — — — TRISC 02CC TRISC15 TRISC14 TRISC13 ...
Page 62
... TABLE 8-2: dsPIC30F4012 PORT REGISTER MAP SFR Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Name TRISB 02C6 — — — — PORTB 02C8 — — — — LATB 02CB — — — — TRISC 02CC TRISC15 TRISC14 TRISC13 — PORTC 02CE RC15 RC14 RC13 — ...
Page 63
... CN7PUE CN6PUE CN5PUE CNPU2 00C6 — — Legend uninitialized bit * Not available on dsPIC30F4012 Note: Refer to the “dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual” (DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 CN4IE CN3IE CN2IE — ...
Page 64
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 62 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 65
... Timer operation during CPU Idle and Sleep modes • Interrupt on 16-bit Period register match or falling edge of external gate signal © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 These operating modes are determined by setting the appropriate bit(s) in the 16-bit SFR, T1CON. Figure 9-1 presents a block diagram of the 16-bit timer module. ...
Page 66
... Period register and be reset to 0x0000. When a match between the timer and the Period regis- ter occurs, an interrupt can be generated if the respective timer interrupt enable bit is asserted. TSYNC 1 Sync 0 TCKPS<1:0> TON 2 Prescaler 1, 8, 64, 256 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 67
... XTAL SOSCO pF 100K © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 9.5.1 RTC OSCILLATOR OPERATION When TON = 1, TCS = 1 and TGATE = 0, the timer increments on the rising edge of the 32 kHz LP oscilla- tor output signal the value specified in the Period register, and is then reset to ‘ ...
Page 68
TABLE 9-1: TIMER1 REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 TMR1 0100 PR1 0102 T1CON 0104 TON — TSIDL — Legend uninitialized bit Note: Refer to the “dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual” (DS70046) ...
Page 69
... Interrupt on a 32-bit Period Register Match These operating modes are determined by setting the appropriate bit(s) in the 16-bit T2CON and T3CON SFRs. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 For 32-bit timer/counter operation, Timer2 is the least significant word and Timer3 is the most significant word of the 32-bit timer ...
Page 70
... Timer configuration bit, T32 (T2CON<3>), must be set to ‘1’ for a 32-bit timer/counter operation. All control bits are respective to the T2CON register. DS70135E-page 68 16 TMR2 Sync LSB PR2 Q D TGATE(T2CON<6> TON 1 x Gate 0 1 Sync TCKPS<1:0> 2 Prescaler 1, 8, 64, 256 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 71
... T3IF Event Flag 1 TGATE Note: The dsPIC30F4011/4012 devices do not have external pin inputs to Timer3. In these devices, the following modes should not be used: 1. TCS = 1. 2. TCS = 0 and TGATE = 1 (gated time accumulation). © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 PR2 TMR2 Q D TGATE Q CK ...
Page 72
... In this mode, the T3IF interrupt flag is used as the source of the interrupt. The T3IF bit must be cleared in software. Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the respective Timer Interrupt Enable bit, T3IE (IEC0<7>). © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 73
TABLE 10-1: TIMER2/3 REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 TMR2 0106 TMR3HLD 0108 TMR3 010A PR2 010C PR3 010E T2CON 0110 TON — TSIDL — T3CON 0112 TON — TSIDL — ...
Page 74
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 72 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 75
... T4CK Note: Timer configuration bit, T32 (T2CON<3>), must be set to ‘ control bits are respective to the T4CON register. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The Timer4/5 module is similar in operation to the Timer 2/3 module. However, there are some differences, which are as follows: • The Timer4/5 module does not support the ADC event trigger feature • ...
Page 76
... FIGURE 11-2: 16-BIT TIMER4 BLOCK DIAGRAM Equal Comparator x 16 Reset 0 T4IF Event Flag 1 TGATE T4CK DS70135E-page 74 PR4 TMR4 Q D TGATE Q CK TON 1 x Gate Sync Sync TCKPS<1:0> 2 Prescaler 1, 8, 64, 256 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 77
... Event Flag 1 TGATE Note: The dsPIC30F4011/4012 devices do not have an external pin input to Timer5. In these devices, the following modes should not be used: 1. TCS = 1. 2. TCS = 0 and TGATE = 1 (gated time accumulation). © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 PR5 Comparator x 16 TMR5 Q D TGATE ...
Page 78
TABLE 11-1: TIMER4/5 REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 TMR4 0114 TMR5HLD 0116 TMR5 0118 PR4 011A PR5 011C T4CON 011E TON — TSIDL — T5CON 0120 TON — TSIDL — Legend: u ...
Page 79
... ICxCON Data Bus Note: Where ‘x’ is shown, reference is made to the registers or bits associated to the respective input capture channels 1 through N. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The key operational features of the input capture module are: • Simple Capture Event mode • Timer2 and Timer3 mode selection • ...
Page 80
... The capture module must be configured for interrupt only on the rising edge (ICM<2:0> = 111) in order for the input capture module to be used while the device is in Sleep mode. The prescale settings of 4:1 or 16:1 are not applicable in this mode. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 81
... ICM<2:0> = 111 in CPU Idle mode, the input capture pin will serve only as an external interrupt pin. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 12.3 Input Capture Interrupts The input capture channels have the ability to generate an interrupt, based upon the selected number of capture events. The selection number is set by control bits, ICI< ...
Page 82
TABLE 12-1: INPUT CAPTURE REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 IC1BUF 0140 IC1CON 0142 — — ICSIDL — IC2BUF 0144 IC2CON 0146 — — ICSIDL — IC7BUF 0158 IC7CON 015A — — ICSIDL ...
Page 83
... TMR3<15:0> TMR2<15:0 Note: Where ‘x’ is shown, reference is made to the registers associated with the respective output compare channels 1 through N. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The key operational features of the output compare module include: • Timer2 and Timer3 Selection mode • Simple Output Compare Match mode • ...
Page 84
... Fault condition has occurred. This state will be maintained until both of the following events have occurred: • The external Fault condition has been removed. • The PWM mode has been re-enabled by writing to the appropriate control bits © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 85
... Timer3) is enabled and the TSIDL bit of the selected timer is set to logic ‘0’. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 When the selected TMRx is equal to its respective Period register, PRx, the following four events occur on the next increment cycle: • ...
Page 86
... OC4CON* 0196 — — OCSIDL — Legend uninitialized bit * Not available on dsPIC30F4012. Note: Refer to the “dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual” (DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields. Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Output Compare 1 Secondary Register Output Compare 1 Main Register — ...
Page 87
... INDX Digital Filter 3 Up/Down Note: In dsPIC30F4011/4012, the UPDN pin is not available. Up/Down logic bit can still be polled by software. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The operational features of the QEI include: • Three input channels for two phase signals and index pulse • ...
Page 88
... UPDN signal is supplied to an SFR bit, UPDN (QEICON<11>), as a read-only bit. Note: QEI pins are multiplexed with analog inputs. The user must insure that all QEI associated pins are set as digital inputs in the ADPCFG register. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 89
... CY To enable the filter output for channels QEA, QEB and INDX, the QEOUT bit must be ‘1’. The filter network for all channels is disabled on POR and BOR. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 14.5 Alternate 16-bit Timer/Counter When the QEI module is not configured for the QEI mode, QEIM< ...
Page 90
... The QEI Interrupt Flag bit, QEIIF, is asserted upon occurrence of any of the above events. The QEIIF bit must be cleared in software. QEIIF is located in the IFS2 register. Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the respec- tive Enable bit, QEIIE. The QEIIE bit is located in the IEC2 register. QEISIDL bit © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 91
TABLE 14-1: QEI REGISTER MAP SFR Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Name QEICON 0122 CNTERR — QEISIDL INDX UPDN DFLTCON 0124 — — — — POSCNT 0126 MAXCNT 0128 ADPCFG 02A8 — — — ...
Page 92
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 90 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 93
... Three-Phase AC Induction Motor • Switched Reluctance (SR) Motor • Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor • Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The PWM module has the following features: • 6 PWM I/O pins with 3 duty cycle generators • 16-bit resolution • ...
Page 94
... Generator and Override Logic PWM Generator Channel 2 Dead-Time #2 Generator and Override Logic PWM Generator Channel 1 Dead-Time #1 Generator and Override Logic Special Event Postscaler PTDIR PWM3H PWM3L PWM2H Output PWM2L Driver Block PWM1H PWM1L FLTA Special Event Trigger © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 95
... Electronically Commutative Motors (ECMs). The interrupt signals generated by the PWM time base depend on the mode selection bits (PTMOD<1:0>) and the postscaler bits (PTOPS<3:0>) in the PTCON SFR. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 15.1.1 FREE-RUNNING MODE In the Free-Running mode, the PWM time base counts upwards until the value in the Time Base Period regis- ter (PTPER) is matched ...
Page 96
... PWM PERIOD (CENTER-ALIGNED MODE) • PTPER + 0. PWM (PTMR Prescale Value) The maximum resolution (in bits) for a given device oscillator and PWM frequency can be determined using Equation 15-3: EQUATION 15-3: PWM RESOLUTION • log ( PWM Resolution = log (2) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. using ) CY ...
Page 97
... New Duty Cycle Latched PTPER PTMR Value 0 Duty Cycle Period © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 15.4 Center-Aligned PWM Center-aligned PWM signals are produced by the module when the PWM time base is configured in a Continuous Up/Down Count mode (see Figure 15-3). The PWM compare output is driven to the active state ...
Page 98
... The two dead times can be assigned to individual PWM I/O pin pairs. This operating mode allows the PWM module to drive different transistor/load combinations with each complementary PWM I/O pin pair. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 99
... The dead-time clock prescaler values are selected using the FIGURE 15-4: DEAD-TIME TIMING DIAGRAM Duty Cycle Generator PWMxH PWMxL Dead-Time A (Active) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 DTAPS<1:0> control bits in the DTCON1 SFR. One of four clock prescaler options ( may be selected. ...
Page 100
... OVDCON register are synchronized to the PWM time base. Synchronous output overrides occur at the following times: • Edge-Aligned mode when PTMR is zero. • Center-Aligned modes when PTMR is zero and when the value of PTMR matches PTPER. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. six bits, ...
Page 101
... FLTACON register are cleared, then the Fault pin could be used as a general purpose interrupt pin. The Fault pin has an interrupt vector, interrupt flag bit and interrupt priority bits associated with it. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 15.12.2 FAULT STATES The FLTACON Special Function Register has 6 bits that determine the state of each PWM I/O pin when it is overridden by a Fault input ...
Page 102
... The PTCON SFR contains a PTSIDL control bit. This bit determines if the PWM module will continue to operate or stop when the device enters Idle mode. If PTSIDL = 0, the module will continue to operate. If PTSIDL = 1, the module will stop operation as long as the CPU remains in Idle mode. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 103
TABLE 15-1: 6-OUTPUT PWM REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 PTCON 01C0 PTEN — PTSIDL — PTMR 01C2 PTDIR PTPER 01C4 — SEVTCMP 01C6 SEVTDIR PWMCON1 01C8 — — — — PWMCON2 01CA ...
Page 104
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 102 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 105
... Note: Both the transmit buffer (SPI1TXB) and the receive buffer (SPI1RXB) are mapped to the same register address, SPI1BUF. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 In Master mode, the clock is generated by prescaling the system clock. Data is transmitted as soon as a value is written to SPI1BUF. The interrupt is generated at the middle of the transfer of the last bit ...
Page 106
... Clock Edge Control Select Secondary Prescaler Enable Master Clock SDO1 SDI1 Serial Input Buffer SDO1 SDI1 MSb Serial Clock SCK1 SCK1 Primary F CY Prescaler 1, 4, 16, 64 SPI Slave (SPI1BUF) Shift Register (SPI1SR) LSb PROCESSOR 2 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 107
... Therefore, when the SS1 pin is asserted low again, transmission/reception will begin at the MSb, even if SS1 had been deasserted in the middle of a transmit/receive. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 16.4 SPI Operation During CPU Sleep Mode During Sleep mode, the SPI module is shut down ...
Page 108
TABLE 16-1: SPI1 REGISTER MAP SFR Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Name SPI1STAT 0220 SPIEN — SPISIDL — SPI1CON 0222 — FRMEN SPIFSD — DISSDO MODE16 SPI1BUF 0224 Legend uninitialized bit Note: ...
Page 109
... Thus, the I C module can operate either as a slave master bus. FIGURE 17-1: PROGRAMMER’S MODEL bit 15 bit 15 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 17.1.1 VARIOUS I The following types • slave operation with 7-bit addressing. 2 • slave operation with 10-bit addressing. ...
Page 110
... DS70135E-page 108 I2CRCV I2CRSR LSB Addr_Match I2CADD Start and Collision Detect Generation Clock Stretching I2CTRN LSB Reload Control I2CBRG BRG Down Counter F CY Internal Data Bus Read Write Read Write Read Write Read Write Read Write Read © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 111
... SCL high (see timing diagram). The inter- rupt pulse is sent on the falling edge of the ninth clock pulse, regardless of the status of the ACK received from the master. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 17.3.2 SLAVE RECEPTION If the R_W bit received is a ‘0’ during an address match, then Receive mode is initiated ...
Page 112
... C bus have deasserted SCL. This ensures that a write to the SCLREL bit will not violate the minimum high time requirement for SCL. If the STREN bit is ‘0’, a software write to the SCLREL bit will be disregarded and have no effect on the SCLREL bit. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 113
... When the interrupt is serviced, the source for the interrupt can be checked by reading the contents of the I2CRCV to determine if the address was device-specific or a general call address. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 2 17. Master Support As a master device, six operations are supported. ...
Page 114
... For the I C, the I2CSIDL bit selects if the module will stop on Idle or continue on Idle. If I2CSIDL = 0, the module will continue operation on assertion of the Idle mode. If I2CSIDL = 1, the module will stop on Idle. C master event Interrupt Service Routine 2 C bus is 2 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. C ...
Page 115
TABLE 17-2: I C™ REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 I2CRCV 0200 — — — — I2CTRN 0202 — — — — I2CBRG 0204 — — — — I2CCON 0206 I2CEN I2CSIDL ...
Page 116
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 114 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 117
... FIGURE 18-1: UART TRANSMITTER BLOCK DIAGRAM Internal Data Bus UTXBRK Data UxTX Parity Note dsPIC30F4012 only has UART1. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 18.1 UART Module Overview The key features of the UART module are: • Full-Duplex 9-bit Data Communication • ...
Page 118
... Receive Buffer Control – Generate Flags – Generate Interrupt – Shift Data Characters 8-9 Load RSR to Buffer Receive Shift Register (UxRSR) ÷ 16 Divider 16x Baud Clock from Baud Rate Generator Read Read Write UxSTA Control Signals UxRXIF © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 119
... The STSEL bit determines whether one or two Stop bits will be used during data transmission. The default (power-on) setting of the UART is 8 bits, no parity and 1 Stop bit (typically represented 1). © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 18.3 Transmitting Data 18.3.1 ...
Page 120
... UxRSR needs to transfer the character to the buffer. Once OERR is set, no further data is shifted in UxRSR (until the OERR bit is cleared in software or a Reset occurs). The data held in UxRSR and UxRXREG remains valid. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. RXB) ...
Page 121
... FERR bit set. The Break character is loaded into the buffer. No further reception can occur until a Stop bit is received. Note that RIDLE goes high when the Stop bit has not been received yet. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 18.6 Address Detect Mode Setting the ADDEN bit (UxSTA< ...
Page 122
... For the UART, the USIDL bit selects if the module will stop operation when the device enters Idle mode, or whether the module will continue on Idle. If USIDL = 0, the module will continue operation during Idle mode. If USIDL = 1, the module will stop on Idle. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 123
... U1BRG 0214 Legend uninitialized bit Note: Refer to the “dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual” (DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields. TABLE 18-2: UART2 REGISTER MAP (NOT AVAILABLE ON dsPIC30F4012) SFR Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Name U2MODE 0216 UARTEN — ...
Page 124
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 122 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 125
... Programmable link to input capture module (IC2, for both CAN1 and CAN2) for time-stamping and network synchronization • Low-power Sleep and Idle mode © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The CAN bus module consists of a protocol engine and message buffering/control. The CAN protocol engine handles all functions for receiving and transmitting messages on the CAN bus ...
Page 126
... RXF3 c Acceptance Filter e (1) RXF4 p t Acceptance Filter (1) RXF5 M Identifier (1) RXB1 A B Data Field Receive RERRCNT Error Counter TERRCNT Transmit ErrPas BusOff Error Counter Protocol Finite State Machine Bit Timing Bit Timing Logic Generator C1RX © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 127
... Disable mode. The I/O pins will revert to normal I/O function when the module is in the Disable mode. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The module can be programmed to apply a low-pass filter function to the C1RX input line while the module or the CPU is in Sleep mode. The WAKFIL bit (C1CFG2< ...
Page 128
... End-of-Frame (EOF) field. Reading the RXxIF flag will indicate which receive buffer caused the interrupt. 19.4.6.2 Wake-up Interrupt The CAN module has woken up from Disable mode or the device has woken up from Sleep mode. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 129
... TXABT (C1TXxCON<6>), TXLARB (C1TXxCON<5>) and TXERR (C1TXxCON<4>) flag automatically cleared. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Setting TXREQ bit simply flags a message buffer as enqueued for transmission. When the module detects an available bus, it begins transmitting the message which has been determined to have the highest priority. ...
Page 130
... By definition, the nominal bit time has a minimum and a maximum the minimum nominal bit time is 1 μsec, corresponding to a maximum bit rate of 1 MHz. Phase Phase Segment 1 Segment 2 Sample Point . Also, by definition, Q Sync © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 131
... SEG1PH<2:0> (C1CFG2<5:3>), and Phase2 Seg is initialized by setting SEG2PH<2:0> (C1CFG2<10:8>). The following requirement must be fulfilled while setting the lengths of the phase segments: Propagation Segment + Phase1 Seg > = Phase2 Seg © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 19.6.5 SAMPLE POINT The sample point is the point of time at which the bus ...
Page 132
TABLE 19-1: CAN1 REGISTER MAP SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 C1RXF0SID 0300 — — — C1RXF0EIDH 0302 — — — — C1RXF0EIDL 0304 Receive Acceptance Filter 0 Extended Identifier<5:0> C1RXF1SID 0308 — — — ...
Page 133
TABLE 19-1: CAN1 REGISTER MAP (CONTINUED) SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 C1TX1B1 0356 Transmit Buffer 1 Byte 1 C1TX1B2 0358 Transmit Buffer 1 Byte 3 C1TX1B3 035A Transmit Buffer 1 Byte 5 C1TX1B4 035C ...
Page 134
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 132 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 135
... The ADC module has a unique REF REF feature of being able to operate while the device is in Sleep mode. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The ADC module has six, 16-bit registers: • A/D Control Register 1 (ADCON1) • A/D Control Register 2 (ADCON2) • A/D Control Register 3 (ADCON3) • ...
Page 136
... AN1 AN4 AN7 AN2 AN2 AN5 AN8 AN0 AN1 AN2 AN3 AN3 AN4 AN4 AN5 AN5 AN6 *AN6 AN7 *AN7 AN8 *AN8 AN1 * Not available on dsPIC30F4012. DS70135E-page 134 CH1 ADC S/H - 10-bit Result + CH2 S/H - 16-word, 10-bit + CH3 S/H - CH1,CH2, CH3,CH0 Sample/Sequence ...
Page 137
... The channels are then converted sequentially. Obviously, if there is only 1 channel selected, the SIMSAM bit is not applicable. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 The CHPS<1:0> bits select how many channels are sampled. This selection can vary from channels. ...
Page 138
... ADCS<5:0> – time AD = 5V). Refer to Section 24.0 DD under AD A/D CONVERSION CLOCK CALCULATION T = 154 nsec nsec (30 MIPS – 154 nsec = 2 • – nsec = 8. (ADCS<5:0> nsec = ( 165 nsec © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 139
... Up to 256. 300 ksps Note 1: External V - and V + pins must be used for correct operation. See Figure 20-2 for recommended circuit. REF REF © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 R Max. V Temperature S DD 500Ω 4.5V to 5.5V -40°C to +85°C 500Ω ...
Page 140
... Sequential sampling must be used in this configuration to allow adequate sampling time on each input μF 0.1 μF 0.01 μ μF 0.1 μF 0.01 μF Multiple Analog Inputs © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 141
... ADCS<5:0> control bits in the ADCON3 register • Configure the sampling time writing: SAMC<4:0> = 00010 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 20.7.3 600 ksps CONFIGURATION GUIDELINE The configuration for 600 ksps operation is dependent on whether a single input pin sampled or whether multiple pins are to be sampled ...
Page 142
... Characteristics” for T requirements. ) impedance ≤ 250Ω Sampling Switch LEAKAGE V = 0.6V T ±500 nA period of sampling AD and sample time AD ≤ 3 kΩ HOLD = DAC Capacitance = 4 negligible if Rs ≤ 5 kΩ. PIN © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 143
... Signed Integer d09 d09 d09 d09 d09 d09 d09 d08 d07 d06 d05 d04 d03 d02 d01 d00 Integer 0 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 If the A/D interrupt is enabled, the device wakes up from Sleep. If the A/D interrupt is not enabled, the ADC module is then turned off, although the ADON bit remains set ...
Page 144
... The R component should be selected to ensure that the sampling time requirements are satisfied. Any external components connected (via high-impedance analog input pin (capacitor, zener diode, etc.) should have very little leakage current at the pin. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. as ESD SS ...
Page 145
... ADCSSL 02AA — — — — Legend uninitialized bit * Not available on dsPIC30F4012. Note: Refer to the “dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual” (DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields. Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 — — ADC Data Buffer 0 — ...
Page 146
... NOTES: DS70135E-page 144 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 147
... In the Idle mode, the clock sources are still active, but the CPU is shut off. The RC oscillator option saves system cost, while the LP crystal option saves power. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 21.1 Oscillator System Overview The dsPIC30F oscillator system has the following modules and features: • ...
Page 148
... The dsPIC30F maximum operating frequency of 120 MHz must be met oscillator can be conveniently shared as a system clock, as well as a Real-Time Clock for Timer1. 3: Requires external R and C. Frequency operation MHz. DS70135E-page 146 Description (1) (2) (1) (1) (1) (3) /4 output OSC (3) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 149
... FIGURE 21-1: OSCILLATOR SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM OSC1 Primary Oscillator OSC2 POR Done SOSCO 32 kHz LP Oscillator SOSCI Internal Fast RC Oscillator (FRC) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 F PLL PLL x4, x8, x16 PLL Lock Primary Osc Primary Oscillator Stability Detector Oscillator Start-up Clock Timer ...
Page 150
... CLKO CLKO OSC2 0 0 OSC2 0 1 OSC2 1 0 OSC2 1 1 OSC2 0 0 OSC2 — — (Notes 1, 2) — — (Notes 1, 2) — — (Notes 1, 2) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 151
... FRC oscillator frequency to be adjusted as close to 7.37 MHz as possible, depending on the device operating conditions. The FRC oscillator frequency has been calibrated during factory testing. Table 21-4 describes the adjustment range of the TUN<3:0> bits. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 TABLE 21-4: TUN<3:0> Bits 0111 ...
Page 152
... Byte Write “0x78” to OSCCON high • Byte Write “0x9A” to OSCCON high Byte Write is allowed for one instruction cycle. Write the desired value or use bit manipulation instruction. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 153
... The POR pulse resets a POR timer and places the device in the Reset state. The POR also selects the device clock source identified by the oscillator Configuration fuses. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Different registers are affected in different ways by various Reset conditions. Most registers are not affected by a WDT wake-up, since this is viewed as the resumption of normal operation ...
Page 154
... OST TIME-OUT PWRT TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET FIGURE 21-5: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR NOT TIED MCLR INTERNAL POR OST TIME-OUT PWRT TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET DS70135E-page 152 T OST T PWRT T OST T PWRT T OST T PWRT ) DD ): CASE CASE 2 DD © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 155
... Note: The BOR voltage trip points indicated here are nominal values provided for design guidance only. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 A BOR generates a Reset pulse, which resets the device. The BOR selects the clock source, based on the device Configuration bit values (FOS<1:0> and FPR< ...
Page 156
... Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 157
... PWRSAV. These are: Sleep and Idle. The format of the PWRSAV instruction is as follows: PWRSAV <parameter>, where ‘parameter’ defines Idle or Sleep mode. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 21.5.1 SLEEP MODE In Sleep mode, the clock to the CPU and peripherals is shut down ...
Page 158
... For additional information, please refer specifications of the device. Note: If the code protection Configuration fuse bits (FGS<GCP> and FGS<GWRP>) have been programmed, an erase of the entire code-protected device is only possible at voltages V to the programming ≥ 4.5V. DD © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 159
... MPLAB IDE. These pin pairs are named EMUD/EMUC, EMUD1/ EMUC1, EMUD2/EMUC2 and EMUD3/EMUC3. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 In each case, the selected EMUD pin is the emulation/ debug data line and the EMUC pin is the emulation/ debug clock line ...
Page 160
TABLE 21-7: SYSTEM INTEGRATION REGISTER MAP SFR Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Name RCON 0740 TRAPR IOPUWR BGST — OSCCON 0742 TUN3 TUN2 COSC<1:0> TUN1 Note: Refer to the “dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual” (DS70046) ...
Page 161
... The file register specified by the value ‘f’ • The destination, which could either be the file register ‘f’ or the W0 register, which is denoted as ‘WREG’ © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Most bit-oriented instructions (including simple rotate/ shift instructions) have two operands: • ...
Page 162
... Moreover, double-word moves require two cycles. The double-word instructions execute in two instruction cycles. Note: For more details on the instruction set, refer to the “dsPIC30F/33F Programmer’s Reference Manual” (DS70157). Description © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 163
... Y Data Space Prefetch Address register for DSP instructions Wy ∈ {[W10]+=6, [W10]+=4, [W10]+=2, [W10], [W10]-=6, [W10]-=4, [W10]-=2, [W11]+=6, [W11]+=4, [W11]+=2, [W11], [W11]-=6, [W11]-=4, [W11]-=2, [W11+W12], none} Y Data Space Prefetch Destination register for DSP instructions ∈ {W4..W7} Wyd © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Description DS70135E-page 161 ...
Page 164
... Branch Unconditionally Branch if Zero Computed Branch Bit Set f Bit Set Ws Write C bit to Ws<Wb> Write Z bit to Ws<Wb> Bit Toggle f Bit Toggle Ws Bit Test f, Skip if Clear Bit Test Ws, Skip if Clear © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc Status Flags cycles Affected 1 1 OA, OB, SA DC, N, OV, Z ...
Page 165
... DIVF Wm, #lit14,Expr DO Wn,Expr Wm*Wm,Acc,Wx,Wy,Wxd © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Description words Bit Test f, Skip if Set Bit Test Ws, Skip if Set Bit Test f Bit Test Bit Test Bit Test Ws<Wb> Bit Test Ws<Wb> Bit Test then Set f ...
Page 166
... Multiply and Subtract from Accumulator {Wnd+1, Wnd} = signed(Wb) * signed(Ws) {Wnd+1, Wnd} = signed(Wb) * unsigned(Ws) {Wnd+1, Wnd} = unsigned(Wb) * signed(Ws) {Wnd+1, Wnd} = unsigned(Wb) * unsigned(Ws) {Wnd+1, Wnd} = signed(Wb) * unsigned(lit5) {Wnd+1, Wnd} = unsigned(Wb) * unsigned(lit5) W3: WREG © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc Status Flags cycles Affected 1 1 OA, OB, OAB, ...
Page 167
... f,WREG SL Ws,Wd SL Wb,Wns,Wnd SL Wb,#lit5,Wnd © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Description words Negate Accumulator WREG = Operation No Operation Pop f from Top-of-Stack (TOS) Pop from Top-of-Stack (TOS) to Wdo Pop from Top-of-Stack (TOS) to W(nd):W( ...
Page 168
... Read Prog<15:0> Write Ws<7:0> to Prog<23:16> Write Ws to Prog<15:0> Unlink Frame Pointer .XOR. WREG WREG = f .XOR. WREG Wd = lit10 .XOR .XOR .XOR. lit5 Wnd = Zero-Extend Ws © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc Status Flags cycles Affected 1 1 OA, OB, OAB, SA, SB, SAB ...
Page 169
... PICSTART Plus Development Programmer - MPLAB PM3 Device Programmer - PICkit™ 2 Development Programmer • Low-Cost Demonstration and Development Boards and Evaluation Kits © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 23.1 MPLAB Integrated Development Environment Software The MPLAB IDE software brings an ease of software development previously unseen in the 8/16-bit micro- controller market ...
Page 170
... MPLAB C30 C Compilers, and the MPASM and MPLAB ASM30 Assemblers. The software simulator offers the flexibility to develop and debug code outside of the hardware laboratory environment, making it an excellent, economical software development tool. ® DSCs on an instruction © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 171
... The PC platform and Microsoft Windows 32-bit operating system were chosen to best make these features available in a simple, unified application. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 23.9 MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger Microchip’s In-Circuit Debugger, MPLAB ICD ...
Page 172
... Check the Microchip web page (www.microchip.com) and the latest “Product Selector Guide” (DS00148) for the complete list of demonstration, development and evaluation kits. ® L security ICs, CAN ® battery management, SEEVAL © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 173
... Temp Range DD 4.5-5.5V -40°C to +85°C 4.5-5.5V -40°C to +125°C 3.0-3.6V -40°C to +85°C 3.0-3.6V -40°C to +125°C 2.5-3.0V -40°C to +85°C © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 (except V and MCLR) (Note 1) ..................................... -0. ....................................................................................................... 0V to +13.25V ) .......................................................................................................... ± > ...................................................................................................± the MCLR pin, inducing currents greater than 80 mA, may cause latch-up. ...
Page 174
... INT – T )/θ Typ Max Unit Notes 41 °C °C °C °C °C/W 1 ≤ +85°C for Industrial A ≤ +125°C for Extended A Conditions Industrial temperature Extended temperature 0- © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 175
... All I/O pins are configured as inputs and pulled to V MCLR = V , WDT, FSCM, LVD and BOR are disabled. CPU, SRAM, program memory and data memory DD are operational. No peripheral modules are operating. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 ) DD Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40° ...
Page 176
... Confidential 0.128 MIPS LPRC (512 kHz) (1.8 MIPS) FRC (7.37 MHz) 4 MIPS 10 MIPS 20 MIPS 30 MIPS © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 177
... Data in “Typ” column is at 5V, 25°C unless otherwise stated. Parameters are for design guidance only and are not tested. 2: These parameters are characterized but not tested in manufacturing. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40°C ≤ T ≤ ...
Page 178
... SMBus disabled V SMBus enabled μ 5V PIN SS μA ≤ V ≤ PIN DD Pin at high-impedance μA ≤ V ≤ PIN DD Pin at high-impedance μA ≤ V ≤ PIN DD μA ≤ V ≤ PIN DD XT, HS and LP Osc mode © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 179
... These parameters are characterized but not tested in manufacturing. FIGURE 24-1: BROWN-OUT RESET CHARACTERISTICS V DD BO10 (Device in Brown-out Reset) Reset (due to BOR) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40°C ≤ T Operating temperature -40°C ≤ T (1) Min Typ ...
Page 180
... Industrial ≤ +125°C for Extended Units Conditions — V Not in operating range — mV ≤ +85°C for Industrial A ≤ +125°C for Extended A Conditions ≤ +85° Minimum operating voltage MIN ≤ +85° Minimum operating voltage MIN © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 181
... LOAD CONDITIONS FOR DEVICE TIMING SPECIFICATIONS Load Condition 1 – for all pins except OSC2 Pin FIGURE 24-3: EXTERNAL CLOCK TIMING Q4 OSC1 CLKO © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40°C ≤ T Operating temperature -40°C ≤ T Operating voltage V range as described in Section 24.0 “ ...
Page 182
... MHz XT MHz XT with 4x PLL MHz XT with 8x PLL MHz XT with 16x PLL MHz HS kHz LP MHz FRC internal kHz LPRC internal — See parameter OS10 for F value OSC ns See Table 24- See parameter D031 ns See parameter D032 ). CY © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 183
... AC CHARACTERISTICS Operating temperature Param Characteristic No. OS61 x4 PLL x8 PLL x16 PLL Note 1: These parameters are characterized but not tested in manufacturing. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 = 2.5 TO 5.5V) DD Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40°C ≤ T Operating temperature A -40°C ≤ (1) (2) ...
Page 184
... Instruction Execution Frequency: MIPS = (F DS70135E-page 182 MIPS MIPS (2) (μsec) (3) w/o PLL w/PLL x4 20.0 0.05 — 1.0 1.0 4.0 0.4 2.5 10.0 0.16 6.25 — 1.0 1.0 4.0 0.4 2.5 10.0 = 1/MIPS PLLx)/4, since there are 4 Q clocks per instruction cycle. OSC Confidential MIPS MIPS (3) (3) (3) w/PLL x8 w/PLL x16 — — 8.0 16.0 20.0 — — — 8.0 16.0 20.0 — © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 185
... Overall FRC variation can be calculated by adding the absolute values of jitter, accuracy and drift percentages. TABLE 24-18: INTERNAL RC ACCURACY AC CHARACTERISTICS Param Characteristic No. (1) LPRC @ Freq. = 512 kHz OS65 Note 1: Change of LPRC frequency as V © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 -40°C ≤ -40°C ≤ Min Typ Max Units (1) -40°C ≤ T — ...
Page 186
... T ≤ +85°C for Industrial Operating temperature A -40°C ≤ T ≤ +125°C for Extended A (1,2,3) (4) Min Typ Max — — — — — — CY Confidential Units Conditions OSC © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 187
... TIMER TIMING CHARACTERISTICS SY12 V DD MCLR Internal POR SY11 PWRT Time-out SY30 Oscillator Time-out Internal Reset Watchdog Timer Reset I/O Pins SY35 FSCM Delay Note: Refer to Figure 24-2 for load conditions. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 SY10 SY20 SY13 Confidential SY13 DS70135E-page 185 ...
Page 188
... User-programmable μs -40°C to +85°C μ 5V, -40°C to +85° 3V, -40°C to +85°C DD μs ≤ (D034) DD BOR — OSC1 period OSC μs -40°C to +85°C V BGAP Band Gap Stable Conditions © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 189
... Input frequency Range (oscillator enabled by setting bit, TCS (T1CON<1>) TA20 T Delay from External T1CK CKEXTMRL Clock Edge to Timer Increment © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 Tx11 Tx10 Tx15 OS60 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40°C ≤ T ≤ +85°C for Industrial ...
Page 190
... N = prescale value (1, 8, 64, 256) 1.5 T — CY ≤ +85°C for Industrial A ≤ +125°C for Extended A Max Units Conditions — ns Must also meet parameter TC15 — ns Must also meet parameter TC15 — prescale value (1, 8, 64, 256) 1.5 T — CY © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 191
... TxCK Input Period Synchronous, TQ20 T Delay from External TxCK Clock CKEXTMRL Edge to Timer Increment Note 1: These parameters are characterized but not tested in manufacturing. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 TQ11 TQ10 TQ15 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40°C ≤ T Operating temperature -40° ...
Page 192
... Operating temperature A -40°C ≤ T ≤ +125°C for Extended A (1) Min No prescaler 0 With prescaler 10 No prescaler 0 With prescaler 40)/N CY Confidential Max Units Conditions — ns — ns — ns — ns — prescale value (1, 4, 16) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 193
... Note 1: These parameters are characterized but not tested in manufacturing. 2: Data in “Typ” column is at 5V, 25°C unless otherwise stated. Parameters are for design guidance only and are not tested. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 OC11 OC10 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40° ...
Page 194
... DS70135E-page 192 OC20 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) Operating temperature (1) (2) Min Typ Max Units — — — — ns Confidential -40°C ≤ T ≤ +85°C for Industrial A -40°C ≤ T ≤ +125°C for Extended A Conditions © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 195
... Note 1: These parameters are characterized but not tested in manufacturing. 2: Data in “Typ” column is at 5V, 25°C unless otherwise stated. Parameters are for design guidance only and are not tested. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 MP30 MP11 MP10 Standard Operating Conditions: 2.5V to 5.5V (unless otherwise stated) -40° ...
Page 196
... CY Confidential -40°C ≤ T ≤ +85°C for Industrial A -40°C ≤ T ≤ +125°C for Extended A Units Conditions 16, 32, 64, 128 and 256 (Note 16, 32, 64, 128 and 256 (Note 2) © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 197
... Alignment of index pulses to QEA and QEB is shown for position counter Reset timing only. Shown for forward direction only (QEA leads QEB). Same timing applies for reverse direction (QEA lags QEB) but index pulse recognition occurs on falling edge. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 TQ50 TQ55 Standard Operating Conditions: 2 ...
Page 198
... Industrial A -40°C ≤ T ≤ +125°C for Extended A Max Units Conditions — ns — ns — ns See parameter DO32 — ns See parameter DO31 — ns See parameter DO32 — ns See parameter DO31 30 ns — ns — ns © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 199
... Data in “Typ” column is at 5V, 25°C unless otherwise stated. Parameters are for design guidance only and are not tested. 3: The minimum clock period for SCK1 is 100 ns. Therefore, the clock generated in Master mode must not violate this specification. 4: Assumes 50 pF load on all SPI pins. © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. dsPIC30F4011/4012 SP10 SP21 SP35 SP20 LSb ...
Page 200
... SCK1 (CKP = 0) SP71 SCK1 (CKP = 1) SP35 SDO1 SDI SDI1 SP40 Note: Refer to Figure 24-2 for load conditions. DS70135E-page 198 SP70 SP73 SP72 SP73 SP72 MSb Bit SP30,SP31 MSb In Bit SP41 Confidential SP52 LSb SP51 LSb In © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. ...