at75c220 ATMEL Corporation, at75c220 Datasheet

at75c220
Available stocks
Related parts for at75c220
at75c220 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Available in a 208-lead PQFP Package Description The AT75C220, Atmel’s latest device in the family of smart internet appliance proces- sors (SIAP high-performance processor designed for professional internet appliance applications such as the Ethernet IP phone. The AT75C220 is built around an ARM7TDMI microcontroller core running at 40 MIPS with an OakDSPCore co-pro- cessor running at 60 MIPS and a dual Ethernet 10/100 Mbps MAC interface ...
Page 2
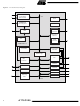
... AT75C220 Pin Configuration Figure 1. AT75C220 Pinout in 208-lead PQFP Package GND 1 SCLKA 2 VDDV3 3 FSA 4 STXA 5 SRXA 6 NTRST 7 MA_COL 8 MA_CRS 9 MA_TXER 10 MA_TXD0 11 MA_TXD1 12 MA_TXD2 13 MA_TXD3 14 MA_TXEN 15 XVDDV3 16 MA_TXCLK 17 GND 18 MA_RXD0 19 MA_RXD1 20 MA_RXD2 21 MA_RXD3 22 MA_RXER 23 MA_RXCLK 24 GND 25 VDD2V5 26 MA_RXDV 27 MA_MDC 28 MA_MDIO 29 MA_LINK 30 MB_COL 31 MB_CRS ...
Page 3
... Pin Description Table 1. AT75C220 Pin Description List Block Pin Name Common Bus A[21:0] D[15:0] NREQ NGNT Synchronous Dynamic DCLK Memory Controller DQM[1:0] CS0 CS1 RAS CAS WE Static Memory Controller NCE0, NCE3 NWE[1:0] NSOE NWR NWAIT I/O Port A PA[12:0] PA[19] I/O Port B PB[9:0] DSP Subsystem OAKAIN[1:0] OAKAOUT[1:0] Timer/Counter 0 TCLK0 ...
Page 4
... Table 1. AT75C220 Pin Description List (Continued) Block Pin Name Serial Peripheral Interface MISO MOSI SPCK NPCSS NPCS1 USART A RXDA TXDA NRTSA NCTSA NDTRA NDSRA/BOOTN NDCDA USART B RXDB TXDB JTAG Interface NTRST TCK TMS TDI TDO Codec Interface SCLKA FSA STXA SRXA ...
Page 5
... Table 1. AT75C220 Pin Description List (Continued) Block Pin Name MAC B Interface MB_COL MB_CRS MB_TXER MB_TXD[3:0] MB_TXEN MB_TXCLK MB_RXD[3:0] MB_RXER MB_RXCLK MB_RXDV MB_MDC MB_MDIO MB_LINK Miscellaneous RESET FIQ/LOWP IRQ0 XREF240 XTALIN XTALOUT TST B0256 DBW32 Function MAC B Collision Detect MAC B Carrier Sense ...
Page 6
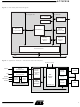
... Figure 2. AT75C220 Block Diagram Dual Ethernet 10/100 Mbps MAC Interface OakDSPCore DSP Subsystem JTAG Embedded ICE ARM7TDMI Core Boot ROM IRQ Controller PIO A PIO B Watchdog Timer AT75C220 6 ASB Reset Clocks SDRAM Controller External Bus Interface SRAM Controller Peripheral Data Controller AMBA Bridge ...
Page 7
... Keyboard Screen Dual-port Ethernet 10/100 Mbps MAC Interface Voice Processing DSP Subsystem ARM7TDMI Core Oak Data Bus Codec Interface 16K x 16 General- purpose RAM 256 x 16 Dual-port Mailbox SDRAM Controller VolP External Bus Protocol Interface Stack SRAM Controller AT75C220 SDRAM Flash 7 ...
Page 8
... Peripheral Data Controller The AT75C220 has a four-channel peripheral data control- ler (PDC) dedicated to the two on-chip USARTs. One PDC channel is connected to the receiving channel and one to the transmitting channel of each USART. ...
Page 9
... The memory map is divided into regions of 256 megabytes. The top memory region (0xF000_0000) is reserved and subdivided for internal memory blocks or peripherals within the AT75C220. The device can define up to six other active external memory regions by means of the static memory controller and SDRAM memory controller. See Table 2. ...
Page 10
... ARM7TDMI to perform the next instruction fetch from address zero. Except for the program counter, the ARM core registers do not have defined reset states. When reset is active, the inputs of the AT75C220 must be held at valid logic levels. There are three ways in which the AT75C220 can enter reset: 1 ...
Page 11
... PLL XREF 240F 100 Ω trol registers in the AT75C220 and its peripherals perform external memory accesses. This allows the Flash to be written. The boot ROM code: • sets CTS active • waits for approximately three seconds for the start of a Flash download sequence from the USART ...
Page 12
... Register Name 0x0 SIAP_MD 0x4 SIAP_ID 0x8 SIAP_RST 0xC SIAP_CLKF Note the PKG flag is set, the reset value is 0x00010220 since the AT75C220 is bonded in large bond-out mode. SIAP-E Mode Register Register Name: SIAP_MD Access: Read/write Reset Value: 0x00B0342 31 30 – – 23 ...
Page 13
SA: Slow ARM Mode On reset this field is low. In normal operating mode, if bit SA is set. The ARM clock is 34Mhz (i.e. the PLL value is divided by 7 not set the ARM ...
Page 14
... IDENT: Identifier This field indicates the device identifier 0x0220. • PKG: Package This bit reflects the state of the data bus width signal DBW and indicates the SIAP package size. AT75C220 14 20 MHz to 40 MHz 10 MHz to 20 MHz 5 MHz to 10 MHz 29 ...
Page 15
SIAP-E Reset Status Register Register Name: SIAP_RST Access: Read/write Reset Value: 0x00000001 31 30 – – – – – – – – • RST[2:0]: Reset These bits indicate the cause of the last reset. ...
Page 16
... This option is controlled by the DBW field in the Chip Select Register (SMC_CSR) of the corresponding chip select. The AT75C220 always boots up with a data bus width of 16 bits set in SMC_CSR0. Byte-write or Byte-select Mode Each chip select with a 32-/16-bit data bus operates with ...
Page 17
For a 32-bit bus: • The signal NWE0 is used as the write enable signal for byte 0. • The signal NWE1 is used as the write enable signal for byte 1. • The signal NWE2 is used as the ...
Page 18
... The Data Float Output Time (TDF) for each external mem TDF fie AT75C220 18 SMC_CSR register for the corresponding chip select. The value ( clock cycles) indicates the number of data float ...
Page 19
... Reserved individual external memories. Each SMC_CSR must be programmed with a different base address, even for unused chip selects. The AT75C220 resets such that SMC_CSR0 is configured as having a 16-bit data bus. Description Chip Select Register Chip Select Register Chip Select Register ...
Page 20
... Cycles after Transfer • BAT: Byte Access Mode 0 = Byte Write Mode 1 = Byte Select Mode AT75C220 20 Wait States × Base ...
Page 21
CSEN: Chip Select Enable Active high. • LCD: LCD Mode Enable Active high. SMC_CSR3 only. • BA: Base Address This field contains the high-order bits of the base address. If the page size is larger than 1M byte, then ...
Page 22
... SIAP pin to guarantee positive hold times. There is an early read wait state between memory 1 write and memory 1 read to provide time for the AT75C220 to disable the output data before the memory is read. If the read was normal mode, i.e., not early, the NSOE strobe would not fall until the rising edge of BCLK and no wait state would be inserted ...
Page 23
Figure 7 shows a write and a read to memory 0 followed by a read and a write to memory 1. SMC_CSR0 is pro- grammed for zero wait states with BAT = 0 and DFT = 0. SMC_CSR1 is programmed ...
Page 24
... SDMC: SDRAM Controller The AT75C220 integrates an SDRAM controller (SDMC). The ARM accesses external SDRAM by means of the SDRAM memory controller. The SDMC shares the same address and data pins as the static memory controller but has separate control signals. The SDMC interface is a memory-mapped APB slave. ...
Page 25
Figure 8. Read with Burst Length of 4 and CAS Latency of 2 BCLK BA BTRAN BWAIT SDRAM CMD NOP addr sdmc_data BD Figure 9. Read with Burst Length of 2 and CAS Latency of 2 BCLK BA BTRAN BWAIT ...
Page 26
... The following access is non-sequential. When any of these conditions occur, the write burst is bro- ken and SDMC goes inactive. Table 11. SDRAM Refresh Rates Clock Speed (MHz 0.025 0.0032 AT75C220 26 A0 NOP PRE NOP ACT BANK ROW SDRAM Refresh Table 11 shows the counter values needed for a refresh rate of 15.625 µ ...
Page 27
SDMC Register Map Base Address: 0xFF008000 Table 12. SDMC Register Map Offset Register Name 0x0000 SDRAM_MODE 0x0004 SDRAM_TIMER 0x0008 SDRAM_CFG 0x000C SDRAM_16BIT 0x0010 SDRAM_CS0_ADDR 0x0014 SDRAM_CS1_ADDR SDRAM_MODE Register Register Name: SDRAM_MODE Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – ...
Page 28
... Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – TRP 7 6 TWR CAS • NC Sets the number of column bits. Default is eight column bits AT75C220 – – – – – – – – CNT ...
Page 29
NR Sets the number of row bits. Default is 11 row bits • NB Sets the number of banks. Default is two banks • CAS Sets the CAS latency. The SDMC ...
Page 30
... Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x50 31 30 – – – – – – • CS1_ADDR This bit is used to set the eight most significant bits of the address of CS1. AT75C220 – – – – – – – – ...
Page 31
... Arbitration Using Multi-layer AMBA The AT75C220 has two separate ASB (multi-layer AMBA) buses that can be decoupled during most normal opera- tions. The ability to couple the two ASB buses is provided to allow the ARM to receive and transmit Ethernet frames via the two Ethernet MACs. ...
Page 32
... Figure 12. ASB-to-ASB Bridge Write Timing BCLK ARM Bus Signals BTRAN BA/BWRITE DSEL BWAIT BD MAC Bus Signals BREQ BGNT BTRAN BA/BWRITE DSEL BWAIT BD AT75C220 32 ...
Page 33
... Ethernet MAC The AT75C220 integrates two identical Ethernet MACs, known as MAC A and MAC B. The Ethernet MAC is described more fully in the IEEE stan- dard 802. programmable device on the APB bus by means of 56 configuration and status registers. The Ether- net MAC is an ASB master. ...
Page 34
... To receive frames, the buffer queue must be initialized by writing an appropriate address to bits [31:2] in the first word of each list entry. Bit zero must be written with zero. After a AT75C220 34 frame is received, bit zero becomes set and the second word indicates what caused the frame to be copied to memory ...
Page 35
Table 14. Received Buffer Descriptor List Bit Function Word 0 31:2 Address of beginning of buffer 1 Wrap bit. If this bit is set, the counter that is ORed with the received buffer queue pointer register to give the pointer ...
Page 36
... ETH_TUE 0x6C ETH_CDE 0x70 ETH_ELR AT75C220 36 whether the frame is multicast or unicast and the appropri- ate match signals will be sent to the DMA block If the copy all frames bit is set in the network configuration register, the store frame pulse will always be sent to the DMA block as soon as any destination address is received ...
Page 37
Table 15. Ethernet MAC Register Map (Continued) Offset Register Name 0x74 ETH_RJB 0x78 ETH_USF 0x7C ETH_SQEE 0x80 ETH_DRFC Address Registers 0x90 ETH_HSH 0x94 ETH_HSL 0x98 ETH_SA1L 0x9C ETH_SA1H 0xA0 ETH_SA2L 0xA4 ETH_SA2H 0xA8 ETH_SA3L 0xAC ETH_SA3H 0xB0 ETH_SA4L 0xB4 ETH_SA4H ...
Page 38
... Multicast hash enable, when set multicast frames will be received when six bits of the CRC of the destination address point to a bit that is set in the hash register. • UNI Unicast hash enable. When set, unicast frames will be received when six bits of the CRC of the destination address point to a bit that is set in the hash register. AT75C220 – ...
Page 39
BIG Receive 1522 bytes. When set, the MAC will receive up to 1522 bytes. Normally the MAC will receive frames up to 1518 bytes in length. • EAE External address match enable. Optional. • CLK The system clock (HCLK) ...
Page 40
... MAC will not append CRC to the transmitted frame. If the buffer is not at least 64 bytes long, a short frame will be sent. This field is buffered so that a new frame can be queued while the previous frame is still being transmitted. Reads as the value of the frame currently being transmitted. AT75C220 40 29 ...
Page 41
MAC Transmit Status Register Register Name: ETH_TSR Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x18 31 30 – – – – – – – UND • OVR Ethernet transmit buffer overrun. Software wrote to the address ...
Page 42
... OVR RX overrun. The DMA block was unable to store the receive frame to memory, either because the ASB bus was not granted in time or because a not OK HRESP was returned. The buffer will be recovered if this happens. Cleared by writing a one to this bit. AT75C220 ...
Page 43
MAC Interrupt Status Register Register Name: ETH_ISR Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – – – TCOM TBRE • DONE Management done. The PHY maintenance register has completed its ...
Page 44
... Enable transmit buffer register empty interrupt. • TCOM Enable transmit complete interrupt. • LINK Enable LINK interrupt. Optional. • TIDLE Enable transmit idle interrupt. • ROVR Enable RX overrun interrupt. • HRESP Enable HRESP not OK interrupt. AT75C220 – – – – – – – ...
Page 45
MAC Interrupt Disable Register Register Name: ETH_IDR Access Type: Write-only Reset Value: – – – – – – – TCOM TBRE • DONE Disable management done interrupt. • RCOM Disable receive complete ...
Page 46
... Transmit buffer register empty interrupt masked. • TCOM Transmit complete interrupt masked. • LINK LINK interrupt masked. • TIDLE Transmit idle interrupt masked. • ROVR Receive overrun interrupt masked. • HRESP HRESP not OK interrupt masked. AT75C220 – – – – – – – ...
Page 47
MAC PHY Maintenance Register Register Name: ETH_MAN Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 LOW HIGH 23 22 PHYA Writing to this register starts the shift register that controls the serial connection to the PHY. ...
Page 48
... ADDR Hash Address bits 63 to 32. MAC Hash Address Low Register Name: ETH_HSL Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 • ADDR Hash Address bits AT75C220 ADDR ADDR ADDR ADDR 29 28 ...
Page 49
MAC Specific Address ( and 4) High Register Name: ETH_SA1H,...ETH_SA4H Access Type: Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – • ADDR Unicast Addresses ( and 4), Bits ...
Page 50
... SQEE test errors. An 8-bit register counting the number of frames where COL was not asserted within a slot time of TXEN being deasserted. ETH_DRFC Discarded receive frames count. This 16-bit counter is incremented every time an address-recognized frame is received but cannot be copied to memory because the receive buffer is available. AT75C220 50 The statistics register block contains the registers found in Table 16. ...
Page 51
... AIC: Advanced Interrupt Controller The AT75C220 integrates the Atmel advanced interrupt controller (AIC). For details on this peripheral, refer to the datasheet, literature number 1246. The interrupt controller is connected to the fast interrupt request (NFIQ) and the standard interrupt request (NIRQ) inputs of the ARM7TDMI processor. The processor’s NFIQ line can only be asserted by the external fast interrupt request input (FIQ) ...
Page 52
... This permits the AIC to assert the NIRQ line again when a higher priority unmasked interrupt occurs. At the end of the interrupt service routine, the End of Inter- rupt Command Register (AIC_EOICR) must be written. This allows pending interrupts to be serviced. AT75C220 52 Interrupt Name Interrupt Description UARTB USART B Interrupt ...
Page 53
The previous step establishes a connection to the corresponding ISR. This begins by saving the link register (R14_IRQ) and the SPSR (SPSR_IRQ). Note that the link register must be decrermented by 4 when it is saved ...
Page 54
... Spurious Interrupt A spurious interrupt is a signal of very short duration on one of the interrupt input lines. A spurious interrupt also arises when an interrupt is triggered and masked in the same cycle. AT75C220 54 Spurious Interrupt Sequence A spurious interrupt is handled by the following sequence of actions. 1. When an interrupt is active, the AIC asserts the nIRQ (or nFIQ) line and the ARM7TDMI enters IRQ (or FIQ) mode ...
Page 55
AIC User Interface Base Address: 0xFF030000 Table 18. AIC Memory Map Offset Register Name 0x000 AIC_SMR0 0x004 AIC_SMR1 – – 0x07C AIC_SMR31 0x080 AIC_SVR0 0x084 AIC_SVR1 – – 0xFC0 AIC_SVR31 0x100 AIC_IVR 0x104 AIC_FVR 0x108 AIC_ISR 0x10C AIC_IPR 0x110 AIC_IMR ...
Page 56
... The IRQ Vector Register contains the vector programmed by the user in the Source Vector Register corresponding to the current interrupt. The SVR Register (1 to 31) is indexed by the current interrupt number when the IVR register is read. When there is no interrupt, the IRQ register reads 0. AT75C220 56 External Sources ...
Page 57
AIC FIQ Vector Register Register Name: AIC_FVR Access Type:Read-only 0 Reset Value • FIQ The vector register contains the vector programmed by the user in SVR Register 0 which corresponds to FIQ. ...
Page 58
... Reset Value PIOB USARTB 7 6 PIOA TC2 Note: 1. IRQ1 is available only in 256-lead PQFP package. • Interrupt Pending 0 = Corresponding interrupt is inactive 1 = Corresponding interrupt is pending AT75C220 MACB OAKA IRQ1 ...
Page 59
AIC Core Interrupt Status Register Register Name: AIC_CISR Access Type:Read-only Reset Value – – – – – – – – • NFIQ: NFIQ Status 0 = NFIQ line inactive NFIQ ...
Page 60
... NFIQ: NFIQ Status 0 = NFIQ line inactive NFIQ line active. • NIRQ: NIRQ Status 0 = NIRQ line inactive NIRQ line active. AT75C220 – – – – – – – – ...
Page 61
AIC Interrupt Set Command Register Register Name: AIC_ISCR Access Type:Write only Reset Value: Undefined 31 30 – – – – – – – – • NFIQ: NFIQ Status 0 = NFIQ line inactive. 1 ...
Page 62
... This register contains the 32-bit address of an interrupt routine which is used to treat cases of spurious interrupts. The programmed address is read in the AIC_IVR read when the nIRQ line is not asserted. The programmed address is read in the AIC_FVR if it read when the nFIQ line is not asserted. AT75C220 62 29 ...
Page 63
... PIO: Programmable I/O Controller The AT75C220 integrates 24 programmable I/O pins (PIO). Each pin can be programmed as an input or an output. Each pin can also generate an interrupt. The programma- ble I/O is implemented as two blocks, called PIO A and PIO B, 14 and 10 pins each, respectively. These pins are used for several functions: • ...
Page 64
... Figure 14. Parallel I/O Multiplexed with a Bid-directional Signal Pad Output Enable Pad Output Pad Pad Input AT75C220 64 PIO_OSR 1 0 PIO_PSR PIO_ODSR PIO_PSR PIO_PDSR Event Detection PIO_ISR PIO_IMR Peripheral Output Enable Peripheral Output Peripheral Input PIOIRQ ...
Page 65
Table 19. PIO Controller A Connection Table Pin Name Signal Name PA0 OAKAIN0 PA1 OAKAIN1 PA2 OAKAOUT0 PA3 OAKAOUT1 PA4 PA5 PA6 PA7 PA8 TCLK0 PA9 TIOA0 PA10 TIOB0 PA11 SCKA PA12 NPCS1 PA19 ACLK Table 20. PIO Controller ...
Page 66
... The reset value of this register depends on the level of the external pins at reset. 2. This register is cleared at reset. However, the first read of the register can give a value not equal to zero if any changes have occurred on any pins between the reset and the read. AT75C220 66 Description ...
Page 67
PIO Enable Register Register Name:PIO_PER Access Type:Write-only 31 30 P31 P30 23 22 P23 P22 15 14 P15 P14 This register is used to enable individual pins to be controlled by the PIO controller instead of ...
Page 68
... P7 P6 This register is used to enable PIO output drivers. If the pin is driven by a peripheral, there is no effect on the pin but the information is stored. The register is programmed as follows Enables the PIO output on the corresponding pin effect. AT75C220 P29 P28 P27 ...
Page 69
PIO Output Disable Register Register Name:PIO_ODR Access Type:Write-only 31 30 P31 P30 23 22 P23 P22 15 14 P15 P14 This register is used to disable PIO output drivers. If the pin is driven by the ...
Page 70
... P7 P6 This register is used to clear PIO output data. It affects the pin only if the corresponding PIO output line is enabled and if the pin is controlled by the PIO. Otherwise, the information is stored PIO output data on the corresponding pin is cleared effect. AT75C220 P29 ...
Page 71
PIO Output Data Status Register Register Name:PIO_ODSR Access Type:Read-only Reset Value P31 P30 23 22 P23 P22 15 14 P15 P14 This register shows the output data status which is programmed in PIO_SODR or ...
Page 72
... P15 P14 This register is used to disable PIO interrupts on the corresponding pin. It has an effect whether the PIO is enabled or not Disables the interrupt on the corresponding pin. Logic level changes are still detected effect. AT75C220 P29 P28 P27 21 20 ...
Page 73
PIO Interrupt Mask Register Register Name:PIO_IMR Access Type:Read-only Reset Value P31 P30 23 22 P23 P22 15 14 P15 P14 This register shows which pins have interrupts enabled updated when interrupts are ...
Page 74
... USART: Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter The AT75C220 provides two identical full-duplex, universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver/transmitters as USART A and USART B. These peripherals sit on the APB bus but are also connected to the ASB bus (and hence external memory) via a dedicated DMA. The main features are: • Programmable baud rate generator • ...
Page 75
Table 22. USART External Signals Signal Name Description NRTS Request to Send NCTS Clear to Send NDTR Data Terminal Ready NDSR Data Set Ready NDCD Data Carrier Detect NRI Ring Indicator Note: After a hardware reset, the USART SC and ...
Page 76
... CD = clock driver 2. For information on obtaining exact baud rates using the value of CD given above, the selected clock frequency must be 23,961,600 Hz (23.9616 MHz). Figure 16. Baud Rate Generator USCLKS [0] USCLKS [1] MCKI MCKI/8 1 SCK AT75C220 Actual CD Actual Baud Rate (bps) 39 38461.5 26 57692.3 13 115384.6 CD ...
Page 77
Receiver Asynchronous Receiver The USART is configured for asynchronous operation when SYNC = 0 (bit 7 of US_MR). In asynchronous mode, the USART detects the start of a received character by sampling the RXD signal until it detects a valid ...
Page 78
... The time-guard function allows the transmitter to insert an idle state on the TXD line between two characters. The duration of the idle state is programmed in US_TTGR. AT75C220 78 0, the TIMEOUT bit in US_CSR is set. The user can restart the wait for a first character with the STTTO (Start Time- out) bit in US_CR ...
Page 79
Figure 20. Synchronous and Asynchronous Mode: Character Transmission Example: 8-bit, parity enabled 1 stop Baud Rate Clock TXD Start Break A break condition is a low signal level which has a duration of at least one character, including start/stop bits ...
Page 80
... Remote loopback mode directly connects the RXD pin to the TXD pin. The transmitter and the receiver are disabled and have no effect. This mode allows bit-by-bit re-transmis- sion. AT75C220 80 Figure 21. Channel Modes Automatic Echo Receiver ...
Page 81
Peripheral Data Controller Each USART channel is closely connected to a corre- sponding peripheral data controller channel. One is dedi- cated to the receiver, the other is dedicated to the transmit- ter. Note: The PDC is disabled if 9-bit character ...
Page 82
... US_MC 0x44 US_MS Notes: 1. This is either 0x18 or 0x418 depending on the value of bootn and modem control inputs. 2. This depends on the value of modem control input signals, as these are reflected in this register. AT75C220 82 Description Control Register Mode Register Interrupt Enable Register Interrupt Disable Register ...
Page 83
USART Control Register Name: US_CR Access Type:Write-only Reset Value:Undefined 31 30 – – – – – – TXDIS TXEN • RSTRX: Reset Receiver effect The receiver logic is reset. ...
Page 84
... In multi-drop mode only, the next character written to the US_THR is sent with the address bit set. AT75C220 84 ...
Page 85
USART Mode Register US_MR Name: Access Type:Read/write Reset Value:0x0 31 30 – – – – CHMODE 7 6 CHRL • USCLKS: Clock Selection (Baud Rate Generator Input Clock) USCLKS Selected Clock ACLK 0 0 ACLK/8 0 ...
Page 86
... MODE9: 9-bit Character Length 0 = CHRL defines character length 9-bit character length. • CKLO: Clock Output Select 0 = The USART does not drive the SCK pin The USART drives the SCK pin if USCLKS[ AT75C220 86 Synchronous (SYNC = 1) 1 stop bit Reserved 2 stop bits ...
Page 87
USART Interrupt Enable Register US_IER Name: Access Type:Write-only Reset Value: Undefined 31 30 – – – – – – PARE FRAME • RXRDY: Enable RXRDY Interrupt effect Enables RXRDY ...
Page 88
... TIMEOUT: Disable Time-out Interrupt effect Disables receiver time-out interrupt. • TXEMPTY: Disable TXEMPTY Interrupt effect Disables TXEMPTY interrupt. • DMSI: Delta Modem Status Indication Interrupt effect Disables DMSI interrupt. AT75C220 – – – – ...
Page 89
USART Interrupt Mask Register US_IMR Name: Access Type:Read-only Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – – – PARE FRAME • RXRDY: RXRDY Interrupt Mask 0 = RXRDY interrupt is disabled ...
Page 90
... No parity bit has been detected false (or a parity bit high in multi-drop mode) since the last reset status bits command. • TIMEOUT: Receiver Time-out 0 = There has not been a time-out since the last start time-out command or the Time-out Register There has been a time-out since the last start time-out command. AT75C220 – ...
Page 91
TXEMPTY: Transmitter Empty 0 = There are characters in either US_THR or the Transmit Shift Register or a break is being transmitted There are no characters in US_THR and the Transmit Shift Register and break is not ...
Page 92
... Baud rate (asynchronous mode) = Selected clock/(16 x CD) Baud rate (synchronous mode) = Selected clock/CD Note: In synchronous mode, the value programmed must be even to ensure a 50:50 mark-to-space ratio. Note: Clock divisor bypass ( must not be used when internal clock ACLK is selected (USCLKS = 0). AT75C220 – ...
Page 93
USART Receiver Time-out Register US_RTOR Name: Access Type:Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – – – • TO: Time-out Value When a value is written to this register, a start time-out ...
Page 94
... Time-guard duration = TG x Bit period USART Receive Pointer Register Name: US_RPR Access Type:Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 • RXPTR: Receive Pointer RXPTR must be loaded with the address of the receive buffer. AT75C220 – – – – – – – ...
Page 95
USART Receive Counter Register US_RCR Name: Access Type:Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – • RXCTR: Receive Counter RXCTR must be loaded with the size of the receive buffer. 0: Stop ...
Page 96
... TXCTR: Transmit Counter TXCTR must be loaded with the size of the transmit buffer. 0: Stop peripheral data transfer dedicated to the transmitter 65535: Start peripheral data transfer if TXRDY is active. AT75C220 – – – – – ...
Page 97
Modem Control Register Register Name:US_MC Access Type:Write-only Reset Value: Undefined 31 30 – – – – – – – – This register controls the interface with the modem or data set (or a peripheral ...
Page 98
... This bit is the complement of the Ring Indicator (NRI) input. • DCD: Data Carrier Detect This bit is the complement of the Data Carrier Detect (NDCD) input. • FCMS: Flow Control Status This bit indicates the value of the FCM in the US_MC. AT75C220 – – ...
Page 99
... TC: Timer/Counter The AT75C220 features a timer/counter block which includes three identical 16-bit timer/counter channels. Each channel can be independently programmed to perform a wide range of functions including frequency measurement, event counting, interval measurement, pulse generation, delay timing and pulse-width modulation. Each timer/counter channel has three external clock inputs, five internal clock inputs, and two multi-purpose input/out- put signals that can be configured by the user ...
Page 100
... In this case, the counter value passes to 0x0000 on the next valid edge of the selected clock. Clock Selection At block level, input clock signals of each channel can either be connected to the external inputs TCLK0, TCLK1 AT75C220 100 Description External clock inputs Capture mode: General-purpose input ...
Page 101
Figure 23. Clock Selection CLKS ACLK/2 ACLK/8 ACLK/32 ACLK/128 ACLK/1024 XC0 XC1 XC2 BURST 1 Clock Control The clock of each counter can be controlled in two different ways: it can be enabled/disabled and started/stopped. 1. The clock can be ...
Page 102
... Register). In this case, the old value is overwritten. Trigger Conditions In addition to the SYNC signal, the software trigger and the RC compare trigger, an external trigger can be defined. AT75C220 102 Bit ABETRG in TC_CMR selects input signal TIOA or TIOB as an external trigger. Parameter ETRGEDG defines the edge (rising, falling or both) detected to generate an exter- nal trigger ...
Page 103
TCCLKS ACLK/2 ACLK/8 ACLK/32 ACLK/128 ACLK/1024 XC0 XC1 XC2 BURST 1 SWTRG SYNC ABETRG ETRGEDG MTIOB Edge Detector TIOB MTIOA not loaded loaded TIOA Timer/Counter Channel CLKSTA CLKI Capture Register ...
Page 104
... RC compare. RA compare controls TIOA and RB compare controls TIOB. Each of these events can be programmed to set, clear or toggle the out- put as defined in the corresponding parameter in TC_CMR. AT75C220 104 The tables below show which parameter in TC_CMR is used to define the effect of each event. ...
Page 105
TCCLKS ACLK/2 CLKI ACLK/8 ACLK/32 ACLK/128 ACLK/1024 XC0 XC1 XC2 BURST 1 SWTRG SYNC EEVT EEVTEDG ENETRG Edge Detector TIOB Timer/Counter Channel CLKSTA CLKEN CLKDIS Register A Register B Register C Compare RA = ...
Page 106
... TC_RB 0x1C TC_RC 0x20 TC_SR 0x24 TC_IER 0x28 TC_IDR 0x2C TC_IMR Note: 1. Read only if WAVE = 0 AT75C220 106 Channel/Register TC Channel 0 TC Channel 1 TC Channel 2 TC Block Control Register TC Block Mode Register Description Channel Control Register Channel Mode Register Reserved Reserved Counter Value Register ...
Page 107
TC Block Control Register Register Name:TC_BCR Access Type:Write-only 31 30 – – – – – – – – • SYNC: Synchro Command effect Asserts the SYNC signal which generates ...
Page 108
... TIOA0 1 1 TIOA2 • TC2XC2S: External Clock Signal 2 Selection TC2XC2S Signal Connected to XC2 0 0 TCLK2 0 1 none 1 0 TIOA0 1 1 TIOA1 AT75C220 108 – – – – – – – – – TC2XC2S 26 25 – ...
Page 109
TC Channel Control Register Register Name:TC_CCR Access Type:Write-only 31 30 – – – – – – – – • CLKEN: Counter Clock Enable Command effect Enables the clock if ...
Page 110
... LDBSTOP: Counter Clock Stopped with RB Loading 0 = Counter clock is not stopped when RB loading occurs Counter clock is stopped when RB loading occurs. • LDBDIS: Counter Clock Disable with RB Loading 0 = Counter clock is not disabled when RB loading occurs Counter clock is disabled when RB loading occurs. AT75C220 110 – – ...
Page 111
ETRGEDG: External Trigger Edge Selection ETRGEDG Edge 0 0 None 0 1 Rising edge 1 0 Falling edge 1 1 Each edge • ABETRG: TIOA or TIOB External Trigger Selection 0 = TIOB is used as an external trigger. ...
Page 112
... CPCSTOP: Counter Clock Stopped with RC Compare 0 = Counter clock is not stopped when counter reaches RC Counter clock is stopped when counter reaches RC. • CPCDIS: Counter Clock Disable with RC Compare 0 = Counter clock is not disabled when counter reaches RC Counter clock is disabled when counter reaches RC. AT75C220 112 BEEVT 21 ...
Page 113
EEVTEDG: External Event Edge Selection EEVTEDG Edge 0 0 None 0 1 Rising edge 1 0 Falling edge 1 1 Each edge • EEVT: External Event Selection Signal Selected as EEVT External Event 0 0 TIOB 0 1 XC0 ...
Page 114
... None 0 1 Set 1 0 Clear 1 1 Toggle • BCPC: RC Compare Effect on TIOB BCPC Effect 0 0 None 0 1 Set 1 0 Clear 1 1 Toggle • BEEVT: External Event Effect on TIOB BEEVT Effect 0 0 None 0 1 Set 1 0 Clear 1 1 Toggle AT75C220 114 ...
Page 115
BSWTRG: Software Trigger Effect on TIOB BSWTRG Effect 0 0 None 0 1 Set 1 0 Clear 1 1 Toggle TC Counter Value Register Register Name:TC_CVR Access Type:Read-only 31 30 – – – – ...
Page 116
... RB contains the Register B value in real-time. TC Register C Register Name:TC_RC Access Type:Read/write Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – • RC: Register C RC contains the Register C value in real-time. AT75C220 116 – – – – – – ...
Page 117
TC Status Register Register Name:TC_SR Access Type:Read-only 31 30 – – – – – – ETRGS LDRBS • COVFS: Counter Overflow Status counter overflow has occurred since the last read of ...
Page 118
... Enables the RC compare interrupt. • LDRAS: RA Loading effect Enables the RA load interrupt. • LDRBS: RB Loading effect Enables the RB load interrupt. • ETRGS: External Trigger effect Enables the external trigger interrupt. AT75C220 118 – – – – – ...
Page 119
TC Interrupt Disable Register Register Name:TC_IDR Access Type:Write-only 31 30 – – – – – – ETRGS LDRBS • COVFS: Counter Overflow effect Disables the counter overflow interrupt. • ...
Page 120
... LDRAS: RA Loading 0 = The load RA interrupt is disabled The load RA interrupt is enabled. • LDRBS: RB Loading 0 = The load RB interrupt is disabled The load RB interrupt is enabled. • ETRGS: External Trigger 0 = The external trigger interrupt is disabled The external trigger interrupt is enabled. AT75C220 120 – – – – ...
Page 121
... SPI: Serial Peripheral Interface The AT75C220 integrates a serial peripheral interface (SPI) that provides communication with external devices in Figure 27. Serial Peripheral Interface Block Diagram APB Table 26. SPI Interface Pins Pin Name Description MISO Master In/Slave Out MOSI Master Out/Slave In SPCK Serial Clock ...
Page 122
... Fixed peripheral select is activated by setting bit PS to zero in SP_MR. The peripheral is defined by the PCS field, also in SP_MR. This option is only available when the SPI is programmed in master mode. AT75C220 122 Variable Peripheral Select Variable peripheral select is activated by setting bit PS to one. The PCS field in SP_TDR is used to select the desti- nation peripheral ...
Page 123
Figure 28. Functional Flow Diagram in Master Mode SPI Enable TDRE 0 PS Variable peripheral 1 NPCS = SP_TDR(PCS) Delay DLYBS Serializer = SP_TDR(TD) TDRE = 1 Data Transfer SP_RDR(RD) = Serializer RDRF = 1 Delay DLYBCT TDRE 1 NPCS ...
Page 124
... Figure 29. SPI in Master Mode SP_MR(ACLK32) ACLK 0 SPI Master ACLK/32 1 Clock SPIDIS SPIEN MISO SP_MR(PS SP_MR(PCS) AT75C220 124 SPCK Clock Generator SP_CSRx[15: SP_RDR PCS RD LSB MSB Serializer SP_TDR PCS TD SP_MR(MSTR) SPCK MOSI NPCS1 NPCSS SP_SR ...
Page 125
Slave Mode In slave mode, the SPI waits for NPCSS to go active low before receiving the serial clock from an external master. Figure 30. SPI in Slave Mode SCK NSS SPIDIS SPIEN S R MOSI CPOL, NCPHA and BITS ...
Page 126
... NPCSS (to slave) Figure 32. SPI Transfer Format (NCPHA Equals Zero, Eight Bits per Transfer) SPCK Cycle (for reference) 1 SPCK (CPOL=0) SPCK (CPOL=1) MOSI (from master) MSB MISO (from slave) X MSB NPCSS (to slave) AT75C220 126 ...
Page 127
Figure 33. Programmable Delays (DLYBCS, DLYBS and DLTBCT) Chip Select 1 Change peripheral Chip Select 2 SPCK Output Clock Generation In master mode, the SPI master clock is either ACLK or ACLK/32, as defined by the MCK32 field of SP_MR. ...
Page 128
... If both SPIEN and SPIDIS are equal to one when the control register is written, the SPI is disabled. • SWRST: SPI Software reset effect Resets the SPI. A software-triggered hardware reset of the SPI interface is performed. AT75C220 128 Register Receive Pointer Register Receive Counter Register Transmit Pointer Register ...
Page 129
SPI Mode Register Register Name:SP_MR Access Type:Read/write Reset Value:0x0 – – – – LLB – • MSTR: Master/Slave Mode 0 = SPI is in slave mode SPI is in master ...
Page 130
... Data received by the SPI interface is stored in this register right-justified. Unused bits read zero. • PCS: Peripheral Chip Select Status In master mode only, these bits indicate the value on the NPCS pins at the end of a transfer. Otherwise, these bits read as zero. AT75C220 130 × – ...
Page 131
SPI Transmit Data Register Register Name:SP_TDR Access Type:Write-only Reset Value:– – – – – • TD: Transmit Data Data that transmitted by the SPI interface is stored in this ...
Page 132
... SPENDTX: SPI End of Transmission end of data transmission detected End of data transmission detected. • SPENDRX: SPI End of Reception end of data reception detected End of data reception detected. • SPIENS: SPI Enable Status 0 = SPI is disabled SPI is enabled. AT75C220 132 – – – – ...
Page 133
SPI Interrupt Enable Register Register Name:SP_IER Access Type:Write-only 31 30 – – – – – – – – • RDRF: Receive Data Register Full Interrupt Enable effect Enables the ...
Page 134
... Disables the transmit data register empty interrupt. • MODF: Mode Fault Error Interrupt Disable effect Disables the mode fault error interrupt. • OVRES: Overrun Error Interrupt Disable effect Disables the overrun error interrupt. AT75C220 134 – – – 21 ...
Page 135
SPI Interrupt Mask Register Register Name:SP_IMR Access Type:Read-only Reset Value: 0x0 31 30 – – – – – – – – • RDRF: Receive Data Register Full Interrupt Mask 0 = Receive data register ...
Page 136
... Access Type:Read/write Reset Value:0x0 • RXCTR: Receive Counter Register RXCTR must be loaded with the size of the receive buffer Stop peripheral data transfer 1 - 4294967295 = Start peripheral data transfer if RDRF is active. AT75C220 136 RXPTR RXPTR RXPTR 5 ...
Page 137
SPI Transmit Pointer Register Register Name:SP_TPR Access Type:Read/write Reset Value:0x0 • TXPTR: Transmit Pointer Register TXPTR must be loaded with the address of the transmit buffer. SPI Transmit Counter Register Register Name:SP_TCR ...
Page 138
... The BITS field determines the number of data bits transferred. Reserved values should not be used. Bits per BITS[3:0] Transfer BITS[3:0] 0000 8 0001 9 0010 10 0011 11 0100 12 0101 13 0110 14 0111 15 AT75C220 138 DLYBCT DLYBS SCBR 5 4 Bits per Transfer 1000 16 1001 ...
Page 139
SCBR: Serial Clock Baud Rate In master mode, the SPI interface uses a modulus counter to derive the SPCK baud rate from the SPI master clock (selected between ACLK and ACLK/32). The baud rate is selected by writing a ...
Page 140
... WD: Watchdog Timer The AT75C220 has an internal watchdog timer which can be used to prevent system lock-up if the software becomes trapped in a deadlock. In normal operation, the user reloads the watchdog at regular intervals before the timer overflow occurs overflow does occur, the watchdog timer generates one or a combination of the following sig- ...
Page 141
WD Overflow Mode Register WD_OMR Name: Read/write Access: Reset Value – – – – OKEY • WDEN: Watchdog Enable 0 = Watchdog is disabled and does not generate any signals ...
Page 142
... Other value: Write access in WD_CMR is prohibited. WD Control Register WD_CR Name: Write-only Access – – – – • RSTKEY: Restart Key 0xC071 = Watchdog counter is restarted. Other value = No effect. AT75C220 142 – – – – – – CKEY HPCV ...
Page 143
WD Status Register WD_SR Name: Access: Read-only 31 30 – – – – – – – – • WDOVF: Watchdog Overflow watchdog overflow watchdog overflow has occurred since ...
Page 144
... Atmel Corporation 2001. Atmel Corporation makes no warranty for the use of its products, other than those expressly contained in the Company’s standard war- ranty which is detailed in Atmel’s Terms and Conditions located on the Company’s web site. The Company assumes no responsibility for any errors which may appear in this document, reserves the right to change devices or specifications detailed herein at any time without notice, and does not make any commitment to update the information contained herein ...