m40z300 STMicroelectronics, m40z300 Datasheet

m40z300
Available stocks
Related parts for m40z300
m40z300 Summary of contents
Page 1
... Precision power monitoring and power switching circuitry ■ Automatic WRITE-protection when V of-tolerance ■ Two-input decoder allows control for SRAMs (with 2 devices active in parallel) ■ Choice of supply voltages and power-fail deselect voltages: – M40Z300 4.5V to 5.5V CC THS = PFD THS = V : 4.2V V OUT PFD – ...
Page 2
Contents 1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 3
List of tables Table 1. Signal names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
... List of figures Figure 1. Logic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 Figure 2. 28-pin SOIC connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Figure 3. M40Z300 16-pin SOIC connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Figure 4. M40Z300W 16-pin SOIC connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 Figure 5. Hardware hookup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Figure 6. Address-decode time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Figure 7. Supply voltage protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Figure 8. AC testing load circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 Figure 9. Power down timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 Figure 10. Power up timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 Figure 11. SOH28 – ...
Page 5
... Description The M40Z300/W NVRAM SUPERVISOR is a self-contained device which converts a standard low-power SRAM into a non-volatile memory. A precision voltage reference and comparator monitors the V When an invalid are forced inactive to write-protect the stored data in the SRAM. During a power CON failure, the SRAM is switched from the V provide the energy required for data retention ...
Page 6
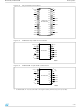
... CON CON A, B RST BL V OUT – For M40Z300W, B– must be connected to the negative battery terminal only (not to Pin 8, V 6/25 ( THS E B M40Z300 A M40Z300W ( – Threshold select input Chip enable input Conditioned chip enable output ...
Page 7
... THS V SS Figure 3. M40Z300 16-pin SOIC connections V OUT NC RST BL THS V SS Figure 4. M40Z300W 16-pin SOIC connections V OUT NC RST BL THS For M40Z300W, B– must be connected to the negative battery terminal only (not to pin ...
Page 8
... Figure 5. Hardware hookup 3.0V, 3. OUT 0.1 F M40Z300 M40Z300W E1 CON A E2 CON B E3 CON E E4 CON Threshold THS RST the second chip enable pin (E2) is unused, it should be tied (1) E2 (1) E2 CMOS CMOS SRAM SRAM 0 Microprocessor To Battery Monitor Circuit ...
Page 9
... E. In this situation, the SRAM is unconditionally write protected as V below an out-of-tolerance threshold (V associated with V PFD on page 15. For the M40Z300W, the THS pin selects both the supply voltage and V shown in Table 6 on page Note: In either case, THS pin must be connected to either V If chip enable access is in progress during a power fail detection, that memory cycle continues to completion before the memory is write protected ...
Page 10
... Two to four decode The M40Z300/W includes a 2 input (A, B) decoder which allows the control independent SRAMs. The Truth Table for these inputs is shown in Table 2. Truth table Inputs Figure 6. Address-decode time CON - E4 CON ...
Page 11
... For a further more detailed review of lifetime calculations, please see Application Note AN1012. 2.3 Power-on reset output All microprocessors have a reset input which forces them to a known state when starting. The M40Z300/W has a reset output (RST) pin which is guaranteed to be low within t V (see Table 7). This signal is an open drain configuration. An appropriate pull-up PFD resistor should be chosen to control the rise time ...
Page 12
... In addition to transients that are caused by normal SRAM operation, power cycling can generate negative voltage spikes on V one volt. These negative spikes can cause data corruption in the SRAM while in battery backup mode. To protect from these voltage spikes, STMicroelectronics recommends connecting a schottky diode from V Schottky diode 1N5817 is recommended for through hole and MBRS120T3 is recommended for surface mount ...
Page 13
... Negative undershoots below –0.3V are not allowed on any pin while in the battery back-up mode. Caution: Do NOT wave solder SOIC to avoid damaging SNAPHAT sockets. Parameter Grade 1 Grade 6 ® SNAPHAT SOIC M40Z300 M40Z300W Value Unit °C – °C – °C –55 to 125 °C 260 ° ...
Page 14
... Input rise and fall times Input pulse voltages Input and output timing ref. voltages Note: Output High Z is defined as the point where data is no longer driven. Figure 8. AC testing load circuit Note: 50pF for M40Z300W. Table 5. Capacitance Symbol C Input capacitance IN (3) ...
Page 15
... V –0.3 OUT CC > V –0.2 OUT CC > V –0.3 100 OUT BAT V SS 4.5 4.6 4.2 4.35 3.0 2.0 2 70°C or –40 to 85° can only sustain CMOS leakage currents in the battery back-up mode. open. CON M40Z300W Max Min Typ Max ±1 ± 0.8 –0.3 0.8 + 0 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 2.4 3.6 2.0 2.9 3.6 250 ...
Page 16
Figure 9. Power down timing PFD (max) V PFD V PFD (min CON - E4 CON RST Figure 10. Power up timing PFD (max) V PFD V PFD (min) ...
Page 17
... Grade 6 device. REC (1) fall time CC M40Z300 fall time M40Z300W rise time CC M40Z300 M40Z300W M40Z300 M40Z300W M40Z300 M40Z300W rise time = 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85° may result in deselection/write protection not occurring F (min). may cause corruption of RAM data. FB Min ...
Page 18
Package mechanical data In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in ECOPACK packages. These packages have a Lead-free second level interconnect. The category of second Level Interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner ...
Page 19
Table 8. SOH28 – 28-lead plastic small outline, battery SNAPHAT, package mechanical data mm Symbol Typ Min A A1 0.05 A2 2.34 B 0.36 C 0.15 D 17.71 E 8.23 e 1.27 eB 3.20 H 11. ...
Page 20
Figure 12. SH – 4-pin SNAPHAT housing for 48mAh battery, package outline Note: Drawing is not to scale. Table 9. SH – 4-pin SNAPHAT housing for 48mAh battery, package mechanical data Symbol Typ ...
Page 21
Figure 13. SH – 4-pin SNAPHAT housing for 120mAh battery, package outline Note: Drawing is not to scale. Table 10. SH – 4-pin SNAPHAT housing for 120mAh battery, package mechanical data Symbol Typ ...
Page 22
Figure 14. SO16 – 16-lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package outline Note: Drawing is not to scale. Table 11. SO16 – 16-lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package mechanical data Symbol ...
Page 23
Part numbering Table 12. Ordering information example Example: Device type M40Z Supply and write protect voltage 300 = V = 4.5 to 5.5V CC THS = V = 4.5V SS THS = V = 4.2V OUT 300W = V ...
Page 24
Revision history Table 14. Document revision history Date Revision Mar-1999 08-Mar-2000 22-Sep-2000 23-Feb-2001 30-May-2001 10-Jul-2001 01-Aug-2001 15-Jan-2002 13-May-2002 31-Oct-2003 04-Nov-2003 23-Feb-2005 05-Nov-2007 24/25 1.0 First Issue Document Layout changed; SO16 package added; Battery Capacity 1.1 changed (Table 13) 1.2 ...
Page 25
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notice. All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale. ...