GS88118BGD-150I GSI Technology, GS88118BGD-150I Datasheet

GS88118BGD-150I
Manufacturer Part Number
GS88118BGD-150I
Description
Manufacturer
GSI Technology
Datasheet
1.GS88136BGT-333I.pdf
(38 pages)
Specifications of GS88118BGD-150I
Pack_quantity
144
Comm_code
85423245
Lead_time
84
100-pin TQFP & 165-bump BGA
Commercial Temp
Industrial Temp
Features
• IEEE 1149.1 JTAG-compatible Boundary Scan
• 2.5 V or 3.3 V +10%/–10% core power supply
• 2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O supply
• LBO pin for Linear or Interleaved Burst mode
• Internal input resistors on mode pins allow floating mode pins
• Byte Write (BW) and/or Global Write (GW) operation
• Internal self-timed write cycle
• Automatic power-down for portable applications
• JEDEC-standard 100-lead TQFP and 165-bump BGA
• RoHS-compliant 100-lead TQFP and 165-bump BGA
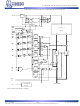
Functional Description
Applications
The GS88118B(T/D)/GS88132B(T/D)/GS88136B(T/D) is a
9,437,184-bit high performance synchronous SRAM with a 2-
bit burst address counter. Although of a type originally
developed for Level 2 Cache applications supporting high
performance CPUs, the device now finds application in
synchronous SRAM applications, ranging from DSP main
store to networking chip set support.
Controls
Addresses, data I/Os, chip enable (E1, E2), address burst
control inputs (ADSP, ADSC, ADV) and write control inputs
(Bx, BW, GW) are synchronous and are controlled by a
positive-edge-triggered clock input (CK). Output enable (G)
and power down control (ZZ) are asynchronous inputs. Burst
cycles can be initiated with either ADSP or ADSC inputs. In
Burst mode, subsequent burst addresses are generated
internally and are controlled by ADV. The burst address
counter may be configured to count in either linear or
interleave order with the Linear Burst Order (LBO) input. The
Burst function need not be used. New addresses can be loaded
on every cycle with no degradation of chip performance.
Rev: 1.06 6/2007
Specifications cited are subject to change without notice. For latest documentation see http://www.gsitechnology.com.
packages
packages available
Flow Through
Pipeline
3-1-1-1
2-1-1-1
Curr (x32/x36)
Curr (x32/x36)
512K x 18, 256K x 32, 256K x 36
Curr (x18)
Curr (x18)
tCycle
tCycle
t
t
KQ
KQ
9Mb Sync Burst SRAMs
Paramter Synopsis
1/38
-333
250
290
200
230
2.5
3.0
4.5
4.5
GS88118B(T/D)/GS88132B(T/D)/GS88136B(T/D)
-300
Flow Through/Pipeline Reads
The function of the Data Output register can be controlled by
the user via the FT mode pin (Pin 14). Holding the FT mode
pin low places the RAM in Flow Through mode, causing
output data to bypass the Data Output Register. Holding FT
high places the RAM in Pipeline mode, activating the rising-
edge-triggered Data Output Register.
SCD Pipelined Reads
The GS88118B(T/D)/GS88132B(T/D)/GS88136B(T/D) is a
SCD (Single Cycle Deselect) pipelined synchronous SRAM.
DCD (Dual Cycle Deselect) versions are also available. SCD
SRAMs pipeline deselect commands one stage less than read
commands. SCD RAMs begin turning off their outputs
immediately after the deselect command has been captured in
the input registers.
Byte Write and Global Write
Byte write operation is performed by using Byte Write enable
(BW) input combined with one or more individual byte write
signals (Bx). In addition, Global Write (GW) is available for
writing all bytes at one time, regardless of the Byte Write
control inputs.
Sleep Mode
Low power (Sleep mode) is attained through the assertion
(High) of the ZZ signal, or by stopping the clock (CK).
Memory data is retained during Sleep mode.
Core and Interface Voltages
The GS88118B(T/D)/GS88132B(T/D)/GS88136B(T/D)
operates on a 2.5 V or 3.3 V power supply. All input are 3.3 V
and 2.5 V compatible. Separate output power (V
used to decouple output noise from the internal circuits and are
3.3 V and 2.5 V compatible.
230
265
185
210
2.5
3.3
5.0
5.0
-250
200
230
160
185
2.5
4.0
5.5
5.5
-200
170
195
140
160
3.0
5.0
6.5
6.5
-150
140
160
128
145
3.8
6.7
7.5
7.5
Unit
mA
mA
mA
mA
ns
ns
ns
ns
© 2002, GSI Technology
333 MHz–150 MHz
2.5 V or 3.3 V V
2.5 V or 3.3 V I/O
DDQ
) pins are
DD