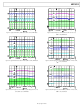
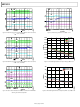
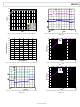
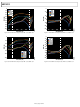
ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7 Analog Devices Inc, ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7 Datasheet - Page 15

ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7
Manufacturer Part Number
ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7
Description
IC REG QD SYNC BUCK/LDO1 16WLCSP
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Series
-r
Datasheet
1.ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7.pdf
(28 pages)
Specifications of ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7
Topology
Step-Down (Buck) Synchronous (2), Linear (LDO) (2)
Function
Any Function
Number Of Outputs
4
Frequency - Switching
3MHz
Voltage/current - Output 1
0.8 V ~ 3.3 V, 800mA
Voltage/current - Output 2
0.8 V ~ 3.3 V, 800mA
Voltage/current - Output 3
0.8 V ~ 3.3 V, 300mA
W/led Driver
No
W/supervisor
No
W/sequencer
No
Voltage - Supply
1.7 V ~ 5.5 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
16-WFBGA, WLCSP
No. Of Outputs
4
No. Of Pins
16
Operating Temperature Range
-40°C To +125°C
Supply Voltage
5.5V
No. Of Step-down Dc - Dc Converters
2
No. Of Ldo Regulators
2
Digital Ic Case Style
WLCSP
No. Of Regulated Outputs
2
Rohs Compliant
Yes
Primary Input Voltage
5.5V
Output Voltage
2.8V
Output Current
800mA
Switching Frequency Max
3MHz
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
ADP5033ACBZ-1-R7TR
POWER DISSIPATION AND THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
The ADP5033 is a highly efficient micropower management
unit (μPMU), and, in most cases, the power dissipated in the
device is not a concern. However, if the device operates at high
ambient temperatures and maximum loading condition, the
junction temperature can reach the maximum allowable
operating limit (125°C).
When the temperature exceeds 150°C, the ADP5033 turns off
all the regulators, allowing the device to cool down. When the
die temperature falls below 130°C, the ADP5033 resumes
normal operation.
This section provides guidelines to calculate the power dissi-
pated in the device and ensure that the ADP5033 operates
below the maximum allowable junction temperature.
The efficiency for each regulator on the ADP5033 is given by
where:
η is the efficiency.
P
P
Power loss is given by
or
Power dissipation can be calculated in several ways. The most
intuitive and practical is to measure the power dissipated at the
input and all the outputs. Perform the measurements at the
worst-case conditions (voltages, currents, and temperature).
The difference between input and output power is dissipated in
the device and the inductor. Use Equation 4 to derive the power
lost in the inductor and, from this, use Equation 3 to calculate
the power dissipation in the ADP5033 buck converter.
A second method to estimate the power dissipation uses the
efficiency curves provided for the buck regulator, and the power
lost on each LDO can be calculated using Equation 12. When
the buck efficiency is known, use Equation 2b to derive the total
power lost in the buck regulator and inductor, use Equation 4 to
derive the power lost in the inductor, and then calculate the
power dissipation in the buck converter using Equation 3. Add
the power dissipated in the buck and in the two LDOs to find
the total dissipated power.
Note that the buck efficiency curves are typical values and may
not be provided for all possible combinations of V
I
safety margin when calculating the power dissipated in the buck.
A third way to estimate the power dissipation is analytical and
involves modeling the losses in the buck circuit provided by
Equation 8 to Equation 11 and the losses in the LDO provided
by Equation 12.
OUT.
IN
OUT
is the input power.
To account for these variations, it is necessary to include a
P
P
η
is the output power.
LOSS
LOSS
=
P
= P
= P
P
OUT
IN
IN
OUT
×
− P
100%
(1− η )/ η
OUT
IN
, V
OUT
, and
(2b)
(2a)
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 28
(1)
BUCK REGULATOR POWER DISSIPATION
The power loss of
where:
P
regulato
P
The inducto
have any effect on the die temper
The inductor losses are estimated (without core losses) by
where:
DCR
I
where r is the inductor ripple cur
where:
L is the inductance.
f
D is the duty cycle.
ADP5033 buck regu
pow
tion losses of each channel. There are other sources of loss, but
these are generally less significant at high output load currents,
where the thermal limit of the application is. Equation 8
captures the calculation that must be made to estimate the
power dissipation in the buck regulator.
The power switch conductive losses are due
I
power switches that have internal resistance, RDS
RDS
where RDS
mate
3.6 V. At VIN1 = VIN2 = 2.3 V, these values change to 0.31 Ω and
0.21 Ω, respectively, and at VIN1 = VIN2 = 5.5 V, the values are
0.16 Ω and 0.14 Ω, respectively.
SW
OUT1(RMS
OUT
DBU
L
is the inductor power losses.
is the s
1
CK
er switch conductive losses, the switch losses, and the transi-
, flowing through the P-MOSFET and the N-MOSFET
ON-N
ly 0.16 Ω at 125°C junction temperature and VIN1 = VIN2 =
P
P
r ≈ V
D = V
P
P
L
I
LOSS
L
is the inductor series resistance.
DBUCK
COND
is the power dissipation on one of the ADP5033 buck
OUT
≈ I
)
rs.
. The amount of conductive power loss is found by
is the rms load curren
( 1
= P
OUT1
witching frequency.
OUT1(RMS)
= [RDS
RMS
OUT1
ON-P
= P
r losses are external to the device, and they do not
DBUCK1
)
× (1 − D)/(I
/V
COND
is approximately 0.2 Ω, and RDS
=
IN1
I
2
ON-P
the buck regulator is approximated by
OUT1
× DCR
+ P
+ P
lator power dissipation, P
× D + RDS
DBUCK2
SW
×
+ P
L
OUT1
1
+
+ P
TRAN
12
× L × f
r
t of the buck regulator.
L
ON-N
ature.
ren
t
SW
× (1 − D)] × I
)
to the output current,
DBUCK
ON-N
ON-P
ADP5033
, includes the
OUT1
is approx
and
2
i-
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)