L6470HTR STMicroelectronics, L6470HTR Datasheet

L6470HTR
Specifications of L6470HTR
Available stocks
Related parts for L6470HTR
L6470HTR Summary of contents
Page 1
... DSon with all of the power switches equipped with an Table 1. Device summary Order codes L6470H L6470HTR November 2010 Fully integrated microstepping motor driver accurate on chip current sensing circuitry suitable for non dissipative current control and overcurrent protections. Thanks to a unique control system a true 1/128 steps resolution is achieved ...
Page 2
Contents Contents 1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 3
L6470 6.12 Reset and standby . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
Contents 9.1.15 9.1.16 9.1.17 9.1.18 9.1.19 9.1.20 9.1.21 9.1.22 9.2 Application commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 5
L6470 List of tables Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 6
List of tables Table 49. ResetPos command structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 7
L6470 List of figures Figure 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 8
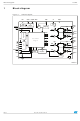
Block diagram 1 Block diagram Figure 1. Block diagram VDD 16MHz Oscillator STBY/RST FLAG SDO SDI BUSY/SYNC STCK DGND 8/64 OSCIN OSCOUT ADCIN VREG Ext. Osc. driver & Clock gen ADC ...
Page 9
L6470 2 Electrical data 2.1 Absolute maximum ratings Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings Symbol V Logic interface supply voltage DD V Motor supply voltage S Differential voltage between AGND, PGND V GND, diff and DGND V Bootstrap peak voltage boot ...
Page 10
Electrical data 2.2 Recommended operating conditions Table 3. Recommended operating conditions Symbol V Logic interface supply voltage DD V Motor supply voltage S Differential voltage between V , OUT1 SA V out_diff and V SB PGND pins V Logic supply ...
Page 11
L6470 3 Electrical characteristics Table 4. Electrical characteristics Symbol Parameter General V V UVLO turn on threshold SthOn UVLO turn off threshold SthOff UVLO threshold ...
Page 12
Electrical characteristics Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued) Symbol Parameter (3) t Fall time f SR Output rising slew-rate out_r SR Output falling slew-rate out_f Dead time and blanking t Dead time DT t Blanking time blank Source-drain diodes V High ...
Page 13
L6470 Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued) Symbol Parameter Logic inputs and outputs V Low level logic input voltage IL V High level logic input voltage IH I High level logic input current IH I Low level logic input current IL ...
Page 14
Electrical characteristics Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued) Symbol Parameter t hCK SPI clock high and low time t lCK t Chip select setup time setCS t Chip select hold time holCS (5) t Deselect time disCS t Data input setup ...
Page 15
L6470 Table 4. Electrical characteristics (continued) Symbol Parameter t Charge pump power-on and wake-up time cpwu Internal voltage regulator V Voltage regulator output voltage REG I Voltage regulator output current REG V Voltage regulator output voltage drop REG, drop I ...
Page 16
Pin connection 4 Pin connection Figure 2. Pin connection (top view) 4.1 Pin list Table 5. Pin description N. Name 17 VDD 6 VREG 7 OSCIN 8 OSCOUT VBOOT 5 ADCIN 2 VSA 26 16/64 Type Power ...
Page 17
L6470 Table 5. Pin description (continued) N. Name 12 VSB 16 27 PGND 13 1 OUT1A 28 OUT2A 14 OUT1B 15 OUT2B 9 AGND DGND 22 BUSY\SYNC Open drain output 18 SDO 20 SDI ...
Page 18
Typical applications 5 Typical applications Table 6. Typical application values Name VSPOL C REG C REGPOL DDPOL D1 C BOOT C FLY Figure 3. ...
Page 19
L6470 6 Functional description 6.1 Device power-up At power-up end, the device state is the following: ● Registers are set to default, ● Internal logic is driven by internal oscillator and a 2MHz clock is provided by OSCOUT pin, ● ...
Page 20
Functional description Figure 4. Charge pump circuitry 6.4 Microstepping The driver is able to divide the single step into up to 128 microsteps. Stepping mode can be programmed by STEP_SEL parameter in STEP_MODE register (see Step mode can be only ...
Page 21
L6470 When motor speed is greater than a programmable full step speed threshold, the L6470 switches automatically to full-step mode; the driving mode returns to microstepping when motor speed decrease below the full step speed threshold. Full step speed threshold ...
Page 22
Functional description 6.7 Motor control commands The L6470 can accept different types of commands: ● constant speed commands (Run, GoUntil, ReleaseSW), ● absolute positioning commands (GoTo, GoTo_DIR, GoHome, GoMark), ● motion commands (Move), ● stop commands (SoftStop, HardStop, SoftHiz, HardHiz). ...
Page 23
L6470 Figure 8. Positioning command examples 6.7.3 Motion commands Motion commands produce a motion in order to perform a user-defined number of microsteps in a user-defined direction that are sent to the device together with the command (see Figure 9). ...
Page 24
Functional description SoftHiZ command causes the motor to decelerate with programmed deceleration value until MIN_SPEED value is reached and then forces the bridges in high impedance state (no holding torque is present). HardHiZ command instantly forces the bridges in high ...
Page 25
L6470 Table 7. CL values according to external oscillator frequency Crystal/resonator freq. 1. First harmonic resonance frequency. 2. Lower ESR value allows driving greater load capacitors direct clock source is used, it must be connected to OSCIN pin ...
Page 26
Functional description The overcurrent threshold can be programmed through the OCD_TH register in one of 16 available values ranging from 375 with steps of 375 mA (see 9.1.17 possible to set if an overcurrent ...
Page 27
L6470 On exit from standby mode the bridges are disabled (HiZ flag high) and whichever motion command makes the device exiting from High Z state (HardStop and SoftStop included). Caution not recommended to reset device when outputs are ...
Page 28
Functional description 6.14 Programmable DMOS slew-rate, dead-time and blanking-time Using the POW_SR parameter in the CONFIG register possible to set the commutation speed of the power bridges output (see 6.15 Integrated analog to digital converter The L6470 integrates ...
Page 29
L6470 6.17 BUSY\SYNC pin This pin is an open drain output which can be used as busy or synchronization signal according to SYNC_EN bit value (STEP_MODE register). 6.17.1 BUSY operation mode The pin works as busy signal when SYNC_EN bit ...
Page 30
Phase current control 7 Phase current control The L6470 controls the phase current applying a sinusoidal voltage to motor windings. Phase current amplitude is not directly controlled but depends on phase voltage amplitude, load torque, motor electrical characteristics and rotation ...
Page 31
L6470 7.2 Sensorless stall detection Depending on motor speed and load angle characteristics, L6470 offers a motor stall condition detection using a programmable current comparator. When a stall event occurs, the respective flag (STEP_LOSS_A or STEP_LOSS_B) is forced low until ...
Page 32
Phase current control 7.4 BEMF compensation Using the speed information, a compensation curve is added to the amplitude of the voltage waveform applied to the motor winding in order to compensate the BEMF variations during acceleration and deceleration (see Compensation ...
Page 33
L6470 Figure 15. Motor supply voltage compensation circuit Motor supply voltage compensation can be enabled setting high the EN_VSCOMP bit of the CONFIG register (see compensation is disabled and the internal analog to digital converter is at user disposal; sampling ...
Page 34
Serial interface 8 Serial interface The integrated 8bit serial peripheral interface (SPI) is used for a synchronous serial communication between the host microprocessor (always master) and the L6470 (always slave). The SPI uses chip select (CS), serial clock (CK), serial ...
Page 35
L6470 Figure 17. Daisy-chain configuration Doc ID 16737 Rev 2 Serial interface 35/64 ...
Page 36
Programming manual 9 Programming manual 9.1 Registers and flags description Following a map of the user registers available (detailed description in respective paragraphs): Table 8. Registers map Address Register name Register function [Hex] h01 ABS_POS Current position h02 EL_POS Electrical ...
Page 37
L6470 Table 8. Registers map (continued) Address Register name Register function [Hex] h18 CONFIG IC configuration h19 STATUS Status h1A RESERVED Reserved address h1B RESERVED Reserved address 1. R: Readable, WH: writable only when outputs are in high impedance, WS: ...
Page 38
Programming manual 9.1.3 MARK The MARK register contains an absolute position called MARK in according to the selected step mode; the stored value unit is equal to the selected step mode (full, half, quarter, etc.). two's complement ...
Page 39
L6470 9.1.6 DEC The DEC register contains the speed profile deceleration expressed in step/tick unsigned fixed point 0.40). In order to convert DEC value in step/s Equation 6 where DEC is the integer number stored into the register and tick ...
Page 40
Programming manual where MIN_SPEED is the integer number stored into the register and tick is the ramp 250 ns. The available range is from 0 to 976.3 step/s with a resolution of 0.238 step/s. When LSPD_OPT bit is set high, ...
Page 41
L6470 Table 11. Voltage amplitude regulation registers 9.1.11 INT_SPEED The INT_SPEED register contains the speed value at which the BEMF compensation curve changes slope (see paragraph convert it in [step/s] the following ...
Page 42
Programming manual 9.1.14 FN_SLP_DEC The FN_SLP_DEC register contains the BEMF compensation curve slope that is used when the speed is greater than the intersect speed during deceleration (see paragraph details). Its value is expressed in s/step and the available range ...
Page 43
L6470 9.1.17 OCD_TH The OCD_TH register contains the overcurrent threshold value (see paragraph details). The available range is from 375 steps of 375 mA as shown in Table 14. Overcurrent detection threshold OCD_TH [3.. ...
Page 44
Programming manual Table 17. Step mode selection STEP_SEL[2.. Every time the step mode is changed the electrical position (i.e. the point of microstepping sinewave that is generated) is reset to the first ...
Page 45
L6470 the synchronization signal is obtained starting from electrical position information (EL_POS register) according to following Table 19. SYNC signal source 9.1.20 ALARM_EN The ALARM_EN register allows selecting which alarm signals are ...
Page 46
Programming manual The OSC_SEL and EXT_CLK bits set the system clock source: Table 22. Oscillator management EXT_CLK OSC_SEL[2.. ...
Page 47
L6470 The OC_SD bit sets if an overcurrent event causes or not the bridges to turn-off; the OCD flag in status register is forced low anyway: Table 24. Overcurrent event OC_SD The POW_SR bits set the slew rate value of ...
Page 48
Programming manual The F_PWM_DEC bits set the multiplication factor of PWM frequency generation. Table 28. PWM frequency: multiplication factor F_PWM_DEC [2.. the following tables all available PWM frequencies are listed according ...
Page 49
L6470 Table 30. Available PWM frequencies [kHz]: 16 MHz oscillator frequency F_PWM_INT 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 Table 31. Available PWM frequencies [kHz]: 24 MHz oscillator frequency F_PWM_INT 000 001 010 011 100 101 110 F_PWM_DEC 000 001 ...
Page 50
Programming manual Table 32. Available PWM frequencies [kHz]: 32 MHz oscillator frequency F_PWM_ 000 INT 000 39.1 001 19.5 010 13.0 011 9.8 100 7.8 101 6.5 110 5.6 Any attempt to write the CONFIG register when the motor is ...
Page 51
L6470 The UVLO, TH_WRN, TH_SD, OCD, STEP_LOSS_A, STEP_LOSS_B, NOTPERF_CMD, WRONG_CMD and SW_EVN flags are latched: when the respective conditions make them active (low or high) they remain in that state until a GetStatus command is sent to the IC. The ...
Page 52
Programming manual 9.2 Application commands The commands summary is given in the Table 36. Application commands Command Mnemonic Command binary code [7..5] [4] NOP 000 SetParam(PARAM,VALUE) 000 GetParam(PARAM) 001 Run(DIR,SPD) 010 StepClock(DIR) 010 Move(DIR,N_STEP) 010 GoTo(ABS_POS) 011 GoTo_DIR(DIR,ABS_POS) 011 GoUntil(ACT,DIR,SPD) ...
Page 53
L6470 9.2.1 Command management The host microcontroller can control motor motion and configure the L6470 through a complete set of commands. All commands are composed by a single byte. After the command byte, some bytes of arguments should be needed ...
Page 54
Programming manual 9.2.3 SetParam (PARAM, VALUE) Table 38. SetParam command structure Bit 7 Bit The SetParam command sets the PARAM register value equal to VALUE; PARAM is the respective register address listed in Some registers cannot be ...
Page 55
L6470 9.2.5 Run (DIR, SPD) Table 40. Run command structure Bit 7 Bit The Run command produces a motion at SPD speed; the direction is selected by DIR bit: '1' forward or '0' reverse. The ...
Page 56
Programming manual 9.2.7 Move (DIR, N_STEP) Table 42. Move command structure Bit 7 Bit The move command produces a motion of N_STEP microsteps; the direction is selected by DIR bit ('1' forward or '0' reverse). ...
Page 57
L6470 9.2.9 GoTo_DIR (DIR, ABS_POS) Table 44. GoTo_DIR command structure Bit 7 Bit The GoTo_DIR command produces a motion to ABS_POS absolute position imposing a forward (DIR = '1 reverse (DIR = '0') ...
Page 58
Programming manual 9.2.11 ReleaseSW (ACT, DIR) Table 46. ReleaseSW command structure Bit 7 Bit The ReleaseSW command produces a motion at minimum speed imposing a forward (DIR = '1') or reverse (DIR = '0') rotation. When SW ...
Page 59
L6470 Any attempt to perform a GoMark command when a previous command is under execution (BUSY low) causes the command to be ignored and the NOTPERF_CMD flag to rise (see paragraph 9.1.22 9.2.14 ResetPos Table 49. ResetPos command structure Bit ...
Page 60
Programming manual When the motor is in high-impedance state, a HardStop command forces the bridges to exit from high impedance state; no motion is performed. 9.2.18 SoftHiZ Table 53. SoftHiZ command structure Bit 7 Bit The SoftHiZ ...
Page 61
L6470 10 Package mechanical data In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of ECOPACK® packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK® specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: ECOPACK is ...
Page 62
Package mechanical data Figure 21. HTSSOP28 mechanical data 62/64 Doc ID 16737 Rev 2 L6470 ...
Page 63
L6470 11 Revision history Table 57. Document revision history Date 06-Nov-2009 05-Nov-2010 Revision 1 Initial release. 2 Document status promoted from preliminary data to datasheet. Doc ID 16737 Rev 2 Revision history Changes 63/64 ...
Page 64
... Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any time, without notice. All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale. ...