SC16C850SVIBS-S NXP Semiconductors, SC16C850SVIBS-S Datasheet
SC16C850SVIBS-S
Specifications of SC16C850SVIBS-S
Related parts for SC16C850SVIBS-S
SC16C850SVIBS-S Summary of contents
Page 1
SC16C754 Quad UART with 64-byte FIFO Rev. 04 — 19 June 2003 1. Description The SC16C754 is a quad universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) with 64-byte FIFOs, automatic hardware/software flow control, and data rates Mbits/s (3.3 V and ...
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Prescaler provides additional divide-by-4 function Fast databus access time Programmable sleep mode Programmable serial interface characteristics False start bit detection Complete status reporting capabilities in both normal and sleep mode Line break generation and detection Internal test and ...
Page 3
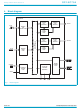
Philips Semiconductors 4. Block diagram SC16C754 D0–D7 DATA BUS IOR AND IOW CONTROL LOGIC RESET A0–A2 REGISTER CSA-CSD SELECT LOGIC INTA-INTD TXRDY RXRDY INTERRUPT CONTROL LOGIC INTSEL Fig 1. Block diagram. 9397 750 11618 Product data TRANSMIT TRANSMIT FIFO SHIFT ...
Page 4
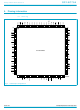
Philips Semiconductors 5. Pinning information 5.1 Pinning handbook, full pagewidth DSRA 3 CTSA 4 DTRA RTSA 7 INTA 8 CSA 9 TXA 10 IOW 11 TXB 12 CSB 13 INTB 14 RTSB ...
Page 5
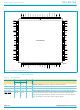
Philips Semiconductors handbook, full pagewidth DSRA 10 CTSA 11 DTRA RTSA 14 INTA 15 CSA 16 TXA 17 IOW 18 TXB 19 CSB 20 INTB 21 RTSB 22 GND 23 DTRB 24 CTSB 25 DSRB 26 ...
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Table 2: Pin description …continued Symbol Pin LQFP80 PLCC68 CLKSEL 26 30 CSA, CSB, 9, 13, 16, 20, CSC, CSD 49, 53 50, 54 CTSA, CTSB, 4, 18, 11, 25, CTSC, CTSD 44, 58 45, 59 D0-D2, 68-70, ...
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Table 2: Pin description …continued Symbol Pin LQFP80 PLCC68 IOW 20, 31 21, 22, 27, 40, 41, 42, 60, 61, 62, 80 RESET 33 37 RIA, RIB, 78, 24, 8, 28, RIC, RID ...
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Table 2: Pin description …continued Symbol Pin LQFP80 PLCC68 V 6, 46, 66 13, 47 XTAL1 31 35 XTAL2 Functional description The SC16C754 UART is pin-compatible with the SC16C554 and SC16C654 UARTs. It ...
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors With Auto-CTS, CTS must be active before the UART can transmit data. Auto-RTS only activates the RTS output when there is enough room in the FIFO to receive data and de-activates the RTS output when the RX FIFO ...
Page 10
Philips Semiconductors RX START BYTE N RTS IOR ( receiver FIFO trigger level. (2) The two blocks in dashed lines cover the case where an additional byte is sent, as described in Fig 5. RTS functional timing. 6.2.2 ...
Page 11
Philips Semiconductors Table 3: EFR[ Remark: When using software flow control, the Xon/Xoff characters cannot be used for data characters. There are two other enhanced features relating to software flow control: • Xon Any ...
Page 12
Philips Semiconductors It is assumed that software flow control and hardware flow control will never be enabled simultaneously. 6.3.3 Software flow control example Fig 7. Software flow control example. Assumptions: using software flow control with single character Xoff (0F) and ...
Page 13
Philips Semiconductors Table 4: Register Interrupt enable register Interrupt identification register FIFO control register Line control register Modem control register Line status register Modem status register Enhanced feature register Receiver holding register Transmitter holding register Transmission control register Trigger level ...
Page 14
Philips Semiconductors 6.5 Interrupts The SC16C754 has interrupt generation and prioritization (six prioritized levels of interrupts) capability. The interrupt enable register (IER) enables each of the six types of interrupts and the INT signal in response to an interrupt generation. ...
Page 15
Philips Semiconductors 6.5.1 Interrupt mode operation In interrupt mode (if any bit of IER[3: the processor is informed of the status of the receiver and transmitter by an interrupt signal, INT. Therefore not necessary to continuously ...
Page 16
Philips Semiconductors 6.6 DMA operation There are two modes of DMA operation, DMA mode 0 or DMA mode 1, selected by FCR[3]. In DMA mode 0 or FIFO disable (FCR[ DMA occurs in single character transfers. In DMA ...
Page 17
Philips Semiconductors 6.6.2 Block DMA transfers (DMA mode 1) Figure 11 wrptr TRIGGER LEVEL wrptr Fig 11. TXRDY and RXRDY in DMA mode 1. Transmitter: available. It becomes inactive when the FIFO is full. Receiver: a time-out interrupt occurs. It ...
Page 18
Philips Semiconductors 6.8 Break and time-out conditions An RX idle condition is detected when the receiver line, RX, has been HIGH for 4 character time. The receiver line is sampled midway through each bit. When a break condition occurs, the ...
Page 19
Philips Semiconductors Table 7: Desired baud rate 50 75 110 134.5 150 300 600 1200 1800 2000 2400 3600 4800 7200 9600 19200 38400 56000 Table 8: Desired baud rate 50 75 110 134.5 150 300 600 1200 1800 2000 ...
Page 20
Philips Semiconductors Fig 13. Crystal oscillator connection. 7. Register descriptions Each register is selected using address lines A0, A1, A2, and in some cases, bits from other registers. The programming combinations for register selection are shown in Table Table 9: ...
Page 21
Philips Semiconductors Table 10 Table 10: SC16C754 internal registers Register Bit 7 [1] General Register Set RHR bit THR bit IER 0/CTS interrupt [2] enable 0 ...
Page 22
Philips Semiconductors Remark: Refer to the notes under 7.1 Receiver holding register (RHR) The receiver section consists of the receiver holding register (RHR) and the receiver shift register (RSR). The RHR is actually a 64-byte FIFO. The RSR receives serial ...
Page 23
Philips Semiconductors 7.3 FIFO control register (FCR) This is a write-only register that is used for enabling the FIFOs, clearing the FIFOs, setting transmitter and receiver trigger levels, and selecting the type of DMA signalling. Table 11: Bit 7-6 5-4 ...
Page 24
Philips Semiconductors 7.4 Line control register (LCR) This register controls the data communication format. The word length, number of stop bits, and parity type are selected by writing the appropriate bits to the LCR. Table 12 Table 12: Bit 7 ...
Page 25
Philips Semiconductors 7.5 Line status register (LSR) Table 13 Table 13: Bit When the LSR is read, LSR[4:2] reflect the error bits (BI, FE, PE) of the character at the top of ...
Page 26
Philips Semiconductors 7.6 Modem control register (MCR) The MCR controls the interface with the mode, data set, or peripheral device that is emulating the modem. Table 14: Bit [1] MCR[7:5] can only ...
Page 27
Philips Semiconductors 7.7 Modem status register (MSR) This 8-bit register provides information about the current state of the control lines from the mode, data set, or peripheral device to the processor. It also indicates when a control input from the ...
Page 28
Philips Semiconductors Table 16: Bit [1] IER[7:4] can only be modified if EFR[4] is set, i.e., EFR[ write enable. Re-enabling IER[1] will not cause a new interrupt if the THR is below the ...
Page 29
Philips Semiconductors Table 18: Priority level 7.10 Enhanced feature register (EFR) This 8-bit register enables or disables the enhanced features of the UART. shows the enhanced feature register bit settings. Table 19: Bit ...
Page 30
Philips Semiconductors 7.11 Divisor latches (DLL, DLH) These are two 8-bit registers which store the 16-bit divisor for generation of the baud clock in the baud rate generator. DLH stores the most significant part of the divisor. DLL stores the ...
Page 31
Philips Semiconductors 7.14 FIFO ready register The FIFO ready register provides real-time status of the transmit and receive FIFOs of both channels. Table 22: Bit 7-4 3-0 The FIFO Rdy register is a read-only register that can be accessed when ...
Page 32
Philips Semiconductors 8. Programmer’s guide The base set of registers that is used during high-speed data transfer have a straightforward access method. The extended function registers require special access bits to be decoded along with the address lines. The following ...
Page 33
Philips Semiconductors Table 23: Command Set TX FIFO and RX FIFO thresholds to VALUE Read FIFO Rdy register Set prescaler value to divide-by-1 Set prescaler value to divide-by-4 [1] 9397 750 11618 Product data Register programming guide sign here means ...
Page 34
Philips Semiconductors 9. Limiting values Table 24: Limiting values In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Parameter V supply voltage CC V input voltage I V output voltage O T operating ambient temperature amb T storage ...
Page 35
Philips Semiconductors 10. Static characteristics Table 25: DC electrical characteristics V = 2.5 V, 3 10%. CC Symbol Parameter Conditions V supply voltage CC V input voltage I V HIGH-level input IH voltage V LOW-level ...
Page 36
Philips Semiconductors 11. Dynamic characteristics Table 26: AC electrical characteristics + 2 5.0 V 10%, unless otherwise specified. amb CC Symbol Parameter clock pulse duration ...
Page 37
Philips Semiconductors 11.1 Timing diagrams A0– CSx t 13d IOW D0–D7 Fig 14. General write timing. A0– CSx t 7d IOR D0–D7 Fig 15. General read timing. 9397 750 11618 Product data t 6h VALID ADDRESS ...
Page 38
Philips Semiconductors IOW ACTIVE RTS CHANGE OF STATE DTR CD CTS DSR INT IOR RI Fig 16. Modem input/output timing EXTERNAL CLOCK Fig 17. External clock timing. 9397 750 11618 Product data t 17d CHANGE OF STATE CHANGE ...
Page 39
Philips Semiconductors START BIT RX INT IOR Fig 18. Receive timing. START BIT RX RXRDY IOR Fig 19. Receive ready timing in non-FIFO mode. 9397 750 11618 Product data DATA BITS (5- DATA ...
Page 40
Philips Semiconductors START BIT RX RXRDY IOR Fig 20. Receive ready timing in FIFO mode. START BIT TX INT t 23d ACTIVE IOW Fig 21. Transmit timing. 9397 750 11618 Product data DATA BITS (5– ...
Page 41
Philips Semiconductors START BIT TX ACTIVE IOW D0–D7 BYTE #1 t 27d TXRDY Fig 22. Transmit ready timing in non-FIFO mode. 9397 750 11618 Product data DATA BITS (5- ACTIVE TRANSMITTER READY TRANSMITTER NOT READY ...
Page 42
Philips Semiconductors START BIT TX ACTIVE IOW D0–D7 BYTE #32 t 27d TXRDY Fig 23. Transmit ready timing in FIFO mode (DMA mode ‘1’). 9397 750 11618 Product data DATA BITS (5- DATA ...
Page 43
Philips Semiconductors 12. Package outline LQFP80: plastic low profile quad flat package; 80 leads; body 1 pin 1 index DIMENSIONS (mm are the ...
Page 44
Philips Semiconductors PLCC68: plastic leaded chip carrier; 68 leads pin 1 index DIMENSIONS (mm dimensions are derived from the original inch dimensions ...
Page 45
Philips Semiconductors 13. Soldering 13.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount packages This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in our Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages ...
Page 46
Philips Semiconductors • For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e): – larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis is preferred to be – smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis must ...
Page 47
Philips Semiconductors [3] These transparent plastic packages are extremely sensitive to reflow soldering conditions and must on no account be processed through more than one soldering cycle or subjected to infrared reflow soldering with peak temperature exceeding 217 C oven. ...
Page 48
Philips Semiconductors 15. Data sheet status [1] Level Data sheet status Product status I Objective data Development II Preliminary data Qualification III Product data Production [1] Please consult the most recently issued data sheet before initiating or completing a design. ...
Page 49
Philips Semiconductors Contents 1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features . . . ...