MT46H64M16LFCK-6:ATR Micron Technology Inc, MT46H64M16LFCK-6:ATR Datasheet - Page 57

MT46H64M16LFCK-6:ATR
Manufacturer Part Number
MT46H64M16LFCK-6:ATR
Description
Manufacturer
Micron Technology Inc
Type
DDR SDRAMr
Datasheet
1.MT46H64M16LFCK-6ATR.pdf
(96 pages)
Specifications of MT46H64M16LFCK-6:ATR
Organization
64Mx16
Density
1Gb
Address Bus
14b
Access Time (max)
6.5/5.5ns
Maximum Clock Rate
166MHz
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
1.8V
Package Type
VFBGA
Operating Temp Range
0C to 70C
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
1.95V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
1.7V
Supply Current
115mA
Pin Count
60
Mounting
Surface Mount
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Compliant
READ Operation
PDF: 09005aef82ce3074
1gb_ddr_mobile_sdram_t48m.pdf - Rev. L 04/10 EN
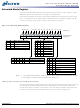
READ burst operations are initiated with a READ command, as shown in Figure 10
(page 35). The starting column and bank addresses are provided with the READ com-
mand, and auto precharge is either enabled or disabled for that burst access. If auto
precharge is enabled, the row being accessed is precharged at the completion of the
burst. For the READ commands used in the following illustrations, auto precharge is
disabled.
During READ bursts, the valid data-out element from the starting column address will
be available following the CL after the READ command. Each subsequent data-out ele-
ment will be valid nominally at the next positive or negative clock edge. Figure 22
(page 58) shows general timing for each possible CL setting.
DQS is driven by the device along with output data. The initial LOW state on DQS is
known as the read preamble; the LOW state coincident with the last data-out element is
known as the read postamble. The READ burst is considered complete when the read
postamble is satisfied.
Upon completion of a burst, assuming no other commands have been initiated, the DQ
will go to High-Z. A detailed explanation of
window hold), and the valid data window is depicted in Figure 29 (page 65) and Fig-
ure 30 (page 66). A detailed explanation of
t
Data from any READ burst can be truncated by a READ or WRITE command to the
same or alternate bank, by a BURST TERMINATE command, or by a PRECHARGE com-
mand to the same bank, provided that the auto precharge mode was not activated.
Data from any READ burst can be concatenated with or truncated with data from a sub-
sequent READ command. In either case, a continuous flow of data can be maintained.
The first data element from the new burst either follows the last element of a completed
burst or the last desired data element of a longer burst that is being truncated. The new
READ command should be issued x cycles after the first READ command, where x
equals the number of desired data element pairs (pairs are required by the 2n-prefetch
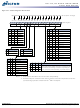
architecture). This is shown in Figure 23 (page 59).
A READ command can be initiated on any clock cycle following a previous READ com-
mand. Nonconsecutive read data is shown in Figure 24 (page 60). Full-speed random
read accesses within a page (or pages) can be performed as shown in Figure 25
(page 61).
Data from any READ burst can be truncated with a BURST TERMINATE command, as
shown in Figure 26 (page 62). The BURST TERMINATE latency is equal to the READ
(CAS) latency; for example, the BURST TERMINATE command should be issued x cy-
cles after the READ command, where x equals the number of desired data element pairs
(pairs are required by the 2n-prefetch architecture).
Data from any READ burst must be completed or truncated before a subsequent WRITE
command can be issued. If truncation is necessary, the BURST TERMINATE command
must be used, as shown in Figure 27 (page 63). A READ burst can be followed by, or
truncated with, a PRECHARGE command to the same bank, provided that auto pre-
charge was not activated. The PRECHARGE command should be issued x cycles after
the READ command, where x equals the number of desired data element pairs. This is
shown in Figure 28 (page 64). Following the PRECHARGE command, a subsequent
AC (data-out transition skew to CK) is depicted in Figure 31 (page 67).
57
1Gb: x16, x32 Mobile LPDDR SDRAM
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
t
DQSCK (DQS transition skew to CK) and
t
DQSQ (valid data-out skew),
© 2007 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
READ Operation
t
QH (data-out