ST72260G1 STMicroelectronics, ST72260G1 Datasheet - Page 81

ST72260G1
Manufacturer Part Number
ST72260G1
Description
8-BIT MCU WITH FLASH OR ROM MEMORY, ADC, TWO 16-BIT TIMERS, I2C, SPI, SCI INTERFACES
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST72262G2.pdf
(172 pages)
Specifications of ST72260G1
4 K Or 8 Kbytes Program Memory
ROM or single voltage extended Flash (XFlash) with read-out protection, write protection, In-Circuit Programming and In-Application Programming (ICP and IAP). 10K write/erase cycles guaranteed, data retention
Clock Sources
crystal/ceramic resonator oscillators, internal RC oscillator and bypass for external clock
4 Power Saving Modes
Halt, Active Halt,Wait and Slow
Two 16-bit Timers With
2 input captures, 2 output compares, external clock input on one timer, PWM and Pulse generator modes
- Current page: 81 of 172
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d)
11.4.5 Error Flags
11.4.5.1 Master Mode Fault (MODF)
Master mode fault occurs when the master device
has its SS pin pulled low.
When a Master mode fault occurs:
Clearing the MODF bit is done through a software
sequence:
1. A read access to the SPICSR register while the
2. A write to the SPICR register.
Notes: To avoid any conflicts in an application
with multiple slaves, the SS pin must be pulled
high during the MODF bit clearing sequence. The
SPE and MSTR bits may be restored to their orig-
inal state during or after this clearing sequence.
Hardware does not allow the user to set the SPE
and MSTR bits while the MODF bit is set except in
the MODF bit clearing sequence.
In a slave device, the MODF bit can not be set, but
in a multi master configuration the
slave mode with the MODF bit set.
The MODF bit indicates that there might have
been a multi-master conflict and allows software to
handle this using an interrupt routine and either
perform to a reset or return to an application de-
fault state.
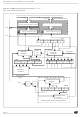
Figure 51. Clearing the WCOL bit (Write Collision Flag) Software Sequence
1st Step
2nd Step
– The MODF bit is set and an SPI interrupt re-
– The SPE bit is reset. This blocks all output
– The MSTR bit is reset, thus forcing the Device
quest is generated if the SPIE bit is set.
from the Device and disables the SPI periph-
eral.
into slave mode.
MODF bit is set.
Clearing sequence after SPIF = 1 (end of a data byte transfer)
Clearing sequence before SPIF = 1 (during a data byte transfer)
1st Step
2nd Step
Read SPICSR
Read SPIDR
RESULT
SPIF =0
WCOL=0
Read SPIDR
Read SPICSR
Device
can be in
RESULT
WCOL=0
11.4.5.2 Overrun Condition (OVR)
An overrun condition occurs, when the master de-
vice has sent a data byte and the slave device has
not cleared the SPIF bit issued from the previously
transmitted byte.
When an Overrun occurs:
– The OVR bit is set and an interrupt request is
In this case, the receiver buffer contains the byte
sent after the SPIF bit was last cleared. A read to
the SPIDR register returns this byte. All other
bytes are lost.
The OVR bit is cleared by reading the SPICSR
register.
11.4.5.3 Write Collision Error (WCOL)
A write collision occurs when the software tries to
write to the SPIDR register while a data transfer is
taking place with an external device. When this
happens, the transfer continues uninterrupted;
and the software write will be unsuccessful.
Write collisions can occur both in master and slave
mode. See also
Management" on page
Note: a "read collision" will never occur since the
received data byte is placed in a buffer in which
access is always synchronous with the CPU oper-
ation.
The WCOL bit in the SPICSR register is set if a
write collision occurs.
No SPI interrupt is generated when the WCOL bit
is set (the WCOL bit is a status flag only).
Clearing the WCOL bit is done through a software
sequence (see
generated if the SPIE bit is set.
ST72260Gx, ST72262Gx, ST72264Gx
Note: Writing to the SPIDR regis-
ter instead of reading it does not
reset the WCOL bit
Figure
Section 11.4.3.2 "Slave Select
51).
78.
81/172
Related parts for ST72260G1
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN Transistor Power Module
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: