TB6572AFG*** Toshiba, TB6572AFG*** Datasheet

TB6572AFG***
Specifications of TB6572AFG***
Related parts for TB6572AFG***
TB6572AFG*** Summary of contents
Page 1
... TOSHIBA Bi- CMOS Integrated Circuit Silicon Monolithic 3-Phase Full-Wave Brushless Motor Controller Featuring Speed Control and Sine Wave PWM Drive The TB6572AFG is a 3-phase full-wave brushless motor controller IC that employs a sine wave PWM drive mechanism with a speed control function. Sine wave current driving with 2-phase modulation enables the IC to drive a motor with high efficiency and low noise ...
Page 2
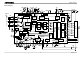
Block Diagram R19 C20 C19 Fref LP1 11 Vref1(5 V) Phase comparator LPF 1/1024 frequency C21 R1 HA+ 51 divider HA− 52 C22 HB+ 1 HB− 2 C23 HC+ 3 HC− Ready R3 circuit Frequency 13 Gain Speed ...
Page 3
Pin Functions Pin No. Name Phase-B hall signal input + pin 1 HB+ Phase-B hall signal input − pin 2 HB− Phase-C hall signal input + pin 3 HC+ Phase-C hall signal input − pin 4 HC− FG amplifier input ...
Page 4
Pin No. Name 38 CP1 Charge pump pin 39 CP3 Charge pump pin 40 Idc2 Input pin for output current detection signal 41 Idc1 Input pin for output current detection signal 42 LA (U) Phase-A energization signal output (U1) 43 ...
Page 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings Characteristics Supply voltage Input voltage Output voltage Output current Power dissipation Operating temperature Storage temperature Note Note 2: CW/CCW, START, BRAKE, Idc2, F Note 3: Ready, FGS Note 4: OUT-A, OUT-B, OUT-C Note 5: ...
Page 6
Functional Description The equivalent circuit diagrams may be simplified or some parts of them may be omitted for explanatory purposes. 1. Sine Wave PWM Drive < Energization Switching > Upon start-up, the TB6572AFG drives the motor with square waves for ...
Page 7
The TB6572AFG uses position detection signals to create modulation waveforms, which it compares with triangular waves to generate sine wave PWM signals. It counts the time between zero-crossing points for the three position detection signals (electrical angle: 60°) and uses ...
Page 8
In addition, the TB6572AFG performs phase alignment with the modulation waveforms at each zero-crossing in the position detection signals. For every 60° of electrical angle, it synchronizes with the rising and falling edges of the position detection signals (Hall amplifier ...
Page 9
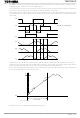
Timing Charts HA Position detection HB (Hall amplifier HC output) LA (U) Energization LB (U) signal output LC (U) when driven LA (L) with square wave LB ( Modulation waveform when driven with sine S B ...
Page 10
Generating an Internal Reference Clock The TB6572AFG uses external C and R to generate a reference clock internally. It uses the reference clock to generate triangular waves, which determine the carrier frequency, and set a dead time. The clock ...
Page 11
External FET Gate Drive Output Impedance must be reduced when FETs are driven. To control impedance, source and sink outputs are configured as shown at right. Resistors are incorporated to control source and sink outputs of FETs, and each ...
Page 12
Gain Control Circuitry The gain control circuitry dynamically selects the gain of the speed discriminator, based on the rpm command (i.e., Fref frequency). The gain control circuitry is designed to change the peak voltage of the deviation signal from ...
Page 13
Control Amplifier INTEG-out • The voltage integrated in the charge pump is input to the control amplifier. The input is placed in high-impedance state because P-ch gate. The equivalent circuit diagrams may be simplified or some ...
Page 14
FG Amplifier/Hysteresis Comparator V ref1 V ref1 + FGin • The FG amplifier supports pattern FG and incorporates an internal reference voltage of 2.5 V. Entering a sine wave The open loop gain ...
Page 15
Hall Amplifier • The Hall amplifier accepts Hall device output signals. If input signals contain noise, connect a capacitor between inputs. • The common-mode input voltage range is: VCMRH = 0.5 to 3.4 V. The Hall amplifier has an ...
Page 16
Forward/Reverse Rotation Circuit CW/CCW The circuit accepts a TTL input and incorporates a pull-up resistor. CW/CCW Input Mode H Reverse L Forwared Forward: Hall device signals HA Note that abrupt switching between forward and reverse rotation may result in ...
Page 17
Operation Sequence VM power supply Vref power supply (+ power DD supply (+ power supply (+8 V) Internal reference clock fx2 Output charge pump voltage External reference clock fref System clock fx1 (fref multiplied) PLL ...
Page 18
Automatic Phase Lead Angle Correction Circuit Timing charts may be simplified for explanatory purposes. • The lead angle correction circuitry is incorporated, and the motor current value flows into the circuit. Automatic Lead angle Correction Gain × V Motor ...
Page 19
V Bounce Prevention CC The TB6572AFG contains a circuit to avoid the V This is accomplished by switching the drive mode from synchronous rectification to high-side PWM. (1) Switching from synchronous rectification to high-side PWM The TB6572AFG continually monitors ...
Page 20
V Bounce Prevention Mode (typ.) V bounce Constant speed Integral amp output (speed command) Deceleration mode LOW START READY output Drive mode Sync. rectification *: The READY ...
Page 21
Constant Voltage Circuit (1) V ref1 The circuit creates 5 V for biasing the internal analog circuit and outputs it from the V Connect a capacitor (0.1 μ μF) between the V S-GND to prevent oscillation and ...
Page 22
Electrical Characteristics Characteristics Supply current Common-mode input voltage range Hall Input amplitude range amplifier Input hysteresis Input current Remaining output Ready voltage circuit Output leakage current Input offset voltage Remaining output voltage (upper) FG amplifier Remaining output voltage (lower) Reference ...
Page 23
Characteristics Phase lead angle Lower clamp limit controller Rising voltage Control Saturation voltage amplifier Input current Reference voltage High-level output voltage Integral Low-level output voltage amplifter Input bias current Open-loop gain Speed Maximum output voltage discrimina Minimum output voltage tor ...
Page 24
... Application Circuits The application circuits shown in this document are provided for reference purposes only. Thorough evaluation is required, especially at the mass production design stage. Toshiba does not grant any license to any industrial property rights by providing these examples of application circuits. 4. Test Circuits Components in the test circuits are used only to obtain and confirm the device characteristics. These components and circuits are not guaranteed to prevent malfunction or failure from occurring in the application equipment ...
Page 25
Points to remember on handling of ICs (1) Over current Protection Circuit Over current protection circuits (referred to as current limiter circuits) do not necessarily protect ICs under all circumstances. If the Over current protection circuits operate against the over ...
Page 26
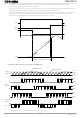
Package Dimensions Weight: 0.50 g (typ.) 26 TB6572AFG 2008-1-21 ...
Page 27
... The information contained herein is presented only as a guide for the applications of our products. No responsibility is assumed by TOSHIBA for any infringements of patents or other rights of the third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other rights of TOSHIBA or the third parties. ...