S1K50000 Epson Electronics America, Inc., S1K50000 Datasheet - Page 16

S1K50000
Manufacturer Part Number
S1K50000
Description
Design Guide S1k50000 Series
Manufacturer
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet
1.S1K50000.pdf
(131 pages)
- Current page: 16 of 131
- Download datasheet (2Mb)
2.4 Hazard Protection
2.5 Fan-Out Limitations
STANDARD CELL S1K50000 SERIES
DESIGN GUIDE
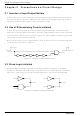
In circuits or decoders configured by combining gates such as NAND or NOR gates, a very
short pulse may be generated due to the difference in delay times between gates. This short
pulse is known as a hazard, and it causes malfunction when fed into the clock or reset pins of
flip-flips.
Therefore, circuits where such a hazard is likely to occur must be configured so as to prevent
the hazard from propagating. For decoders, it may be necessary to use a circuit that has an
enable pin.
The tpd of logic gates is determined by the load capacitance of their output pin. An
excessively large load capacitance may not only cause the tpd to become large, but may also
cause malfunction. Therefore, there are limitations on the number of loads that can be
connected to the output pins of each logic gate. These are known as “fan-out” limitations.
The input-pin capacitance of each logic gate, however, tends to differ depending on the logic-
gate input. The input capacitance of each logic gate, in terms of the input capacitance of an
inverter (KINI) = 1, is known as “fan-in.”
In the design of your circuit, make sure the total number of fan-ins connected to the output pins
of each logic gate does not exceed the fan-out limitations of those output pins.
Furthermore, for logic gates operating at high speed, such as high-speed clock lines (fmax =
40 MHz or more), make sure the output-pin capacitance of those gates is approximately half
the fan-out limitation.
EPSON
Chapter 2: Precautions on Circuit Design
11
Related parts for S1K50000
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Optical Devicepbs-prism For Blue
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Optical Device Ir-cut Filter
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Optical Device
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d15000 Series Lcd Driver With Ram
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d12000 Series Lcd Driver Ic Technical Manual Technical Manual
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d13521 Epd Controller
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d13710 Mobile Graphics Engine
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d13711 Mobile Graphics Engine
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Liquid Crystal Display =lcd Driver
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Embedded Memory Graphics Lcd Controller
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d13705 Embedded Memory Lcd Controller
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
S1d13503 Graphics Lcd Controller
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Embedded Memory Graphics Lcd Controller
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Interlace Progressive Conversion Ic
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Dual Camera Controller With Jpeg Encoder
Manufacturer:
Epson Electronics America, Inc.
Datasheet: