epf6016ati144-2 Altera Corporation, epf6016ati144-2 Datasheet - Page 17

epf6016ati144-2
Manufacturer Part Number
epf6016ati144-2
Description
Programmable Logic Device Family
Manufacturer
Altera Corporation
Datasheet
1.EPF6016ATI144-2.pdf
(52 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
EPF6016ATI144-2
Manufacturer:
ALTERA
Quantity:
115
Company:
Part Number:
epf6016ati144-2N
Manufacturer:
ALTERA
Quantity:
1
FLEX 6000 Programmable Logic Device Family Data Sheet
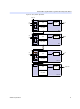
Figure 8. LE Clear & Preset Modes
Asynchronous Clear
Asynchronous Preset
labctrl1 or
labctrl2
Chip-Wide Reset
D
Q
PRN
D
Q
CLRN
labctrl1 or
labctrl2
Chip-Wide Reset
Asynchronous Clear
The flipflop can be cleared by either LABCTRL1 or LABCTRL2.
Asynchronous Preset
An asynchronous preset is implemented with an asynchronous clear. The
Altera software provides preset control by using the clear and inverting
the input and output of the register. Inversion control is available for the
inputs to both LEs and IOEs. Therefore, this technique can be used when
a register drives logic or drives a pin.
In addition to the two clear and preset modes, FLEX 6000 devices provide
a chip-wide reset pin (DEV_CLRn) that can reset all registers in the device.
The option to use this pin is set in the Altera software before compilation.
The chip-wide reset overrides all other control signals. Any register with
an asynchronous preset will be preset when the chip-wide reset is asserted
because of the inversion technique used to implement the asynchronous
preset.
The Altera software can use a programmable NOT-gate push-back
technique to emulate simultaneous preset and clear or asynchronous load.
However, this technique uses an additional three LEs per register.
FastTrack Interconnect
In the FLEX 6000 OptiFLEX architecture, connections between LEs and
device I/O pins are provided by the FastTrack Interconnect, a series of
continuous horizontal and vertical routing channels that traverse the
device. This global routing structure provides predictable performance,
even for complex designs. In contrast, the segmented routing in FPGAs
requires switch matrices to connect a variable number of routing paths,
increasing the delays between logic resources and reducing performance.
Altera Corporation
17