m28256 STMicroelectronics, m28256 Datasheet - Page 5

m28256
Manufacturer Part Number
m28256
Description
256 Kbit 32kb X8 Parallel Eeprom With Software Data Protection
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.M28256.pdf
(21 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
m28256-15W6
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
51
Status Register
The devices provide several Write operation status
flags that can be used to minimize the application
write time. These signals are available on the I/O
port bits during programming cycle only.
Data Polling bit (DQ7). During the internal write
cycle, any attempt to read the last byte written will
produce on DQ7 the complementary value of the
previously latched bit. Once the write cycle is fin-
ished the true logic value appears on DQ7 in the
read cycle.
Toggle bit (DQ6). The devices offer another way
for determining when the internal write cycle is
completed. During the internal Erase/Write cycle,
DQ6 will toggle from ”0” to ”1” and ”1” to ”0” (the
first read value is ”0”) on subsequent attempts to
read any byte of the memory. When the internal
cycle is completed the toggling will stop and the
data read on DQ7-DQ0 is the addressed memory
byte. The device is now accessible for a new Read
or Write operation.
Page Load TimerStatus bit(DQ5). Duringa Page
Write instruction, the devices expect to receive the
stream of data with a minimum period of time
between each data byte. This period of time
(t
which running/overflow status is available on DQ5.
DQ5 Low indicates that the timer is running, DQ5
High indicates the time-out after which the internal
write cycle will start.
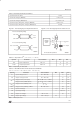
Figure 4. Status Bit Assignment
WHWH
DP
TB
PLTS = Page Load Timer Status
DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 DQ4 DQ3 DQ2 DQ1 DQ0
DP
) is defined by the on-chip Page Load timer
= Data Polling
= Toggle Bit
TB
PLTS
X
X
X
X
X
Software Data Protection
The devices offer a software controlled write pro-
tection facility that allows the user to inhibit all write
modes to the device. This can be useful in protect-
ing the memory from inadvertent write cycles that
may occur due to uncontrolledbus conditions.
The devices are shipped as standardin the ”unpro-
tected” state meaning that the memory contents
can be changed as required by the user. After the
Software Data Protection enable algorithm is is-
sued, the device enters the ”Protect Mode” of
operation where no further write commands have
any effect on the memory contents.
The devices remain in this mode until a valid
Software Data Protection (SDP) disable sequence
is received whereby the device reverts to its ”un-
protected” state. The Software Data Protection is
fully non-volatile and is not changed by power
on/off sequences. To enable the Software Data
Protection (SDP) the device requires the user to
write (with a Page Write addressing three specific
data bytes to three specific memorylocations,each
location in a different page) as per Figure 6. Simi-
larly to disable the Software Data Protection the
user has to write specific data bytes into six differ-
ent locations as per Figure 5 (with a Page Write
adressing different bytes in different pages).
This complexseries ensures that the userwill never
enable or disable the Software Data Protection
accidentally.
To write into the devices when SDP is set, the
sequence shown in Figure 6 must be used. This
sequence provides an unlock key to enable the
write action, and at the same time SDP continues
to be set.
An extension to this is where SDP is required to be
set, and data is to be written.
Using the same sequence as above, the data can
be written and SDP is set at the same time, giving
both these actions in the same Write cycle (t
M28256
WC
5/21
).