LED7708 STMicroelectronics, LED7708 Datasheet - Page 25

LED7708
Manufacturer Part Number
LED7708
Description
LED Lighting Drivers 16 Ch 85mA LED 3.6 to 36V 250kHz
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.LED7708TR.pdf
(53 pages)
Specifications of LED7708
Rohs
yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LED7708TR
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Quantity:
10 000
LED7708
8.3.3
In addition, when the FSW pin is tied to LDO3, the LED7708 uses a default 610 kHz fixed
switching frequency, allowing the saving of a resistor in minimum component-count
applications.
The FSW pin can also be used as synchronization input, allowing the LED7708 to operate
both as master or slave device. If a clock signal having a frequency within the capture range
is applied to this pin, the device locks synchronized. The minimum pulse width which allows
the synchronizing pulses to be detected is 270 ns (typ.). The SYNC pin is a synchronization
output and provides a 35% (typ.) duty cycle clock when the LED7708 is set as master or a
replica of the FSW pin when it is set as slave. It is used to connect multiple devices in a
daisy chain configuration or to synchronize other switching converters running in the system
with the LED7708. When an external synchronization clock is applied to the FSW pin, the
internal oscillator is overdriven and the external power MOSFET is ignited on the rising edge
of the synchronization signal while the slope compensation ramp starts on the falling edge
of the same signal. For this reason, the duty cycle of the external synchronization clock
should be 30% to 40% to prevent sub-harmonic instability when the boost converter is
working in continuous-conduction mode (CCM).
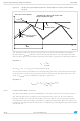
Slope compensation
The constant frequency, peak current-mode topology has the advantage of very easy loop
compensation with output ceramic caps (reduced cost and size of the application) and fast
transient response. In addition, the intrinsic peak current measurement simplifies the current
limit protection, avoiding undesired saturation of the inductor. On the other side, this
topology has a drawback: there is inherent open loop instability when operating with a duty
cycle greater than 0.5. This phenomenon is known as “sub-harmonic instability” and can be
avoided by adding an external ramp to the one coming from the sensed current. This
compensating technique, based on the additional ramp, is called “slope compensation”. As
seen in
dies away in subsequent cycles thanks to the slope compensation and the system reverts to
a stable situation.
Figure
6, when the switching duty cycle is higher than 0.5, the small perturbation ΔIL
Doc ID 022698 Rev 1
Recommended operating conditions
25/53