E-L6565D STMicroelectronics, E-L6565D Datasheet - Page 8

E-L6565D
Manufacturer Part Number
E-L6565D
Description
IC CTRLR PWM SMPS CM UVLO 8SOIC
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.L6565DTR.pdf
(17 pages)
Specifications of E-L6565D
Output Isolation
Isolated
Voltage - Input
10.3 ~ 18 V
Power (watts)
650mW
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 150°C
Package / Case
8-SOIC (0.154", 3.90mm Width)
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
For Use With
497-9051 - BOARD DEMO STC03DE220HV/ L6565
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
L6565
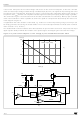
Zero Current Detection and Triggering Block (see fig. 13):
The Zero Current Detection (ZCD) block switches on the external MOSFET if a negative-going edge falling be-
low 1.6 V is applied to the input (pin 5, ZCD). However, to ensure high noise immunity, the triggering block must
be armed first: prior to falling below 1.6V, the voltage on pin 5 must experience a positive-going edge exceeding
2.1 V.
This feature is typically used to detect transformer demagnetization for QR operation, where the signal for the
ZCD input is obtained from the transformer's auxiliary winding used also to supply the IC. Alternatively, this can
be used to synchronize MOSFET's turn-on to the negative-going edge of an external clock signal, in case the
device is not required to work in QR mode but as a standard PWM controller in a synchronized system (e.g.
monitor SMPS).
The triggering block is blanked for a certain time after the MOSFET has been turned off. This has two goals:
first, to prevent any negative-going edge that follows leakage inductance demagnetization from triggering the
ZCD circuit erroneously; second, to realize the Frequency Foldback function (see the relevant description).
Figure 13. Zero Current Detection and Triggering Block; Disable and Frequency Foldback Blocks
A circuit is needed that turns on the external MOSFET at start-up since no signal is coming from the ZCD pin.
This is realized with an internal starter, which forces the driver to deliver a pulse to the gate of the MOSFET.
To minimize the external interface with the synchronization source (either the auxiliary winding or an external
clock), the voltage at the pin is both top and bottom limited by a double clamp, as illustrated in the internal dia-
gram of the ZCD block of figure 13. The upper clamp is typically located at 5.2 V, while the lower clamp is at
one V
by and sunk from the pin within the rated capability of the internal clamps.
Disable Block (see fig. 13):
The ZCD pin is used also to activate the Disable Block. If the voltage on the pin is taken below 150 mV the de-
vice will be shut down. To do so, it is necessary to override the source capability (10 mA max.) of the internal
lower clamp. While in disable, the current consumption of the IC will be reduced. To re-enable device operation,
the pull-down on the pin must be released.
Frequency Foldback Block (see fig. 13):
To prevent the switching frequency from reaching too high values, which is a typical drawback of QR operation,
8/17
Q
BE
+Vin
above ground. The interface will then be made by just one resistor that has to limit the current sourced
R
ZCD
ZCD
5
L6565
0.2V
0.3V
1.6V
2.1V
+
+
-
-
5.2V
DISABLE
STABLE
MONO
BLANKING
TIME
COMP
STARTER
FFWD
to line
E/A
+
blanking
START
-
2.5V
starter STOP
INV
R
S
Q
PWM
DRIVER
7
GD